LeetCode(91-100)
91. Decode Ways¶
- Dynamic Programming
A message containing letters from
A-Zis being encoded to numbers using the following mapping:'A' -> 1
'B' -> 2
...
'Z' -> 26Given a non-empty string containing only digits, determine the total number of ways to decode it.
Example 1:
Input: "12"
Output: 2
Explanation: It could be decoded as "AB" (1 2) or "L" (12).
Example 2:
Input: "226"
Output: 3
Explanation: It could be decoded as "BZ" (2 26), "VF" (22 6), or "BBF" (2 2 6).
Solution
对于任意的i,i的上一步可能是i-1(如果是1~9的数)也可能是i-2(10~26的数)
所以动态规划可以求解,注意一下dp[0]的取值。
Runtime 2 ms
class Solution {
public int numDecodings(String s) {
if(s == null || s.length() == 0) {
return 0;
}
int n = s.length();
int[] dp = new int[n + 1];
dp[0] = 1;
dp[1] = s.charAt(0) != '0' ? 1 : 0;
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
int first = Integer.valueOf(s.substring(i - 1, i));
int second = Integer.valueOf(s.substring(i - 2, i));
if(first >= 1 && first <= 9) {
dp[i] += dp[i - 1];
}
if(second >= 10 && second <= 26) {
dp[i] += dp[i - 2];
}
}
return dp[n];
}
}
92. Reverse Linked List II¶
- Linked List
Reverse a linked list from position m to n. Do it in one-pass.
Note: 1 ≤ m ≤ n ≤ length of list.
Example:
Input: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL, m = 2, n = 4
Output: 1->4->3->2->5->NULL
Solution
此题可以理解为将后面的节点依次插入到前面的节点中,
比如1->2->3->4->5->NULL,m指向2,n-m=2,也就是要插入两次
第一次,将m后面的3插入到m前面,变成了:
1->3->2->4->5->NULL,m还原到第二个节点,现在指向3,
第二次,将m后面的后面的4插入到m前面,所以最后变成为
1->4->3->2->5->NULL
Runtime 0 ms
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int m, int n) {
if (--m == --n) return head;
if (head == null || head.next == null) return head;
ListNode h = new ListNode(0);
h.next = head;
ListNode p = h, m1 = p.next, q, n1;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
p = p.next;
m1 = p.next;
}
q = m1;
n1 = m1.next;
for (int i = m; i < n; i++) {
q.next = n1.next;
n1.next = m1;
p.next = n1;
n1 = q.next;
m1 = p.next;
}
return h.next;
}
}
93. Restore IP Addresses¶
- String
- Backtracking
Given a string containing only digits, restore it by returning all possible valid IP address combinations.
Example:
Input: "25525511135"
Output: ["255.255.11.135", "255.255.111.35"]
Solution
回溯法求解耗时 4 ms:
class Solution {
public List<String> restoreIpAddresses(String s) {
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (s == null || s.length() < 4 || s.length() > 12) {
return result;
}
restoreIpAddressesInner(s, 0, new ArrayList<>(), result);
return result;
}
private void restoreIpAddressesInner(String s, int index, List<String> solu, List<String> result) {
if (index == 4 && s.length() == 0) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
sb.append(solu.get(i));
if (i != 3) {
sb.append(".");
}
}
result.add(sb.toString());
return;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= Math.min(3, s.length()); i++) {
String temp = s.substring(0, i);
Integer value = Integer.parseInt(temp);
if (value >= 0 && value <= 255 && temp.length() == String.valueOf(value).length()) {
solu.add(temp);
restoreIpAddressesInner(s.substring(i), index + 1, solu, result);
solu.remove(solu.size() - 1);
}
}
}
}
下面的推荐解法耗时 2 ms:
class Solution {
public List<String> restoreIpAddresses(String s) {
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (s == null || s.length() < 4 || s.length() > 12) {
return result;
}
final int n = s.length();
for (int a = 1; a <= 3; a++) {
for (int b = a + 1; b <= a + 3; b++) {
for (int c = b + 1; c <= b + 3; c++) {
for (int d = c + 1; d <= c + 3; d++) {
if (d != n) continue;
int A = Integer.parseInt(s.substring(0, a));
int B = Integer.parseInt(s.substring(a, b));
int C = Integer.parseInt(s.substring(b, c));
int D = Integer.parseInt(s.substring(c, d));
String candidate = A + "." + B + "." + C + "." + D;
if (A <= 255 && B <= 255 && C <= 255 && D <= 255 && candidate.length() == n + 3) {
result.add(candidate);
}
}
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
94. Binary Tree Inorder Traversal¶
- Stack
- Tree
Given a binary tree, return the inorder traversal of its nodes' values.
Example:
Input:
1
2
/
3
Output: [1,3,2]
Follow up: Recursive solution is trivial, could you do it iteratively?
Solution
树的前、中、后序遍历算法以及层序遍历算法在剑指offer第二版——树中都有解释以及算法实现,本题就是考察中序遍历。
下面分别是递归以及循环实现:
递归实现
递归实现 Runtime 0 ms
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null)
return result;
inorderInner(root, result);
return result;
}
private void inorderInner(TreeNode root, List<Integer> result) {
if (root.left != null)
inorderInner(root.left, result);
result.add(root.val);
if (root.right != null)
inorderInner(root.right, result);
}
}
循环实现
循环实现 Runtime 1 ms,注意一下左子树回溯的情况,避免死循环。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null)
return result;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push(root);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = stack.peek();
while (node != null) {
stack.push(node.left);
node = stack.peek();
}
stack.pop();
if (!stack.isEmpty()) {
node = stack.pop();
result.add(node.val);
stack.push(node.right);
}
}
return result;
}
}
95. Unique Binary Search Trees II¶
- Tree
- Dynamic Programming
Given an integer n, generate all structurally unique BST's (binary search trees) that store values 1 ... n.
Example:
Input: 3
Output:
[
[1,null,3,2],
[3,2,null,1],
[3,1,null,null,2],
[2,1,3],
[1,null,2,null,3]
]
Explanation:
The above output corresponds to the 5 unique BST's shown below:
Solution
在下一题的指引下,我们知道可以用中序遍历的思想在 1..n 中以任意一个值为二叉搜索树的根节点,对左右两边剩余的数字进行递归,最后将所有得到的左右子树进行组合即可。
Runtime 2 ms.
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<TreeNode> generateTrees(int n) {
if (n == 0) return new ArrayList<>();
return generateTreesInner(1, n);
}
private List<TreeNode> generateTreesInner(int from, int to) {
List<TreeNode> trees = new ArrayList<>();
if (from > to) {
trees.add(null);
}
for (int i = from; i <= to; i++) {
List<TreeNode> leftTrees = generateTreesInner(from, i - 1);
List<TreeNode> rightTrees = generateTreesInner(i + 1, to);
for (TreeNode left : leftTrees) {
for (TreeNode right : rightTrees) {
TreeNode node = new TreeNode(i);
node.left = left;
node.right = right;
trees.add(node);
}
}
}
return trees;
}
}
96. Unique Binary Search Trees¶
- Tree
- Dynamic Programming
Given n, how many structurally unique BST's (binary search trees) that store values 1 ... n.
Example:
Input: 3
Output: 5
Explanation:
Given n = 3, there are a total of 5 unique BST's:
Solution
在数组[1, n]中任选一个数字m,以m为根结点,此时左边有m - 1个节点,右边有n - m个节点,显然此刻解为
想要求出\(G(n)\),就要使m从1开始依次累加到n,累加每一步之和,即
Runtime 0 ms.
class Solution {
public int numTrees(int n) {
int[] f = new int[n + 1];
f[0] = 1;
f[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
f[i] += f[j - 1] * f[i - j];
}
}
return f[n];
}
}
97. Interleaving String¶
- Dynamic Programming
Given s1, s2, s3, find whether s3 is formed by the interleaving of s1 and s2.
Example 1:
Input: s1 = "aabcc", s2 = "dbbca", s3 = "aadbbcbcac"
Output: true
Example 2:
Input: s1 = "aabcc", s2 = "dbbca", s3 = "aadbbbaccc"
Output: false
Solution
使用二维数组的动态规划算法可解:
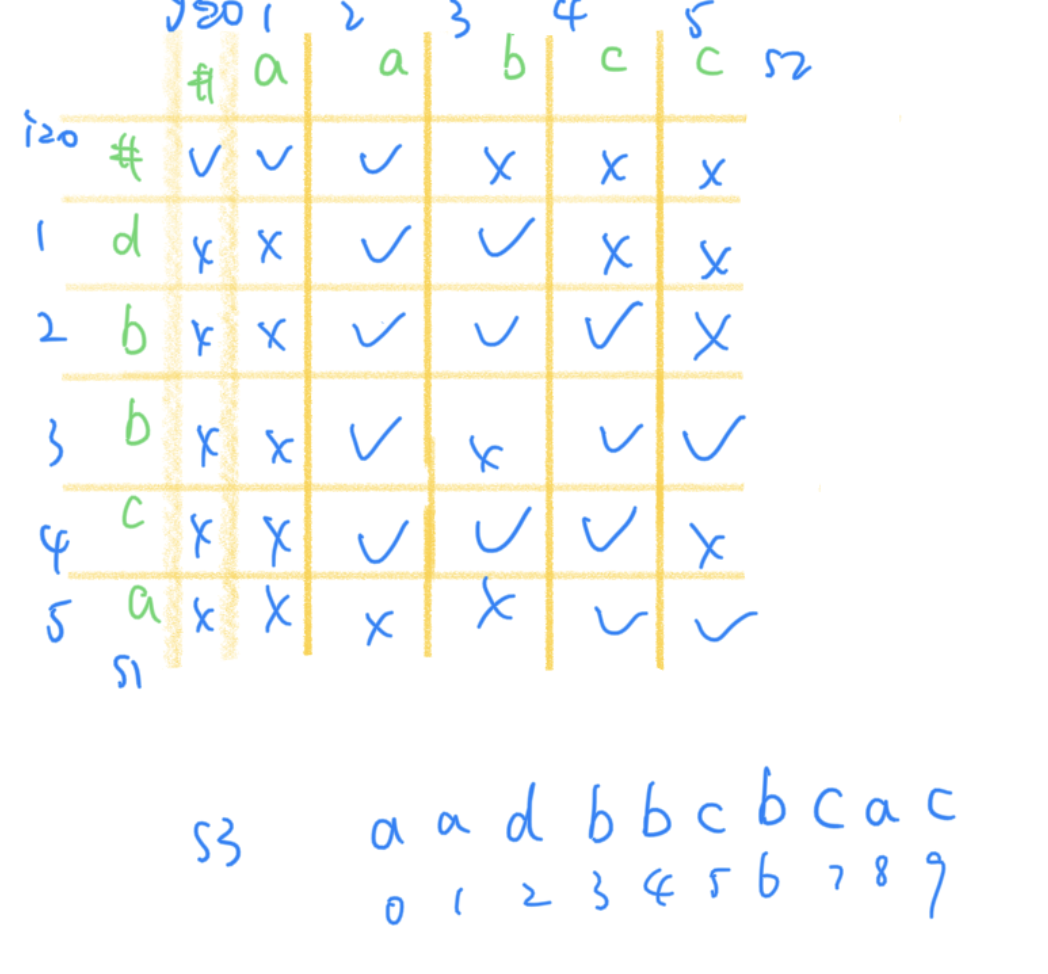
Runtime 2 ms.
class Solution {
public boolean isInterleave(String s1, String s2, String s3) {
final int n1 = s1.length();
final int n2 = s2.length();
final int n3 = s3.length();
if (n3 != n1 + n2) return false;
boolean[][] dp = new boolean[n1 + 1][n2 + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= n1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= n2; j++) {
if (i == 0 && j == 0)
dp[i][j] = true;
else if (i == 0)
dp[i][j] = dp[i][j - 1] && s2.charAt(j - 1) == s3.charAt(i + j - 1);
else if (j == 0)
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j] && s1.charAt(i - 1) == s3.charAt(i + j - 1);
else
dp[i][j] = (dp[i][j - 1] && s2.charAt(j - 1) == s3.charAt(i + j - 1)) ||
(dp[i - 1][j] && s1.charAt(i - 1) == s3.charAt(i + j - 1));
}
}
return dp[n1][n2];
}
}
98. Validate Binary Search Tree¶
- Tree
- Depth-first Search
Assume a BST is defined as follows:
- The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys less than the node's key.
- The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than the node's key.
- Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
Example 1:
2
/ 1 3
Input: [2,1,3]
Output: true
Example 2:
5
/ 1 4
/ 3 6
Input: [5,1,4,null,null,3,6]
Output: false
Solution
解题思路为比较中序遍历中相邻的两个节点,如果前面的节点大于或等于后面节点的值,则BST不合法。
以树的中序遍历算法为模版,就可以写出下面的答案。Runtime 2 ms.
神奇的是,如果先递归求BST的中序序列,然后判断序列是否是升序,这种解法竟然只要1 ms,比上面算法还要快。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode pre = null;
while (root != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (root != null) {
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stack.pop();
if (pre != null && pre.val >= root.val) return false;
pre = root;
root = root.right;
}
return true;
}
}
99. Recover Binary Search Tree¶
- Tree
- Depth-first Search
Two elements of a binary search tree (BST) are swapped by mistake.
Recover the tree without changing its structure.
Example 1:
Input: [1,3,null,null,2]
1
/
3
2
Output: [3,1,null,null,2]
3
/
1
2
Example 2:
Input: [3,1,4,null,null,2]
3
/ 1 4
/
2
Output: [2,1,4,null,null,3]
2
/ 1 4
/
3
Follow up:
- A solution using O(n) space is pretty straight forward.
- Could you devise a constant space solution?
Solution
还是同上一题一样,用树的中序遍历中比较相邻的两个节点,找出一段不符合递增规律的数组,交换这一段节点的头尾节点的值即可。Runtime 2 ms.
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private TreeNode firstNode, secondNode, prev;
public void recoverTree(TreeNode root) {
inorder(root);
int temp = firstNode.val;
firstNode.val = secondNode.val;
secondNode.val = temp;
}
private void inorder(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return;
if (root.left != null) {
inorder(root.left);
}
if (firstNode == null && prev != null && prev.val >= root.val) {
firstNode = prev;
}
if (firstNode != null && prev != null && prev.val >= root.val) {
secondNode = root;
}
prev = root;
if (root.right != null) {
inorder(root.right);
}
}
}
100. Same Tree¶
- Tree
- Depth-first Search
Given two binary trees, write a function to check if they are the same or not.
Two binary trees are considered the same if they are structurally identical and the nodes have the same value.
Example 1:
Example 2:
Example 3:
Solution
很简单的题目,递归即可。300达成(LeetCode 第100题, 耗时、空间都是100%)
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (p == null && q == null) return true;
if (p == null || q == null) return false;
if (p.val == q.val) {
return isSameTree(p.left, q.left) && isSameTree(p.right, q.right);
} else {
return false;
}
}
}



