LeetCode(81-90)
81. Search in Rotated Sorted Array II¶
- Binary Search
Suppose an array sorted in ascending order is rotated at some pivot unknown to you beforehand.
(i.e.,
[0,0,1,2,2,5,6]might become[2,5,6,0,0,1,2]).You are given a target value to search. If found in the array return
true, otherwise returnfalse.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [2,5,6,0,0,1,2], target = 0
Output: true
Example 2:
Input: nums = [2,5,6,0,0,1,2], target = 3
Output: false
Follow up:
- This is a follow up problem to Search in Rotated Sorted Array, where
numsmay contain duplicates. - Would this affect the run-time complexity? How and why?
Solution
此题与CI-(11)旋转数组的最小数字非常类似。
也就是说在Search in Rotated Sorted Array基础上考虑一种特殊情况:{1, 0, 1, 1, 1}和{1, 1, 1, 0, 1}。在这两个数组中最小数字为别位于左右半区。所以上面的算法一定会失败一种情况。因此,当lo,mid,hi对应的数字都相等时,我们必须采用顺序查找。
Runtime 1 ms
class Solution {
public boolean search(int[] nums, int target) {
final int N = nums.length;
int lo = 0, hi = N - 1;
int mid;
while (lo < hi) {
mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1;
if (nums[mid] == nums[lo] && nums[lo] == nums[hi]) {
lo = searchInOrder(nums, lo, hi);
break;
}
if (nums[mid] > nums[hi]) {
lo = mid + 1;
} else {
hi = mid;
}
}
int pivot = lo;
lo = 0;
hi = N - 1;
while (lo <= hi) {
mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1;
int realMid = (mid + pivot) % N;
if (nums[realMid] == target) {
return true;
} else if (nums[realMid] > target) {
hi = mid - 1;
} else {
lo = mid + 1;
}
}
return false;
}
private int searchInOrder(int[] nums, int start, int end) {
for (int i = start + 1; i <= end; i++) {
if (nums[i - 1] > nums[i]) {
return i;
}
}
return start;
}
}
82. Remove Duplicates from Sorted List II¶
- Linked List
Given a sorted linked list, delete all nodes that have duplicate numbers, leaving only distinct numbers from the original list.
Example 1:
Input: 1->2->3->3->4->4->5
Output: 1->2->5
Example 2:
Input: 1->1->1->2->3
Output: 2->3
Solution
Runtime 1 ms
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
// create a head node
ListNode h = new ListNode(0);
h.next = head;
ListNode t = h, p = t.next, q = p.next;
while (q != null) {
if (p.val == q.val) {
while (q != null && p.val == q.val) {
p = p.next;
q = q.next;
}
t.next = q;
if (q != null) {
q = q.next;
p = p.next;
}
} else {
q = q.next;
p = p.next;
t = t.next;
}
}
return h.next;
}
}
83. Remove Duplicates from Sorted List¶
- Linked List
Given a sorted linked list, delete all duplicates such that each element appear only once.
Example 1:
Input: 1->1->2
Output: 1->2
Example 2:
Input: 1->1->2->3->3
Output: 1->2->3
Solution
Runtime 0 ms
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) return head;
ListNode q = head, p = q.next;
while (p != null) {
if (q.val == p.val) {
q.next = p.next;
p.next = null;
p = q.next;
} else {
q = q.next;
p = p.next;
}
}
return head;
}
}
84. Largest Rectangle in Histogram¶
- Array
- Stack
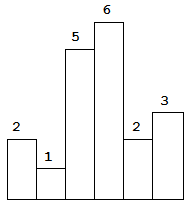
Given n non-negative integers representing the histogram's bar height where the width of each bar is 1, find the area of largest rectangle in the histogram.
1. Above is a histogram where width of each bar is 1, given height = [2,1,5,6,2,3].
2. The largest rectangle is shown in the shaded area, which has area =10unit.
Example:
Input: [2,1,5,6,2,3]
Output: 10
Solution
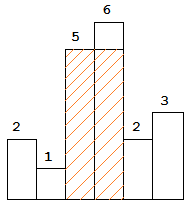
对任意的i,从左边往前找到第一个小于当前高度的bar,其下标记为lessFromLeft[i],若没有找到,则设为-1。
同样,对于任意的i,从右边往后找到第一个小于当前高度的bar,其下标记为lessFromRight[i],若没有找到,则设为n。
(lessFromRight[i] - lessFromLeft[i] - 1)表示的就是当前i的解,图解如下图:
![(lessFromRight[i] - lessFromLeft[i] - 1)的意义](/assets/images/leetcode/question_84_3.png)
这样就容易理解为什么lessFromLeft[i]的默认值为-1,lessFromRight[i]的默认值为n了。
Runtime 2 ms
class Solution {
public int largestRectangleArea(int[] height) {
if (height == null || height.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int[] lessFromLeft = new int[height.length]; // idx of the first bar the left that is lower than current
int[] lessFromRight = new int[height.length]; // idx of the first bar the right that is lower than current
lessFromRight[height.length - 1] = height.length;
lessFromLeft[0] = -1;
for (int i = 1; i < height.length; i++) {
int p = i - 1;
while (p >= 0 && height[p] >= height[i]) {
p = lessFromLeft[p];
}
lessFromLeft[i] = p;
}
for (int i = height.length - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
int p = i + 1;
while (p < height.length && height[p] >= height[i]) {
p = lessFromRight[p];
}
lessFromRight[i] = p;
}
int maxArea = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < height.length; i++) {
maxArea = Math.max(maxArea, height[i] * (lessFromRight[i] - lessFromLeft[i] - 1));
}
return maxArea;
}
}
85. Maximal Rectangle¶
- Dynamic Programming
Given a 2D binary matrix filled with 0's and 1's, find the largest rectangle containing only 1's and return its area.
Example:
Input:
[
["1","0","1","0","0"],
["1","0","1","1","1"],
["1","1","1","1","1"],
["1","0","0","1","0"]
]
Output: 6
Solution: Dynamic Programming
Solution比较难理解。总体来说可以采用DP解法,一行一行遍历。对某一个具体的坐标,有如下解:
其中:
- \(height(i,j)\)表示上方连续的1的个数
- \(left(i, j)\)表示对任意k∈[j, i],使得height[k] >= height[i]成立的最左边的索引j
- \(right(i, j)\)表示对任意k∈[i, j],使得height[k] >= height[i]成立的最右边的索引j
这样一来,\(left\)和\(right\)就能表示包含当前点的、且高为\(height\)的矩形的边界。
Runtime 7 ms
class Solution {
public int maximalRectangle(char[][] matrix) {
if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0) return 0;
final int M = matrix.length;
final int N = matrix[0].length;
int[] left = new int[N];
int[] right = new int[N];
int[] height = new int[N];
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
Arrays.fill(right, N);
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
int curL = 0, curR = N;
// right
for (int j = N - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
if (matrix[i][j] == '1') {
right[j] = Math.min(right[j], curR);
} else {
right[j] = N;
curR = j;
}
}
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
if (matrix[i][j] == '1') {
// height
height[j]++;
// left
left[j] = Math.max(left[j], curL);
} else {
// height
height[j] = 0;
// left
left[j] = 0;
curL = j + 1;
}
max = Math.max(max, (right[j] - left[j]) * height[j]);
}
}
return max;
}
}
86. Partition List¶
- Linked List
Given a linked list and a value x, partition it such that all nodes less than x come before nodes greater than or equal to x.
You should preserve the original relative order of the nodes in each of the two partitions.
Example:
Input: head = 1->4->3->2->5->2, x = 3
Output: 1->2->2->4->3->5
Solution
本题要求将值小于x的节点放置到值大于等于x的节点之前,同时要保持相对位置不变。实际上就是一个链表的插入问题。
我们可以使用指针p表示可以插入的位置,使用指针q来表示待插入的节点。q遍历时判断是否需要插入,以及往后找到第一个可以待插入的节点,插入到p.next上。注意插入完成后,重置指针时考虑[3,1,2], x=3的情况。
Runtime 0 ms
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode partition(ListNode h, int x) {
if (h == null || h.next == null) {
return h;
}
ListNode head = new ListNode(0);
head.next = h;
ListNode p = head, q = head.next;
while (q != null) {
if(q.val < x) {
p = p.next;
q = q.next;
} else {
ListNode t = q;
while (q != null && q.val >= x) {
t = q;
q = q.next;
}
if (q != null) {
ListNode t1 = p.next, t2 = q.next;
p.next = q;
q.next = t1;
t.next = t2;
p = p.next;
q = t;
}
}
}
return head.next;
}
}
87. Scramble String¶
- String
- Dynamic Programming
Given a string s1, we may represent it as a binary tree by partitioning it to two non-empty substrings recursively.
Below is one possible representation of s1 =
"great":great
/ gr eat
/ \ / g r e at
/ a tTo scramble the string, we may choose any non-leaf node and swap its two children.
For example, if we choose the node
"gr"and swap its two children, it produces a scrambled string"rgeat".rgeat
/ rg eat
/ \ / r g e at
/ a tWe say that
"rgtae"is a scrambled string of"great".Given two strings s1 and s2 of the same length, determine if s2 is a scrambled string of s1.
Example 1:
Input: s1 = "great", s2 = "rgeat"
Output: true
Example 2:
Input: s1 = "abcde", s2 = "caebd"
Output: false
Solution
不要被题目所迷惑,不需要建立二叉树,可以直接字符串层面进行比较。两边各取[1, N-1]的长度的字符串进行比较,同时拿剩下的字符串进行比较即可。
Runtime 2 ms
class Solution {
public boolean isScramble(String s1, String s2) {
if (s1.equals(s2)) return true;
if (s1.length() != s2.length()) return false;
final int N = s1.length();
int[] map = new int[26];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
map[s1.charAt(i) - 'a']++;
map[s2.charAt(i) - 'a']--;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
if (map[i] != 0) return false;
}
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
if (isScramble(s1.substring(0, i), s2.substring(0, i)) && isScramble(s1.substring(i), s2.substring(i))) {
return true;
}
if (isScramble(s1.substring(0, i), s2.substring(N - i)) && isScramble(s1.substring(i), s2.substring(0, N - i))) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
88. Merge Sorted Array¶
- Array
- Two Pointers
Given two sorted integer arrays nums1 and nums2, merge nums2 into nums1 as one sorted array.
Note:
- The number of elements initialized in nums1 and nums2 are m and n respectively.
- You may assume that nums1 has enough space (size that is greater or equal to m + n) to hold additional elements from nums2.
Example:
Input:
nums1 = [1,2,3,0,0,0], m = 3
nums2 = [2,5,6], n = 3
Output: [1,2,2,3,5,6]
Solution
Runtime 0 ms
class Solution {
public void merge(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n) {
int i = m + n - 1;
m--;
n--;
while (i >= 0) {
if (m < 0)
nums1[i--] = nums2[n--];
else if (n < 0)
nums1[i--] = nums1[m--];
else if (nums1[m] > nums2[n]) {
nums1[i--] = nums1[m--];
} else {
nums1[i--] = nums2[n--];
}
}
}
}
89. Gray Code¶
- Backtracking
The gray code is a binary numeral system where two successive values differ in only one bit.
Given a non-negative integer n representing the total number of bits in the code, print the sequence of gray code. A gray code sequence must begin with 0.
Example 1:
Input: 2
Output: [0,1,3,2]
Explanation:
00 - 0
01 - 1
11 - 3
10 - 2
For a given n, a gray code sequence may not be uniquely defined. For example, [0,2,3,1] is also a valid gray code sequence.
00 - 0
10 - 2
11 - 3
01 - 1
Example 2:
Input: 0
Output: [0]
Explanation: We define the gray code sequence to begin with 0. A gray code sequence of n has size = 2n, which for n = 0 the size is 20 = 1. Therefore, for n = 0 the gray code sequence is [0].
Solution
从下面的解题过程中可以看出,\(f(n)\)与\(f(n-1)\)之间有很大的关系,只需要在原来\(f(n-1)\)的基础上加上一份最高位置为1的 顺序相反 的\(f(n-1)\)就得到了\(f(n)\)。
Runtime 1 ms
class Solution {
public List<Integer> grayCode(int n) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
result.add(0);
if (n == 0) return result;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = result.size() - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
int tmp = result.get(j) | (int) Math.pow(2, i);
result.add(tmp);
}
}
return result;
}
}
90. Subsets II¶
- Backtracking
Given a collection of integers that might contain duplicates, nums, return all possible subsets (the power set).
Note: The solution set must not contain duplicate subsets.
Example:
Input: [1,2,2]
Output:
[
[2],
[1],
[1,2,2],
[2,2],
[1,2],
[]
]
Solution
我们可以注意到,如果两个相邻的数相同,且前者没有被使用过,那么这个组合是被允许的。
为了使大小相等的数都在一起,可以先排序一下。
Runtime 1 ms, faster than 100.00%.
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> subsetsWithDup(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
Arrays.sort(nums);
subsetsWithDupInner(nums, 0, new ArrayList<>(), new boolean[nums.length], result);
return result;
}
private void subsetsWithDupInner(int[] nums, int index, List<Integer> solution, boolean[] visited, List<List<Integer>> result) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(solution));
for (int i = index; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (i == 0 ||
(nums[i - 1] != nums[i]) ||
(nums[i - 1] == nums[i] && visited[i - 1])) {
solution.add(nums[i]);
visited[i] = true;
subsetsWithDupInner(nums, i + 1, solution, visited, result);
visited[i] = false;
solution.remove(solution.size() - 1);
}
}
}
}