LeetCode(61-70)
61. Rotate List¶
- Linked List
Given a linked list, rotate the list to the right by k places, where k is non-negative.
Example 1:
Input: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL, k = 2
Output: 4->5->1->2->3->NULL
Explanation:
rotate 1 steps to the right: 5->1->2->3->4->NULL
rotate 2 steps to the right: 4->5->1->2->3->NULL
Example 2:
Input: 0->1->2->NULL, k = 4
Output: 2->0->1->NULL
Explanation:
rotate 1 steps to the right: 2->0->1->NULL
rotate 2 steps to the right: 1->2->0->NULL
rotate 3 steps to the right: 0->1->2->NULL
rotate 4 steps to the right: 2->0->1->NULL
Solution
首先,遍历一遍链表得到链表的长度以及链表末尾的节点。然后,将链表链成一个环;最后从头节点移动n-k步,得到的节点就是新链表的头节点。别忘了要断开环。
Runtime 1ms。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode rotateRight(ListNode head, int k) {
if (k == 0 || head == null || head.next == null) return head;
// 获取链表长度以及末尾的指针
int length = 0;
ListNode p = head, tail = head;
while (p != null) {
length++;
tail = p;
p = p.next;
}
k = length - (k % length);
// 链成环状
tail.next = head;
// 从头节点移动n-k步,此时p就是新链表的头节点
p = head;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
tail = p;
p = p.next;
}
// 断开环,返回p即可
tail.next = null;
return p;
}
}
62. Unique Paths¶
- Dynamic Programming
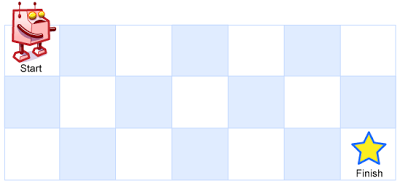
A robot is located at the top-left corner of a m x n grid (marked 'Start' in the diagram below).
The robot can only move either down or right at any point in time. The robot is trying to reach the bottom-right corner of the grid (marked 'Finish' in the diagram below).
How many possible unique paths are there?
Above is a 7 x 3 grid. How many possible unique paths are there?
Note: m and n will be at most 100.
Example 1:
Input: m = 3, n = 2
Output: 3
Explanation:
From the top-left corner, there are a total of 3 ways to reach the bottom-right corner:
1.Right -> Right -> Down
2.Right -> Down -> Right
3.Down -> Right -> Right
Example 2:
Input: m = 7, n = 3
Output: 28
Solution
经过分析,我们不难发现这实际上是一个递归问题。对于某个点来说,该点的值等于其右边和下边的解的和。
即:\(f(m, n)=f(m - 1, n) + f(m, n - 1)\),而且问题具有对称性,也就是说\(f(m, n)=f(n, m)\)。
所以下面的代码中会将m、n中较大者命名为m,较小者命为n,这样如果有对称的解,可以直接利用。
最后,需要注意的是,在求解一个较大的m、n时会递归求出比子问题的解,我们可以使用static修饰的map保存起来,这样遇到子问题,就不需要重新计算。
Runtime 0ms
class Solution {
private static Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
public int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
return f(m, n);
}
private int f(int m, int n) {
if (m < n) {
int temp = m;
m = n;
n = temp;
}
if (m == 1 || n == 1) {
return 1;
}
int key = m * 1000 + n;
Integer value = map.get(key);
if (value != null) {
return value;
} else {
value = f(m - 1, n) + f(m, n - 1);
map.put(key, value);
return value;
}
}
}
63. Unique Paths II¶
- Dynamic Programming
A robot is located at the top-left corner of a m x n grid (marked 'Start' in the diagram below).
The robot can only move either down or right at any point in time. The robot is trying to reach the bottom-right corner of the grid (marked 'Finish' in the diagram below).
Now consider if some obstacles are added to the grids. How many unique paths would there be?
Above is a 7 x 3 grid. How many possible unique paths are there?
An obstacle and empty space is marked as1and0respectively in the grid.
Note: m and n will be at most 100.
Example 1:
Input:
[
[0,0,0],
[0,1,0],
[0,0,0]
]
Output: 2
Explanation:
There is one obstacle in the middle of the 3x3 grid above.
There are two ways to reach the bottom-right corner:
1.Right -> Right -> Down -> Down
2.Down -> Down -> Right -> Right
Solution
在上一题解法的基础上,加入一个障碍的判断即可。由于有了障碍,所以只有成功到达Finish点的路径才返回1;如果遇到了障碍或超过了边界,都会返回0。
Runtime 1ms
class Solution {
private Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
public int uniquePathsWithObstacles(int[][] obstacleGrid) {
final int m = obstacleGrid.length;
final int n = obstacleGrid[0].length;
return f(obstacleGrid, m, 0, n, 0);
}
private int f(int[][] obstacleGrid, int m, int row, int n, int col) {
if (row >= m ||
col >= n ||
obstacleGrid[row][col] == 1) {
return 0;
}
if (row == m - 1 && col == n - 1) {
return 1;
}
int key = row * 1000 + col;
Integer value = map.get(key);
if (value != null) {
return value;
} else {
value = f(obstacleGrid, m, row + 1, n, col) + f(obstacleGrid, m, row, n, col + 1);
map.put(key, value);
return value;
}
}
}
64. Minimum Path Sum¶
- Dynamic Programming
Given a m x n grid filled with non-negative numbers, find a path from top left to bottom right which minimizes the sum of all numbers along its path.
Note: You can only move either down or right at any point in time.
Example:
Input:
[
[1,3,1],
[1,5,1],
[4,2,1]
]
Output: 7
Explanation: Because the path 1→3→1→1→1 minimizes the sum.
Solution
这是一个典型的动态规划问题了。没啥好说的。
此题类似于CI-(47)礼物的最大价值
Runtime 2ms, beats 93.47%
class Solution {
public int minPathSum(int[][] grid) {
final int rows = grid.length;
final int cols = grid[0].length;
int[] dp = new int[cols];
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
int min = 0;
if (i > 0 && j > 0) {
min = Math.min(dp[j - 1], dp[j]);
} else if (i > 0) {
min = dp[j];
} else if (j > 0) {
min = dp[j - 1];
}
dp[j] = min + grid[i][j];
}
}
return dp[cols - 1];
}
}
65. Valid Number¶
- String
Validate if a given string can be interpreted as a decimal number.
Some examples:
"0" => true
" 0.1 " => true
"abc" => false
"1 a" => false
"2e10" => true
" -90e3 " => true
" 1e" => false
"e3" => false
" 6e-1" => true
" 99e2.5 " => false
"53.5e93" => true
" --6 " => false
"-+3" => false
"95a54e53" => false
Note: It is intended for the problem statement to be ambiguous. You should gather all requirements up front before implementing one. However, here is a list of characters that can be in a valid decimal number:
- Numbers - 0-9
- Exponent - "e"
- Positive/negative sign - "+"/"-"
- Decimal point - "."
Of course, the context of these characters also matters in the input.
Solution
直接采用CI-20-表示数值的字符串的解法。不过需要注意的是,此处输入的字符串,头尾可能会有空格,需要处理下。
class Solution {
private int index;
public boolean isNumber(String s) {
if (s == null) {
return false;
}
return isNumber(s.toCharArray());
}
private boolean isNumber(char[] ch) {
final int n = ch.length;
skipEmpty(ch, n);
boolean isNumber = scanInteger(ch, n);
if (index < n && ch[index] == '.') {
index++;
isNumber = scanUnsignedInteger(ch, n) || isNumber;
}
if (index < n && ch[index] == 'e') {
index++;
isNumber = isNumber && scanInteger(ch, n);
}
skipEmpty(ch, n);
return isNumber && index == n;
}
private void skipEmpty(char[] ch, int n) {
while (index < n) {
if (ch[index] == ' ') {
index++;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
private boolean scanInteger(char[] ch, int n) {
if (index < n && (ch[index] == '-' || ch[index] == '+')) {
index++;
}
return scanUnsignedInteger(ch, n);
}
private boolean scanUnsignedInteger(char[] ch, int n) {
int originIndex = index;
while (index < n && ch[index] >= '0' && ch[index] <= '9') {
index++;
}
return index > originIndex;
}
}
66. Plus One¶
- Array
Given a non-empty array of digits representing a non-negative integer, plus one to the integer.
The digits are stored such that the most significant digit is at the head of the list, and each element in the array contain a single digit.
You may assume the integer does not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
Example 1:
Input: [1,2,3]
Output: [1,2,4]
Explanation: The array represents the integer 123.
Example 2:
Input: [4,3,2,1]
Output: [4,3,2,2]
Explanation: The array represents the integer 4321.
Solution
从后往前遍历,每一位与进位相加即可。最后检查一下是否需要创建新的数组来容纳最后的一个进位。
Runtime 0ms
class Solution {
public int[] plusOne(int[] digits) {
if (digits == null || digits.length == 0)
return digits;
final int n = digits.length;
int carry = 1;
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
int sum = digits[i] + carry;
digits[i] = sum % 10;
carry = sum / 10;
}
if (carry > 0) {
int[] temp = new int[n + 1];
System.arraycopy(digits, 0, temp, 1, n);
temp[0] = carry;
digits = temp;
}
return digits;
}
}
67. Add Binary¶
- Math
Given two binary strings, return their sum (also a binary string).
The input strings are both non-empty and contains only characters
1or0.
Example 1:
Input: a = "11", b = "1"
Output: "100"
Example 2:
Input: a = "1010", b = "1011"
Output: "10101"
Solution
本题相当于上一次的进阶版,也是两个数都从后往前开始按位累加,最后考虑一下最后的一次进位。
Runtime 1ms
Tip
Tips: char转int不需要强转,int转char是需要的。
char转int: '9' - '0'
int转char: (char) (9 + '0')
class Solution {
public String addBinary(String a, String b) {
// make a becomes the larger one
if (a.length() < b.length()) {
String temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
return addBinary(a.toCharArray(), b.toCharArray());
}
private String addBinary(char[] a, char[] b) {
final int m = a.length;
final int n = b.length;
int i = m - 1, j = n - 1, carry = 0, sum = 0;
while (i >= 0) {
if (j >= 0) {
sum = a[i] + b[j] - '0' - '0' + carry;
} else {
sum = a[i] - '0' + carry;
}
a[i] = (char) ((sum % 2) + '0');
carry = sum / 2;
i--;
j--;
}
if (carry > 0) {
char[] result = new char[m + 1];
System.arraycopy(a, 0, result, 1, m);
result[0] = (char) (carry + '0');
return new String(result);
} else {
return new String(a);
}
}
}
68. Text Justification¶
- String
Given an array of words and a width maxWidth, format the text such that each line has exactly maxWidth characters and is fully (left and right) justified.
You should pack your words in a greedy approach; that is, pack as many words as you can in each line. Pad extra spaces
' 'when necessary so that each line has exactly maxWidth characters.Extra spaces between words should be distributed as evenly as possible. If the number of spaces on a line do not divide evenly between words, the empty slots on the left will be assigned more spaces than the slots on the right.
For the last line of text, it should be left justified and no extra space is inserted between words.
Note:
- A word is defined as a character sequence consisting of non-space characters only.
- Each word's length is guaranteed to be greater than 0 and not exceed maxWidth.
- The input array
wordscontains at least one word.
Example 1:
Input:
words = ["This", "is", "an", "example", "of", "text", "justification."]
maxWidth = 16
Output:
[
"This is an",
"example of text",
"justification. "
]
Example 2:
Input:
words = ["What","must","be","acknowledgment","shall","be"]
maxWidth = 16
Output:
[
"What must be",
"acknowledgment ",
"shall be "
]
Explanation: Note that the last line is "shall be " instead of "shall be", because the last line must be left-justified instead of fully-justified. Note that the second line is also left-justified becase it contains only one word.
Example 3:
Input:
words = ["Science","is","what","we","understand","well","enough","to","explain", "to","a","computer.","Art","is","everything","else","we","do"]
maxWidth = 20
Output:
[
"Science is what we",
"understand well",
"enough to explain to",
"a computer. Art is",
"everything else we",
"do "
]
Solution
这题没啥特别技巧。先计算输入字符串数组中每个字符串的长度,然后尝试助逐行逐行摆放。在尝试摆放时,每两个word之间预留一个空格,避免出现摆好了word但是word之间没有空格的情况。当计算出某行可以摆放的字符串后,开始进行摆放,此时需要注意空格的规律:每一段空格的长度先定为(空格的总长度/空格数),然后多出来的部分给前面每个空格(空格的总长度%空格数)都加一。比如,3个空格要分10长度,所以先每个空格为10/3=3,然后前面的10%3=1个空格可以多一个,于是4、3、3。最后,特别处理一下最后一行的对齐方式。
Runtime 0ms
class Solution {
public List<String> fullJustify(String[] words, int maxWidth) {
final int n = words.length;
int[] width = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
width[i] = words[i].length();
}
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
int index = 0;
while (index < n) {
int currentWidth = 0;
int spaceCount = -1;
while (index < n) {
currentWidth += width[index++];
spaceCount++;
if (currentWidth + spaceCount > maxWidth) {
currentWidth -= width[--index];
spaceCount--;
break;
}
}
int totalSpace = maxWidth - currentWidth;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
if (index != n) {
int space = spaceCount == 0 ? 0 : totalSpace / spaceCount;
int extraSpace = spaceCount == 0 ? 0 : totalSpace % spaceCount;
int begin = index - spaceCount - 1;
for (int i = begin; i < index; i++) {
sb.append(words[i]);
if (space == 0) {
appendSpace(sb, totalSpace);
} else if (i <= index - 2) {
int size = space + (i < begin + extraSpace ? 1 : 0);
appendSpace(sb, size);
}
}
} else { // last line
int begin = index - spaceCount - 1;
for (int i = begin; i < index; i++) {
sb.append(words[i]);
if (i <= index - 2) {
appendSpace(sb, 1);
} else if (i == index - 1) {
appendSpace(sb, totalSpace - spaceCount);
}
}
}
result.add(sb.toString());
}
return result;
}
private void appendSpace(StringBuilder sb, int size) {
char[] ch = new char[size];
Arrays.fill(ch, ' ');
sb.append(ch);
}
}
69. Sqrt(x)¶
- Binary Search
Implement
int sqrt(int x).Compute and return the square root of x, where x is guaranteed to be a non-negative integer.
Since the return type is an integer, the decimal digits are truncated and only the integer part of the result is returned.
Example 1:
Input: 4
Output: 2
Example 2:
Input: 8
Output: 2
Explanation: The square root of 8 is 2.82842..., and since the decimal part is truncated, 2 is returned.
Solution
如果不知道数学方式——牛顿迭代法快速寻找平方根,可以直接在[0, x]之间二分查找。
Runtime 1ms
class Solution {
public int mySqrt(int x) {
int begin = 0;
int end = x;
while (begin <= end) {
int mid = (begin + end) >> 1;
long result = (long) mid * mid;
if (result == x) {
return mid;
} else if (result > x) {
end = mid - 1;
} else {
begin = mid + 1;
}
}
return end;
}
}
70. Climbing Stairs¶
-> Dynamic Programming
You are climbing a stair case. It takes n steps to reach to the top.
Each time you can either climb 1 or 2 steps. In how many distinct ways can you climb to the top?
Note: Given n will be a positive integer.
Example 1:
Input: 2
Output: 2
Explanation: There are two ways to climb to the top.
1. 1 step + 1 step
2. 2 steps
Example 2:
Input: 3
Output: 3
Explanation: There are three ways to climb to the top.
1. 1 step + 1 step + 1 step
2. 1 step + 2 steps
3. 2 steps + 1 step
Solution
研究发现,这就是一个斐波那契数列。
Runtime 0ms, beats 100%
class Solution {
public int climbStairs(int n) {
if (n <= 1) return 1;
int[] results = new int[n + 1];
results[0] = 1;
results[1] = 1;
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
results[i] = results[i - 1] + results[i - 2];
}
return results[n];
}
}
O(1)空间复杂度:
class Solution {
public int climbStairs(int n) {
if (n <= 1) return 1;
int a = 1;
int b = 1;
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
int temp = a + b;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
return b;
}
}