LeetCode(51-60)
51. N-Queens¶
- Backtracking
The n-queens puzzle is the problem of placing n queens on an n×n chessboard such that no two queens attack each other.
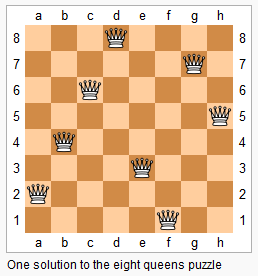
Given an integer n, return all distinct solutions to the n-queens puzzle.
Each solution contains a distinct board configuration of the n-queens' placement, where
'Q'and'.'both indicate a queen and an empty space respectively.
Example:
Input: 4
Output: [
[". Q . .", // Solution 1
". . . Q",
"Q . . .",
". . Q ."],
[". . Q .", // Solution 2
"Q . . .",
". . . Q",
". Q . ."]
]
Explanation: There exist two distinct solutions to the 4-queens puzzle as shown above.
Solution
根据规则,任意两个皇后不能在同一行、同一列、同一对角线上。
所以,可以定义行、两条对角线上的标志位,表示对应的线上是否存在皇后。然后我们每次在一行上的所有位置尝试放置皇后,放置成功则设置标志位,然后进行回溯算法,回溯完成后复位标志位。
当放置完最后一个皇后时,这就是问题的一个解。
class Solution {
public List<List<String>> solveNQueens(int n) {
List<List<String>> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (n <= 0) return result;
char[] solution = new char[n * n];
Arrays.fill(solution, '.');
solveNQueensInner(0, n, new boolean[n], new boolean[2 * n - 1], new boolean[2 * n - 1], solution, result);
return result;
}
private void solveNQueensInner(int row, int n, boolean[] flags, boolean[] flags45, boolean[] flags135, char[] solution, List<List<String>> result) {
if (row == n) {
List<String> soluList = new ArrayList<String>(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
soluList.add(new String(solution, i * n, n));
}
result.add(soluList);
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (flags[i] || flags135[n - 1 + i - row] || flags45[row + i]) continue;
flags[i] = flags135[n - 1 + i - row] = flags45[row + i] = true;
solution[row * n + i] = 'Q';
solveNQueensInner(row + 1, n, flags, flags45, flags135, solution, result);
solution[row * n + i] = '.';
flags[i] = flags135[n - 1 + i - row] = flags45[row + i] = false;
}
}
}
52. N-Queens II¶
- Backtracking
The n-queens puzzle is the problem of placing n queens on an n×n chessboard such that no two queens attack each other.

Given an integer n, return all distinct solutions to the n-queens puzzle.
Each solution contains a distinct board configuration of the n-queens' placement, where
'Q'and'.'both indicate a queen and an empty space respectively.
Example:
Input: 4
Output: 2
Explanation: There are two distinct solutions to the 4-queens puzzle as shown below.
[
[". Q . .", // Solution 1
". . . Q",
"Q . . .",
". . Q ."],
[". . Q .", // Solution 2
"Q . . .",
". . . Q",
". Q . ."]
]
Solution
解法流程和上面N-Queens类似,唯一不同的是,此时我们不需要保存的解,所以只需要只用标志位即可。
class Solution {
private int mCount;
public int totalNQueens(int n) {
if (n <= 0) return 0;
totalNQueensInner(0, n, new boolean[n], new boolean[2 * n - 1], new boolean[2 * n - 1]);
return mCount;
}
private void totalNQueensInner(int row, int n, boolean[] flags, boolean[] flags45, boolean[] flags135) {
if (row == n) {
mCount++;
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (flags[i] || flags135[n - 1 + i - row] || flags45[row + i]) continue;
flags[i] = flags135[n - 1 + i - row] = flags45[row + i] = true;
totalNQueensInner(row + 1, n, flags, flags45, flags135);
flags[i] = flags135[n - 1 + i - row] = flags45[row + i] = false;
}
}
}
53. Maximum Subarray¶
- Array
- Dynamic Programming
Given an integer array
nums, find the contiguous subarray (containing at least one number) which has the largest sum and return its sum.
Example:
Input: [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4],
Output: 6
Explanation: [4,-1,2,1] has the largest sum = 6.
Follow up:
If you have figured out the \(O(n)\) solution, try coding another solution using the divide and conquer approach, which is more subtle.
Solution
如果某步累加的结果不是正数,那么这些累加是可以抛弃的;否则可正常进行累加。在每步累加结束后存下这步最大的值。
class Solution {
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int sum = 0;
for (int num : nums) {
if (sum < 0)
sum = num;
else
sum += num;
if (sum > max) {
max = sum;
}
}
return max;
}
}
54. Spiral Matrix¶
- Array
Given a matrix of
mxnelements (mrows,ncolumns), return all elements of the matrix in spiral order.
Example 1:
Input:
[
[ 1, 2, 3 ],
[ 4, 5, 6 ],
[ 7, 8, 9 ]
]
Output: [1,2,3,6,9,8,7,4,5]
Example 2:
Input:
[
[1, 2, 3, 4],
[5, 6, 7, 8],
[9,10,11,12]
]
Output: [1,2,3,4,8,12,11,10,9,5,6,7]
Solution
此题需要注意矩阵的行列数不相等时的边界条件。
如果按照打印每条边时最大限度地进行打印的策略,矮胖矩阵(col>row)需要注意下边的边的判定,瘦高矩阵(col<row)需要注意左边的边的判定。
下方代码简直awesome、wow man般收放自如,每打印一条边都会缩小范围,判定更简单:
class Solution {
public List<Integer> spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) {
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0)
return result;
int colBegin = 0;
int colEnd = matrix[0].length - 1;
int rowBegin = 0;
int rowEnd = matrix.length - 1;
while (colBegin <= colEnd && rowBegin <= rowEnd) {
// top side
for (int i = colBegin; i <= colEnd; i++) {
result.add(matrix[rowBegin][i]);
}
rowBegin++;
// right side
for (int i = rowBegin; i <= rowEnd; i++) {
result.add(matrix[i][colEnd]);
}
colEnd--;
// bottom side
if (rowBegin <= rowEnd) {
for (int i = colEnd; i >= colBegin; i--) {
result.add(matrix[rowEnd][i]);
}
}
rowEnd--;
// left side
if (colBegin <= colEnd) {
for (int i = rowEnd; i >= rowBegin; i--) {
result.add(matrix[i][colBegin]);
}
}
colBegin++;
}
return result;
}
}
55. Jump Game¶
- Greedy
Given an array of non-negative integers, you are initially positioned at the first index of the array.
Each element in the array represents your maximum jump length at that position.
Determine if you are able to reach the last index.
Example 1:
Input: [2,3,1,1,4]
Output: true
Explanation: Jump 1 step from index 0 to 1, then 3 steps to the last index.
Example 2:
Input: [3,2,1,0,4]
Output: false
Explanation: You will always arrive at index 3 no matter what. Its maximum jump length is 0, which makes it impossible to reach the last index.
Solution
本题最好的解法是贪婪算法,从最右边开始,能到达终点的点就是最新的终点,这样一直判断完整个数组,最后判断最后一个终点是不是0即可。
时间复杂度为\(O(n)\),空间复杂度为\(O(1)\)。
一个疑问是,如果确定了一个点是最新的终点,那么一旦无法从开始跳到该点,是否有回溯的可能。
答案是没有必要回溯,因为假设存在这个一个点P,位于最新的终点与终点之间。如果位于最新终点之前的点可以到达点P,那么肯定可以到达最新的终点。所以,回溯在本题是没有必要的,本题只是求存不存在路径。
class Solution {
public boolean canJump(int[] nums) {
final int n = nums.length;
int last = n - 1;
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (i + nums[i] >= last) {
last = i;
}
}
return last == 0;
}
}
56. Merge Intervals¶
- Array
- Sort
Given a collection of intervals, merge all overlapping intervals.
Example 1:
Input: [[1,3],[2,6],[8,10],[15,18]]
Output: [[1,6],[8,10],[15,18]]
Explanation: Since intervals [1,3] and [2,6] overlaps, merge them into [1,6].
Example 2:
Input: [[1,4],[4,5]]
Output: [[1,5]]
Explanation: Intervals [1,4] and [4,5] are considered overlapping.
Solution
Approach 1: Sorting
先排序,排完序后可以两两之间进行比较:如果可以merge,那么更新较后者的值;若是最后一个,或者不可以merge,前者就是结果之一。
时间主要在排序上,所以时间复杂度为\(O(nlogn)\)。
Runtime 36ms,beats 41.79%
class Solution {
public int[][] merge(int[][] intervals) {
Arrays.sort(intervals, (o1, o2) -> o1[0] - o2[0]);
List<int[]> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < intervals.length; i++) {
if (i == intervals.length - 1 ||
intervals[i][1] < intervals[i + 1][0]) {
result.add(new int[] {
intervals[i][0],
intervals[i][1]
});
} else if (intervals[i][1] >= intervals[i + 1][0]) {
intervals[i + 1][0] = intervals[i][0];
intervals[i + 1][1] = Math.max(intervals[i][1], intervals[i + 1][1]);
}
}
return result.toArray(new int[result.size()][2]);
}
}
Approach 2
经典的两层for-loop,每次尝试处理最前面一个还未处理的数据;处理后break,继续处理下一个未处理的数据。
由于数据事先没有经过排序,所以判断任意两个区间是否可以merge时,注意交换一下前后循序。
Runtime 1ms,beats 100%,真是amazing!!
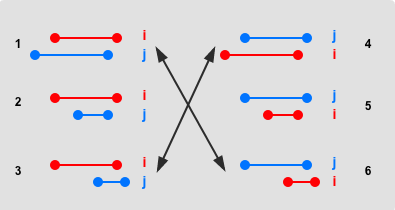
判断区间可不可以merge时,先固定住一条线条,然后看另外一条线条在什么位置满足条件。我们发现,有些情况是一样的,比如上图中的1与6,3与4一样,所以实际上只需要判断1、2、4、5即可。
class Solution {
public int[][] merge(int[][] intervals) {
final int n = intervals.length;
boolean[] invalid = new boolean[n];
int validCount = n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
if ((intervals[i][1] >= intervals[j][1] && intervals[i][0] <= intervals[j][1]) ||
(intervals[j][1] >= intervals[i][1] && intervals[j][0] <= intervals[i][1])) {
invalid[i] = true;
intervals[j][0] = Math.min(intervals[i][0], intervals[j][0]);
intervals[j][1] = Math.max(intervals[i][1], intervals[j][1]);
break;
}
}
if (invalid[i]) validCount--;
}
int[][] result = new int[validCount][2];
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (!invalid[i]) {
result[index++] = intervals[i];
}
}
return result;
}
}
57. Insert Interval¶
- Array
- Sort
Given a set of non-overlapping intervals, insert a new interval into the intervals (merge if necessary).
You may assume that the intervals were initially sorted according to their start times.
Example 1:
Input: intervals = [[1,3],[6,9]], newInterval = [2,5]
Output: [[1,5],[6,9]]
Example 2:
Input: intervals = [[1,2],[3,5],[6,7],[8,10],[12,16]], newInterval = [4,8]
Output: [[1,2],[3,10],[12,16]]
Explanation: Because the new interval [4,8] overlaps with [3,5],[6,7],[8,10].
Solution
该题的需要我们插入一个区间,然后合并可以合并的区间。所以我们先将原来的区间和需要插入的区间合并成为一个新的区间,然后问题就转化为上一题了。
需要注意的是,输入的区间是有序的,所以我们在合并成为新区间时,采用插入排序的思路,在\(O(n)\)的时间内完成新区间的合并和生成,且完成也是有序的。
既然目前数组是有序的,所以我们采用上一题的解法1的思路:对有序的数组可以两两之间进行比较:如果可以merge,那么更新较后者的值;若是最后一个,或者不可以merge,前者就是结果之一。
Runtime 2ms,beats 75.79%
class Solution {
public int[][] insert(int[][] intervals, int[] newInterval) {
final int n = intervals.length;
int[][] inserted = new int[n + 1][];
int index = 0;
boolean used = false;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (!used && intervals[i][0] >= newInterval[0]) {
inserted[index++] = newInterval;
inserted[index++] = intervals[i];
used = true;
} else {
inserted[index++] = intervals[i];
}
}
if (!used) {
inserted[index++] = newInterval;
}
return merge(inserted);
}
private int[][] merge(int[][] intervals) {
List<int[]> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < intervals.length; i++) {
if (i == intervals.length - 1 ||
intervals[i][1] < intervals[i + 1][0]) {
result.add(new int[] {
intervals[i][0],
intervals[i][1]
});
} else if (intervals[i][1] >= intervals[i + 1][0]) {
intervals[i + 1][0] = intervals[i][0];
intervals[i + 1][1] = Math.max(intervals[i][1], intervals[i + 1][1]);
}
}
return result.toArray(new int[result.size()][2]);
}
}
58. Length of Last Word¶
- String
Given a string s consists of upper/lower-case alphabets and empty space characters
' ', return the length of last word in the string.If the last word does not exist, return 0.
Note: A word is defined as a character sequence consists of non-space characters only.
Example:
Input: "Hello World"
Output: 5
Solution
解法很简单,从后往前开始统计。注意处理以' '结尾的情况。
Runtime 0ms,beats 100%
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLastWord(String s) {
if (s == null || s.length() == 0) return 0;
final int n = s.length();
boolean counting = false;
int length = 0;
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
boolean space = s.charAt(i) == ' ';
if (space && !counting) {
continue;
} else if (!space && counting) {
length++;
} else if (space && counting) {
break;
} else {
counting = true;
length++;
}
}
return length;
}
}
59. Spiral Matrix II¶
- Array
Given a positive integer n, generate a square matrix filled with elements from 1 to \(n^2\) in spiral order.
Example:
Input: 3
Output:
[
[ 1, 2, 3 ],
[ 8, 9, 4 ],
[ 7, 6, 5 ]
]
Solution
此题可以使用LC-54-Spiral Matrix的思路——每打印一条边都会缩小范围,问题不难解决。
Runtime 0ms
class Solution {
public int[][] generateMatrix(int n) {
int[][] matrix = new int[n][n];
int rowBegin = 0;
int rowEnd = n - 1;
int colBegin = 0;
int colEnd = n - 1;
int index = 1;
while (rowBegin <= rowEnd && colBegin <= colEnd) {
// print top
for (int i = colBegin; i <= colEnd; i++) {
matrix[rowBegin][i] = index++;
}
rowBegin++;
// print right
for (int i = rowBegin; i <= rowEnd; i++) {
matrix[i][colEnd] = index++;
}
colEnd--;
// print bottom
if (rowBegin <= rowEnd) {
for (int i = colEnd; i >= colBegin; i--) {
matrix[rowEnd][i] = index++;
}
}
rowEnd--;
// print left
if (colBegin <= colEnd) {
for (int i = rowEnd; i >= rowBegin; i--) {
matrix[i][colBegin] = index++;
}
}
colBegin++;
}
return matrix;
}
}
60. Permutation Sequence¶
- Math
The set
[1,2,3,...,n]contains a total of n! unique permutations.By listing and labeling all of the permutations in order, we get the following sequence for n = 3:
"123""132""213""231""312""321"Given n and k, return the \(k^{th}\) permutation sequence.
Note:
- Given n will be between 1 and 9 inclusive.
- Given k will be between 1 and n! inclusive.
Example 1:
Input: n = 3, k = 3
Output: "213"
Example 2:
Input: n = 4, k = 9
Output: "2314"
Solution
该题可以使用数学解法,效率更高。
我们用例子1来描述这个过程。
首先在n=3的情况(剩下的数字位[1,2,3]):由于(n-1)!=(3-1)!=2!=2,也就是说,每一个最高位对应有2个全排列,而我们要求的k为3,所以在第2个全排列里面。所以我们取数字序列中第2大的数:2。
此时问题就变成了在n=2、k=3-2=1的情况下确定新的最高位。
接下来看一下n=2的情况(剩下的数字位[1,3]):由于(n-1)!=(2-1)!=1!=1,也就是说,每一个最高位对应有1个全排列,而我们要求的k为1,所以在第1个全排列里面,所以我们取数字序列中第1大的数:1。
问题就变成了在n=1的情况。显然,此时只有最后一个数字3了。因此结果就是213。
总结一下,首先先根据k和(n-1)!确定要求的数在哪个大区间里面,确定了区间就确定了此时的最高位。然后将k减去可以忽略的大区间的元素个数,得到了当前小区间里面的k,然后接着继续确定次高位的数。这样一直下去就可以获得第k个全排列的所有的数字。
在举一个n = 4, k = 9时的例子,计算过程如下:
- n=4 k=9
[1,2,3,4]
m=(n-1)!=3!=6 → k∈(m * 1, m * 2] → 取集合中的第 2 个元素——2 - n=3 k=k-(2-1)*m=9-6=3
[1,3,4]
m=(n-1)!=2!=2 → k∈(m * 1, m * 2] → 取集合中的第 2 个元素——3 - n=2 k=k-(2-1)*m=3-2=1
[1,4]
m=(n-1)!=1!=1 → k∈(m * 0, m * 1] → 取集合中的第 1 个元素——1 - n=1 k=k-(1-1)*m=1-0=1
[4]
m=(n-1)!=0!=1 → k∈(m * 0, m * 1] → 取集合中的第 1 个元素——4
所以n = 4, k = 9时,结果就是2314。
Runtime 1ms, beats 99.61%
class Solution {
public String getPermutation(int n, int k) {
char[] ch = new char[n];
// 0..n
List<Integer> numbers = new LinkedList<>();
// 0!..n!
int[] fact = new int[n + 1];
numbers.add(0);
fact[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
fact[i] = fact[i - 1] * i;
numbers.add(i);
}
int index = 0;
while (n > 0) {
int m = (k - 1) / fact[n - 1] + 1;
ch[index++] = (char) (numbers.get(m) + '0');
numbers.remove(m);
k -= (m - 1) * fact[n - 1];
n--;
}
return new String(ch);
}
}
为了方面的从剩下的数字中取到第m大的,这里使用了0..n共n+1长度的LinkedList。