LeetCode(41-50)
41. First Missing Positive¶
- Array
Given an unsorted integer array, find the smallest missing positive integer.
Example 1:
Input: [1,2,0]
Output: 3
Example 2:
Input: [3,4,-1,1]
Output: 2
Example 3:
Input: [7,8,9,11,12]
Output: 1
Note: Your algorithm should run in O(n) time and uses constant extra space.
Solution
class Solution {
public int firstMissingPositive(int[] nums) {
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
while (nums[i] > 0 && nums[i] <= nums.length && nums[nums[i] - 1] != nums[i]) {
swap(nums, nums[i] - 1, i);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] != i + 1)
return i + 1;
}
return nums.length + 1;
}
private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
int t = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = t;
}
}
我们将nums[i]放置到nums[i]-1这个位置(比如将num[i]=3放置到下标为2的位置),然后遍历一遍就可以得出答案。
42. Trapping Rain Water¶
- Array
- Two Pointers
- Dynamic Programming
Given n non-negative integers representing an elevation map where the width of each bar is 1, compute how much water it is able to trap after raining.
The above elevation map is represented by array [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]. In this case, 6 units of rain water (blue section) are being trapped.
Example:
Input: [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]
Output: 6
Solution
Approach 1: Brute force
遍历数组,对于每一个i,从自身开始往左找出当前最大的值max_left,从自身开始往右找出最大的值max_right,两者较小者减去当前i的值,即为这一格可以容纳的雨水的含量。
时间复杂度为\(O(n^2)\),空间复杂度为\(O(1)\)。
class Solution {
public int trap(int[] height) {
if (height == null || height.length == 0)
return 0;
final int n = height.length;
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
int max_left = 0, max_right = 0;
// 左半边最高的bar
for (int j = i; j >= 0; j--) {
max_left = Math.max(max_left, height[j]);
}
// 右半边最高的bar
for (int j = i; j < n; j++) {
max_right = Math.max(max_right, height[j]);
}
ans += Math.min(max_left, max_right) - height[i];
}
return ans;
}
}
Approach 2: Dynamic Programming
在上面的解法中,我们每一步都需要算出两侧最高的bar。这些值都可以存储起来的,哦,这就是动态规划算法。
该方法时间复杂度为\(O(n)\),空间复杂度为\(O(n)\)。
该思想可以使用下面的图来表示:

class Solution {
public int trap(int[] height) {
if (height == null || height.length == 0)
return 0;
final int n = height.length;
int[] leftMax = new int[n];
int[] rightMax = new int[n];
leftMax[0] = height[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
leftMax[i] = Math.max(leftMax[i - 1], height[i]);
rightMax[n - 1] = height[n - 1];
for (int i = n - 2; i >= 0; i--)
rightMax[i] = Math.max(rightMax[i + 1], height[i]);
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
ans += Math.min(leftMax[i], rightMax[i]) - height[i];
return ans;
}
}
43. Multiply Strings¶
- String
Given two non-negative integers
num1andnum2represented as strings, return the product ofnum1andnum2, also represented as a string.
Example 1:
Input: num1 = "2", num2 = "3"
Output: "6"
Example 2:
Input: num1 = "123", num2 = "456"
Output: "56088"
Note:
- The length of both
num1andnum2is < 110. - Both
num1andnum2contain only digits 0-9. - Both
num1andnum2do not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself. - You must not use any built-in BigInteger library or convert the inputs to integer directly.
Solution
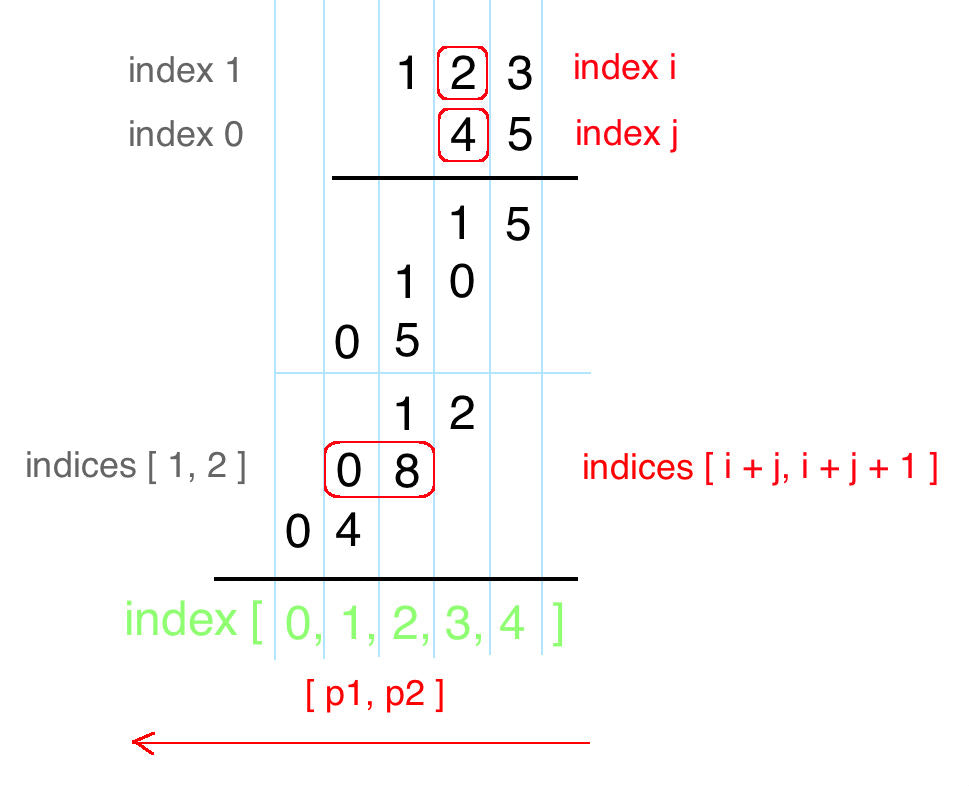
该题就是一个大数问题,这里用一个int数组存放结果,数组中每一位都表示结果的一位。下面就是如何运算的问题,下面是老外做乘法的思路:
Remember how we do multiplication?
Start from right to left, perform multiplication on every pair of digits, and add them together. Let's draw the process! From the following draft, we can immediately conclude:
num1[i] * num2[j]will be placed at indices[i + j,i + j + 1]
class Solution {
public String multiply(String num1, String num2) {
if (num1 == null || num2 == null || "0".equals(num1) || "0".equals(num2)) {
return "0";
}
final int n = num1.length();
final int m = num2.length();
int[] result = new int[n + m];
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
for (int j = m - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
// 对于每一个i,j 先相乘
int mul = (num1.charAt(i) - '0') * (num2.charAt(j) - '0');
// 然后和原本的个位(进位)相加
mul += result[i + j + 1];
// 赋值给个位
result[i + j + 1] = mul % 10;
// 累加,因为被乘数上一位乘以乘数时,该位置会有值
result[i + j] += mul / 10;
}
}
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int r : result) {
// 打头的0可以去掉
if (!(r == 0 && sb.length() == 0)) {
sb.append(r);
}
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
44. Wildcard Matching¶
- String Backtracking
Given an input string (
s) and a pattern (p), implement wildcard pattern matching with support for '?' and '*'.'?' Matches any single character.
'*' Matches any sequence of characters (including the empty sequence).The matching should cover the entire input string (not partial).
Note:
scould be empty and contains only lowercase lettersa-z.pcould be empty and contains only lowercase lettersa-z, and characters like?or*.
Example 1:
Input:
s = "aa"
p = "a"
Output: false
Explanation: "a" does not match the entire string "aa".
Example 2:
Input:
s = "aa"
p = "*"
Output: true
Explanation: '*' matches any sequence.
Example 3:
Input:
s = "cb"
p = "?a"
Output: false
Explanation: '?' matches 'c', but the second letter is 'a', which does not match 'b'.
Example 4:
Input:
s = "adceb"
p = "*a*b"
Output: true
Explanation: The first '*' matches the empty sequence, while the second '*' matches the substring "dce".
Example 5:
Input:
s = "acdcb"
p = "a*c?b"
Output: false
Solution
该题是一个通配符问题,与LC-10-Regular Expression Matching题目不同,第10题要求*可以匹配0或多个前面的元素,而此题*则是可以匹配0个或多个任意元素。
所以此题肯定是要进行回溯的。具体表现在,如果出现了*,则记录下当前的位置以待回溯,同时记录当前str的索引match,p++继续后面的匹配。如果匹配不成功,那么进行回溯。回溯时需要注意一点,p要进一步,不然会导致进入死循环,s和match也要进一步,因为前面是一次失败的匹配。
public boolean isMatch(String str, String pattern) {
int s = 0, p = 0, match = 0, starIdx = -1;
while (s < str.length()) {
// advancing both pointers
if (p < pattern.length() && (pattern.charAt(p) == '?' || str.charAt(s) == pattern.charAt(p))){
s++;
p++;
}
// * found, only advancing pattern pointer
else if (p < pattern.length() && pattern.charAt(p) == '*'){
starIdx = p;
match = s;
p++;
}
// last pattern pointer was *, advancing string pointer
else if (starIdx != -1){
p = starIdx + 1;
s = ++match;
}
//current pattern pointer is not star, last patter pointer was not *
//characters do not match
else return false;
}
//check for remaining characters in pattern
while (p < pattern.length() && pattern.charAt(p) == '*')
p++;
return p == pattern.length();
}
45. Jump Game II¶
- Greedy
- Dynamic Programming
同类型题:LC-55-Jump Game
Given an array of non-negative integers, you are initially positioned at the first index of the array.
Each element in the array represents your maximum jump length at that position.
Your goal is to reach the last index in the minimum number of jumps.
Example:
Input: [2,3,1,1,4]
Output: 2
Explanation: The minimum number of jumps to reach the last index is 2. Jump 1 step from index 0 to 1, then 3 steps to the last index.
Note:
You can assume that you can always reach the last index.
Solution
Approach 1: Dynamic Programming
class Solution {
public int jump(int[] nums) {
final int n = nums.length;
int[] dp = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < n && j <= nums[i] + i; j++) {
if (dp[j] == 0) {
dp[j] = dp[i] + 1;
} else {
dp[j] = Math.min(dp[j], dp[i] + 1);
}
}
}
return dp[n - 1];
}
}
Approach 2: Greedy
计算出每一步能到达的最远的位置,然后当i到达上一步最远距离时,step++,且扩充最远距离。
class Solution {
public int jump(int[] nums) {
final int n = nums.length;
int curEnd = 0, furthest = 0, step = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
furthest = Math.max(i + nums[i], furthest);
if (curEnd == i) {
step++;
curEnd = furthest;
}
}
return step;
}
}
46. Permutations¶
- Backtracking
Given a collection of distinct integers, return all possible permutations.
Example:
Input: [1,2,3]
Output:
[
[1,2,3],
[1,3,2],
[2,1,3],
[2,3,1],
[3,1,2],
[3,2,1]
]
全排列问题,与CI-(38)字符串的排列类似。
Solution
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return result;
}
permuteInner(nums, 0, nums.length, result);
return result;
}
private void permuteInner(int[] nums, int begin, final int n, List<List<Integer>> result) {
if (n - 1 == begin) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(n);
for (int num : nums) {
list.add(num);
}
result.add(list);
} else {
for (int i = begin; i < n; i++) {
swap(nums, begin, i);
permuteInner(nums, begin + 1, n, result);
swap(nums, begin, i);
}
}
}
private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
int temp = nums[j];
nums[j] = nums[i];
nums[i] = temp;
}
}
47. Permutations II¶
- Backtracking
Given a collection of numbers that might contain duplicates, return all possible unique permutations.
Example:
Input: [1,1,2]
Output:
[
[1,1,2],
[1,2,1],
[2,1,1]
]
Solution
Use an extra boolean array " boolean[] used" to indicate whether the value is added to list.
Sort the array "int[] nums" to make sure we can skip the same value.
when a number has the same value with its previous, we can use this number only if his previous is used
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return result;
}
final int n = nums.length;
Arrays.sort(nums);
permuteUniqueInner(nums, n, new boolean[n], new ArrayList<Integer>(n), result);
return result;
}
private void permuteUniqueInner(int[] nums, final int n, boolean[] used, List<Integer> tmp, List<List<Integer>> result) {
if (tmp.size() == n) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(tmp));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (used[i]) continue;
if (i > 0 && nums[i - 1] == nums[i] && !used[i - 1]) continue;
used[i] = true;
tmp.add(nums[i]);
permuteUniqueInner(nums, n, used, tmp, result);
tmp.remove(tmp.size() - 1);
used[i] = false;
}
}
}
48. Rotate Image¶
- Array
You are given an n x n 2D matrix representing an image.
Rotate the image by 90 degrees (clockwise).
Note:
You have to rotate the image in-place, which means you have to modify the input 2D matrix directly. DO NOT allocate another 2D matrix and do the rotation.
Example 1:
Given input matrix =
[
[1,2,3],
[4,5,6],
[7,8,9]
],
rotate the input matrix in-place such that it becomes:
[
[7,4,1],
[8,5,2],
[9,6,3]
]
Example 2:
Given input matrix =
[
[ 5, 1, 9,11],
[ 2, 4, 8,10],
[13, 3, 6, 7],
[15,14,12,16]
],
rotate the input matrix in-place such that it becomes:
[
[15,13, 2, 5],
[14, 3, 4, 1],
[12, 6, 8, 9],
[16, 7,10,11]
]
Solution
矩阵旋转问题有通用方法
- 顺时针,先将矩阵上下反转,然后对角线对称交换
- 逆时针,先将矩阵左右反转,然后对角线对称交换
/*
* clockwise rotate
* first reverse up to down, then swap the symmetry
* 1 2 3 7 8 9 7 4 1
* 4 5 6 => 4 5 6 => 8 5 2
* 7 8 9 1 2 3 9 6 3
*/
void rotate(vector<vector<int> > &matrix) {
reverse(matrix.begin(), matrix.end());
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.size(); ++i) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < matrix[i].size(); ++j)
swap(matrix[i][j], matrix[j][i]);
}
}
/*
* anticlockwise rotate
* first reverse left to right, then swap the symmetry
* 1 2 3 3 2 1 3 6 9
* 4 5 6 => 6 5 4 => 2 5 8
* 7 8 9 9 8 7 1 4 7
*/
void anti_rotate(vector<vector<int> > &matrix) {
for (auto vi : matrix) reverse(vi.begin(), vi.end());
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.size(); ++i) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < matrix[i].size(); ++j)
swap(matrix[i][j], matrix[j][i]);
}
}
采用上面的方式,我们可以给出下面的答案:
class Solution {
public void rotate(int[][] matrix) {
final int n = matrix.length;
if (n <= 1) return;
// reserve
for (int i = 0; i < n / 2; i++) {
int[] tmp = matrix[i];
matrix[i] = matrix[n - 1 - i];
matrix[n - 1 - i] = tmp;
}
// swap
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
int tmp = matrix[i][j];
matrix[i][j] = matrix[j][i];
matrix[j][i] = tmp;
}
}
}
}
49. Group Anagrams¶
- Hash Table
- String
Given an array of strings, group anagrams together.
Example:
Input: ["eat", "tea", "tan", "ate", "nat", "bat"],
Output:
[
["ate","eat","tea"],
["nat","tan"],
["bat"]
]
Note:
- All inputs will be in lowercase.
- The order of your output does not matter.
Solution
该问题的核心就是如何确定两个字符串是否是相同字母异序词(anagrams)。
有两种思路:
- 将字符串里面的字符进行排序,排序后组成一个新的字符串,比较新字符串是否相等即可
- 使用HashMap统计字符串里面每个字符出现的个数,按照a-z的顺序组成新字符串,比较新字符串是否相等即可
假设这里有N个字符串,字符串中最长字符的长度为K,那么两种方式的时间、空间复杂度为:
- 时间复杂度为\(O(N \cdot KlogK)\),空间复杂度为\(O(NK)\)
- 时间复杂度为\(O(N \cdot K)\),空间复杂度为\(O(NK)\)
Approach 1: Categorize by Sorted String
class Solution {
public List<List<String>> groupAnagrams(String[] strs) {
Map<String, List<String>> bucket = new HashMap<>();
for (String str : strs) {
char[] ch = str.toCharArray();
Arrays.sort(ch);
String key = new String(ch);
List<String> list = bucket.getOrDefault(key, new ArrayList<String>());
list.add(str);
bucket.put(key, list);
}
return new ArrayList<>(bucket.values());
}
}
Approach 2: Categorize by Count
class Solution {
public List<List<String>> groupAnagrams(String[] strs) {
List<List<String>> result = new ArrayList<>();
Map<String, List<String>> map = new HashMap<>();
int[] counts = new int[26];
for (String str : strs) {
Arrays.fill(counts, 0);
for (char ch : str.toCharArray())
counts[ch - 'a']++;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++)
if (counts[i] > 0)
sb.append(counts[i]).append(i + 'a');
String key = sb.toString();
if (!map.containsKey(key)) map.put(key, new ArrayList<>());
map.get(key).add(str);
}
return new ArrayList<>(map.values());
}
}
50. Pow(x, n)¶
- Math
Implement
pow(x, n), which calculates x raised to the power n \((x^n)\).
Example 1:
Input: 2.00000, 10
Output: 1024.00000
Example 2:
Input: 2.10000, 3
Output: 9.26100
Example 3:
Input: 2.00000, -2
Output: 0.25000
Explanation: 2-2 = 1/22 = ¼ = 0.25
Note:
- -100.0 < x < 100.0
- n is a 32-bit signed integer, within the range \([−2^{31}, 2^{31} − 1]\)
Solution
同CI-16-数值的整数次方,需要注意n的溢出问题。
public class Solution {
public double myPow(double base, int exponent) {
if (exponent < 0 && base == 0) {
return 0;
}
long absExponent = Math.abs(exponent * 1L);
double result = powerInner(base, absExponent);
return exponent < 0 ? 1.0 / result : result;
}
private double powerInner(double base, long exponent) {
if (exponent == 0) {
return 1;
} else if (exponent == 1) {
return base;
}
double result = powerInner(base, exponent >> 1);
result *= result;
if ((exponent & 0x1) == 1) {
result *= base;
}
return result;
}
}
![The above elevation map is represented by array [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]. In this case, 6 units of rain water (blue section) are being trapped.](/assets/images/leetcode/rainwatertrap.png)