LeetCode(31-40)
31. Next Permutation¶
- Array
Implement next permutation, which rearranges numbers into the lexicographically next greater permutation of numbers.
If such arrangement is not possible, it must rearrange it as the lowest possible order (ie, sorted in ascending order).
The replacement must be in-place and use only constant extra memory.
Here are some examples. Inputs are in the left-hand column and its corresponding outputs are in the right-hand column.
1,2,3→1,3,2
3,2,1→1,2,3
1,1,5→1,5,1
Solution
class Solution {
public void nextPermutation(int[] nums) {
int i = nums.length - 2;
while (i >= 0 && (nums[i + 1] <= nums[i])) {
i--;
}
if (i >= 0) {
int j = nums.length - 1;
while (j >= 0 && (nums[j] <= nums[i])) {
j--;
}
swap(nums, i, j);
}
reverse(nums, i + 1);
}
private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
int k = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = k;
}
private void reverse(int[] nums, int start) {
int end = nums.length - 1;
while (end > start) {
swap(nums, start, end);
start++;
end--;
}
}
}

首先从尾部开始查找,找到第一个递减(从尾部看)的元素i
从i往尾部查找,找到第一个大于i的元素j,交换i,j
将nums从i+1开始,反转
32. Longest Valid Parentheses¶
- String
- Dynamic Programming
Given a string containing just the characters '(' and ')', find the length of the longest valid (well-formed) parentheses substring.
Example 1:
Input: "(()"
Output: 2
Explanation: The longest valid parentheses substring is "()"
Example 2:
Input: ")()())"
Output: 4
Explanation: The longest valid parentheses substring is "()()"
Solution
Approach 1: Using Dynamic Programming
class Solution {
public int longestValidParentheses(String s) {
final int N = s.length();
int[] dp = new int[N];
int longest = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
if (s.charAt(i) == ')') {
if (s.charAt(i - 1) == '(') {
dp[i] = ((i >= 2) ? dp[i - 2] : 0) + 2;
} else { // s.charAt(i - 1) == ')'
if (i - dp[i - 1] > 0 && s.charAt(i - dp[i - 1] - 1) == '(') {
dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + (i - dp[i - 1] >= 2 ? dp[i - dp[i - 1] - 2] : 0) + 2;
}
}
longest = Math.max(longest, dp[i]);
}
}
return longest;
}
}
采用动态规划算法,在遇到')'时开始计算阶段的值(当前下标记为i),最后取阶段值和最大值的较大者。
而难题在于如何用上一个阶段的结果得出这个阶段的结果。我们可以分为两种情况讨论:
1、i-1为'('时,此时我们只需要将i-2的dp值加上'()'的长度2即可。
2、i-1为')'时,dp[i-1]的值就表示了上一个阶段的值,所以i-dp[i-1]就得到了上个阶段起始的坐标。这里我们只要关心i-dp[i-1]-1是'('的情况,因为'('才能和s[i]=')'匹配。因此,dp[i] = dp[i - 1] + dp[i - dp[i - 1] - 2] + 2。
Approach 2: Using Stack
class Solution {
public int longestValidParentheses(String s) {
final int N = s.length();
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
int longest = 0;
stack.push(-1);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if (s.charAt(i) == '(') {
stack.push(i);
} else {
stack.pop();
if (stack.isEmpty()) {
stack.push(i);
} else {
longest = Math.max(longest, i - stack.peek());
}
}
}
return longest;
}
}
经中此篇如此高深,难道你当真懂得?
经中此篇如此高深,我的确不懂!
不过在讨论区的高票答案也是Stack解法,理解起来简单多了。两者核心思想应该是一致的。
Approach 2.2: Using Stack
class Solution {
public int longestValidParentheses(String s) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
char c = s.charAt(i);
if (c == '(') stack.push(i);
else if (!stack.empty() && s.charAt(stack.peek()) == '(') stack.pop();
else stack.push(i);
}
if (stack.empty()) return s.length();
int res = 0, high = s.length();
while (!stack.empty()) {
int low = stack.pop();
res = Math.max(res, high - low - 1);
high = low;
}
return Math.max(res, high);
}
}
将匹配不成功的索引push进栈,元素处理完后,栈中元素就是合法元素的临界点。两两之间都是合法的元素集合。直接其计算长度取较大者即可。
Approach 3: Without extra space
public class Solution {
public int longestValidParentheses(String s) {
int left = 0, right = 0, maxlength = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
if (s.charAt(i) == '(') {
left++;
} else {
right++;
}
if (left == right) {
maxlength = Math.max(maxlength, 2 * right);
} else if (right >= left) {
left = right = 0;
}
}
left = right = 0;
for (int i = s.length() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (s.charAt(i) == '(') {
left++;
} else {
right++;
}
if (left == right) {
maxlength = Math.max(maxlength, 2 * left);
} else if (left >= right) {
left = right = 0;
}
}
return maxlength;
}
}
33. Search in Rotated Sorted Array¶
- Array
- Binary Search
Suppose an array sorted in ascending order is rotated at some pivot unknown to you beforehand.
(i.e.,
[0,1,2,4,5,6,7]might become[4,5,6,7,0,1,2]).You are given a target value to search. If found in the array return its index, otherwise return
-1.You may assume no duplicate exists in the array.
Your algorithm's runtime complexity must be in the order of O(log n).
Example 1:
Input: nums = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2], target = 0
Output: 4
Example 2:
Input: nums = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2], target = 3
Output: -1
Solution
class Solution {
public int search(int[] nums, int target) {
final int N = nums.length;
int lo = 0, hi = nums.length - 1;
while (lo < hi) {
int mid = (lo + hi) / 2;
if (nums[mid] > nums[hi])
lo = mid + 1;
else
hi = mid;
}
int pivot = lo;
lo = 0;
hi = nums.length - 1;
while (lo <= hi) {
int mid = (lo + hi) / 2;
int realMid = (mid + pivot) % N;
if (nums[realMid] == target) return realMid;
if (nums[realMid] < target)
lo = mid + 1;
else
hi = mid - 1;
}
return -1;
}
}
题目要求O(log n)的时间复杂度,因此需要用到二分查找算法。
首先二分查找pivot的下标,然后二分查找target。
34. Find First and Last Position of Element in Sorted Array¶
- Array
- Binary Search
Given an array of integers nums sorted in ascending order, find the starting and ending position of a given target value.
Your algorithm's runtime complexity must be in the order of O(log n).
If the target is not found in the array, return [-1, -1].
Example 1:
Input: nums = [5,7,7,8,8,10], target = 8
Output: [3,4]
Example 2:
Input: nums = [5,7,7,8,8,10], target = 6
Output: [-1,-1]
Solution
class Solution {
// returns leftmost (or rightmost) index at which `target` should be
// inserted in sorted array `nums` via binary search.
private int extremeInsertionIndex(int[] nums, int target, boolean left) {
int lo = 0;
int hi = nums.length;
while (lo < hi) {
int mid = (lo + hi) / 2;
if (nums[mid] > target || (left && target == nums[mid])) {
hi = mid;
}
else {
lo = mid+1;
}
}
return lo;
}
public int[] searchRange(int[] nums, int target) {
int[] targetRange = {-1, -1};
int leftIdx = extremeInsertionIndex(nums, target, true);
// assert that `leftIdx` is within the array bounds and that `target`
// is actually in `nums`.
if (leftIdx == nums.length || nums[leftIdx] != target) {
return targetRange;
}
targetRange[0] = leftIdx;
targetRange[1] = extremeInsertionIndex(nums, target, false)-1;
return targetRange;
}
}
注意二分查找的左右边界问题。
因为左右边界的边界更新不一样,所以extremeInsertionIndex方法使用left值判断要求的左边界还是右边界。
35. Search Insert Position¶
- Array
- Binary Search
Given a sorted array and a target value, return the index if the target is found. If not, return the index where it would be if it were inserted in order.
You may assume no duplicates in the array.
Example 1:
Input: [1,3,5,6], 5
Output: 2
Example 2:
Input: [1,3,5,6], 2
Output: 1
Example 3:
Input: [1,3,5,6], 7
Output: 4
Example 4:
Input: [1,3,5,6], 0
Output: 0
Solution
class Solution {
public int searchInsert(int[] nums, int target) {
int lo = 0, hi = nums.length - 1;
while (lo <= hi) {
int mid = (lo + hi) / 2;
if (nums[mid] == target) {
return mid;
} else if (nums[mid] > target) {
hi = mid - 1;
} else {
lo = mid + 1;
}
}
return lo;
}
}
本题考察的标准的二分查找,在lo==hi这一轮时,lo为满足条件的位置。
36. Valid Sudoku¶
- Hash Table
- Hash Set]
Determine if a 9x9 Sudoku board is valid. Only the filled cells need to be validated according to the following rules:
- Each row must contain the digits
1-9without repetition.- Each column must contain the digits
1-9without repetition.- Each of the 9
3x3sub-boxes of the grid must contain the digits1-9without repetition.
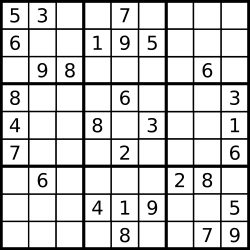
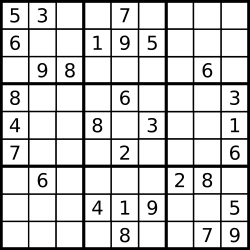
A partially filled sudoku which is valid. The Sudoku board could be partially filled, where empty cells are filled with the character
'.'.
Example 1:
Input:
[
["5","3",".",".","7",".",".",".","."],
["6",".",".","1","9","5",".",".","."],
[".","9","8",".",".",".",".","6","."],
["8",".",".",".","6",".",".",".","3"],
["4",".",".","8",".","3",".",".","1"],
["7",".",".",".","2",".",".",".","6"],
[".","6",".",".",".",".","2","8","."],
[".",".",".","4","1","9",".",".","5"],
[".",".",".",".","8",".",".","7","9"]
]
Output: true
Example 2:
Input:
[
["8","3",".",".","7",".",".",".","."],
["6",".",".","1","9","5",".",".","."],
[".","9","8",".",".",".",".","6","."],
["8",".",".",".","6",".",".",".","3"],
["4",".",".","8",".","3",".",".","1"],
["7",".",".",".","2",".",".",".","6"],
[".","6",".",".",".",".","2","8","."],
[".",".",".","4","1","9",".",".","5"],
[".",".",".",".","8",".",".","7","9"]
]
Output: false
Explanation: Same as Example 1, except with the 5 in the top left corner being modified to 8. Since there are two 8's in the top left 3x3 sub-box, it is invalid.
Note:
- A Sudoku board (partially filled) could be valid but is not necessarily solvable.
- Only the filled cells need to be validated according to the mentioned rules.
- The given board contain only digits
1-9and the character'.'. - The given board size is always
9x9.
Solution
HashTable
class Solution {
public boolean isValidSudoku(char[][] board) {
final int N = 9;
Map<Integer, Character>[] rowMaps = new HashMap[N];
Map<Integer, Character>[] colMaps = new HashMap[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
rowMaps[i] = new HashMap<Integer, Character>(N);
colMaps[i] = new HashMap<Integer, Character>(N);
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
char ch = board[i][j];
if (ch == '.') {
continue;
} else if (!rowMaps[i].containsValue(ch) && !colMaps[j].containsValue(ch)) {
rowMaps[i].put(j, ch);
colMaps[j].put(i, ch);
} else {
return false;
}
}
}
return checkBox(board, N);
}
private boolean checkBox(char[][] board, int N) {
Map<Integer, Character> map = new HashMap<Integer, Character>(N);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i+= 3) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j += 3) {
map.clear();
for (int r = i; r < i + 3; r++) {
for (int l = j; l < j + 3; l++) {
char ch = board[r][l];
if (ch == '.') {
continue;
} else if (!map.containsValue(ch)) {
map.put((r - i) * 3 + (l - j), ch);
} else {
return false;
}
}
}
}
}
return true;
}
}
HashSet
class Solution {
public boolean isValidSudoku(char[][] board) {
final int N = 9;
Set<String> set = new HashSet();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
char ch = board[i][j];
if (ch != '.') {
if (!set.add(ch + " in row " + i) ||
!set.add(ch + " in col " + j) ||
!set.add(ch + " in box " + (i / 3) + "-" + (j / 3))) {
return false;
}
}
}
}
return true;
}
}
本题要求的是数独棋盘是否 满足规则 ,而不是求解。
HashTable的解法比较自然,HashSet的解法更加牛逼。但是runtime差不多。
37. Sudoku Solver¶
- Hash Table
- Backtracking
Determine if a 9x9 Sudoku board is valid. Only the filled cells need to be validated according to the following rules:
- Each row must contain the digits
1-9without repetition.- Each column must contain the digits
1-9without repetition.- Each of the 9
3x3sub-boxes of the grid must contain the digits1-9without repetition.
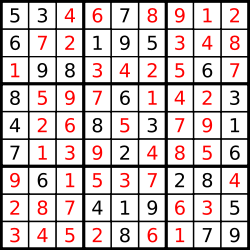
A sudoku puzzle...
...and its solution numbers marked in red.
Note:
- The given board contain only digits
1-9and the character'.'. - You may assume that the given Sudoku puzzle will have a single unique solution.
- The given board size is always
9x9.
Solution
class Solution {
static final int N = 9;
public boolean solveSudoku(char[][] board) {
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
char ch = board[i][j];
if (ch != '.') continue;
for (char c = '1'; c <= '9'; c++) {
if (isValid(board, i, j, c)) {
board[i][j] = c;
if (solveSudoku(board)) {
return true;
} else {
board[i][j] = '.';
}
}
}
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
private boolean isValid(char[][] board, int row, int col, char ch) {
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
// check row
if (board[row][i] == ch) return false;
// check col
if (board[i][col] == ch) return false;
// check box
if (board[row / 3 * 3 + i / 3][col / 3 * 3 + i % 3] == ch) return false;
}
return true;
}
}
使用 暴力法 求解:
1、遍历每一个格子,在当前格子没有值的情况下尝试放置1~9
2.1、如果可以放置,在此基础上递归调用求解算法,如果算法返回true则求解成功,否则清除放置的值,继续下次循环
2.2、如果都不能放置,返回false
38. Count and Say¶
- String
The count-and-say sequence is the sequence of integers with the first five terms as following:
1. 1
2. 11
3. 21
4. 1211
5. 111221
6. 312211
7. 13112221
8. 1113213211
9. 31131211131221
10. 13211311123113112211
1is read off as"one 1"or11.
11is read off as"two 1s"or21.
21is read off as"one 2, then one 1"or1211.Given an integer n where 1 ≤ n ≤ 30, generate the *n*th term of the count-and-say sequence.
Note: Each term of the sequence of integers will be represented as a string.
Solution
class Solution {
public String countAndSay(int n) {
String result = "1";
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
result = countAndSay(result);
}
return result;
}
private String countAndSay(String str) {
final int N = str.length();
int count = 1;
char first = str.charAt(0);
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
if (i != N && str.charAt(i) == first) {
count++;
} else {
result.append(count).append(first);
if (i != N) {
count = 1;
first = str.charAt(i);
}
}
}
return result.toString();
}
}
此题理解题意很重要,我们注意到除开1之外,其他数的结果都是前一个数结果的读音。
39. Combination Sum¶
- Array
- Backtracking
Given a set of candidate numbers (candidates) (without duplicates) and a target number (target), find all unique combinations in candidates where the candidate numbers sums to target.
The same repeated number may be chosen from candidates unlimited number of times.
Note:
- All numbers (including target) will be positive integers.
- The solution set must not contain duplicate combinations.
Example 1:
Input: candidates = [2,3,6,7], target = 7,
A solution set is:
[
[7],
[2,2,3]
]
Example 2:
Input: candidates = [2,3,5], target = 8,
A solution set is:
[
[2,2,2,2],
[2,3,3],
[3,5]
]
Solution
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
Arrays.sort(candidates);
backtrace(result, new ArrayList<Integer>(), candidates, target, 0);
return result;
}
private void backtrace(List<List<Integer>> result, List<Integer> tmp, int[] candidates, int remain, int start) {
if (remain < 0)
return;
else if (remain == 0)
result.add(new ArrayList(tmp));
else
for (int i = start; i < candidates.length; i++) {
tmp.add(candidates[i]);
backtrace(result, tmp, candidates, remain - candidates[i], i);
tmp.remove(tmp.size() - 1);
}
}
}
回溯法求解此题,比较标准的回溯法。
40. Combination Sum II¶
- Array
- Backtracking
Given a set of candidate numbers (candidates) and a target number (target), find all unique combinations in candidates where the candidate numbers sums to target.
Each number in candidates may only be used once in the combination.
Note:
- All numbers (including target) will be positive integers.
- The solution set must not contain duplicate combinations.
Example 1:
Input: candidates = [10,1,2,7,6,1,5], target = 8,
A solution set is:
[
[1, 7],
[1, 2, 5],
[2, 6],
[1, 1, 6]
]
Example 2:
Input: candidates = [2,5,2,1,2], target = 5,
A solution set is:
[
[1,2,2],
[5]
]
Solution
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
Arrays.sort(candidates);
backtrace(result, new ArrayList<Integer>(), candidates, target, 0);
return result;
}
private void backtrace(List<List<Integer>> result, List<Integer> tmp, int[] candidates, int remain, int start) {
if (remain < 0) {
return;
} else if (remain == 0) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(tmp));
} else {
for (int i = start; i < candidates.length; i++) {
if(i > start && candidates[i] == candidates[i-1]) continue; // skip duplicates
tmp.add(candidates[i]);
backtrace(result, tmp, candidates, remain - candidates[i], i + 1);
tmp.remove(tmp.size() - 1);
}
}
}
}
此题也是采用回溯法求解,注意如何去掉重复的情况。
if(i > start && candidates[i] == candidates[i-1])非常容易令人困惑。
[0..start-1]已经处理了,当i>start时,我们已经尝试过了[start, i-1]之间的元素了,此时candidates[i] == candidates[i-1]可以略过。