LeetCode(11-20)
11. Container With Most Water¶
- Array
- Two Pointers
Given n non-negative integers a1, a2, ..., an , where each represents a point at coordinate (i, ai). n vertical lines are drawn such that the two endpoints of line i is at (i, ai) and (i, 0). Find two lines, which together with x-axis forms a container, such that the container contains the most water.
Note: You may not slant the container and n is at least 2.
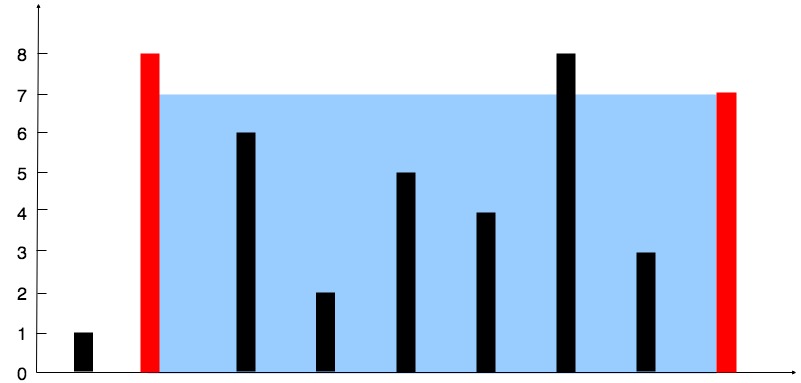
The above vertical lines are represented by array [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]. In this case, the max area of water (blue section) the container can contain is 49.
Example:
Input: [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]
Output: 49
class Solution {
public int maxArea(int[] height) {
int n = height.length, i = 0, j = n - 1, max = 0;
while (j > i) {
max = Math.max(max, Math.min(height[i], height[j]) * (j - i));
if (height[i] < height[j]) {
i++;
} else {
j--;
}
}
return max;
}
}
可以常规暴力破解法;也可以使用Two Pointer Approach解法,从两头开始遍历,每次移动高度小的一端即可。
12. Integer to Roman¶
- String
Roman numerals are represented by seven different symbols:
I,V,X,L,C,DandM.
Symbol Value I 1 V 5 X 10 L 50 C 100 D 500 M 1000 For example, two is written as
IIin Roman numeral, just two one's added together. Twelve is written as,XII, which is simply >X+II. The number twenty seven is written asXXVII, which isXX+V+II.Roman numerals are usually written largest to smallest from left to right. However, the numeral for four is not
IIII. Instead, the number four is written asIV. Because the one is before the five we subtract it making four. The same principle applies to the number nine, which is written asIX. There are six instances where subtraction is used:
Ican be placed beforeV(5) andX(10) to make 4 and 9.Xcan be placed beforeL(50) andC(100) to make 40 and 90.Ccan be placed beforeD(500) andM(1000) to make 400 and 900.Given an integer, convert it to a roman numeral. Input is guaranteed to be within the range from 1 to 3999.
Example 1:
Input: 3
Output: "III"
Example 2:
Input: 4
Output: "IV"
Example 3:
Input: 9
Output: "IX"
Example 4:
Input: 58
Output: "LVIII"
Explanation: C = 100, L = 50, XXX = 30 and III = 3.
Example 5:
Input: 1994
Output: "MCMXCIV"
Explanation: M = 1000, CM = 900, XC = 90 and IV = 4.
class Solution {
public String intToRoman(int num) {
String[] keys = {"M", "CM", "D", "CD", "C", "XC", "L", "XL", "X", "IX", "V", "IV", "I"};
int[] values = {1000, 900, 500, 400, 100, 90, 50, 40, 10, 9, 5, 4, 1};
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < values.length; i++) {
while (num >= values[i]) {
num -= values[i];
result.append(keys[i]);
}
}
return result.toString();
}
}
该问题比较讨巧,我们可以把所有可能的希腊字母和对应的阿拉伯数字列举出来,然后从高到底依次去减。
13. Roman to Integer¶
- String
Roman numerals are represented by seven different symbols:
I,V,X,L,C,DandM.
Symbol Value I 1 V 5 X 10 L 50 C 100 D 500 M 1000 For example, two is written as
IIin Roman numeral, just two one's added together. Twelve is written as,XII, which is simplyX+II. The number twenty seven is written asXXVII, which isXX+V+II.Roman numerals are usually written largest to smallest from left to right. However, the numeral for four is not
IIII. Instead, the number four is written asIV. Because the one is before the five we subtract it making four. The same principle applies to the number nine, which is written asIX. There are six instances where subtraction is used:
Ican be placed beforeV(5) andX(10) to make 4 and 9.Xcan be placed beforeL(50) andC(100) to make 40 and 90.Ccan be placed beforeD(500) andM(1000) to make 400 and 900.Given a roman numeral, convert it to an integer. Input is guaranteed to be within the range from 1 to 3999.
Example 1:
Input: "III"
Output: 3
Example 2:
Input: "IV"
Output: 4
Example 3:
Input: "IX"
Output: 9
Example 4:
Input: "LVIII"
Output: 58
Explanation: C = 100, L = 50, XXX = 30 and III = 3.
Example 5:
Input: "MCMXCIV"
Output: 1994
Explanation: M = 1000, CM = 900, XC = 90 and IV = 4.
class Solution {
public int romanToInt(String s) {
String[] keys = {"M", "CM", "D", "CD", "C", "XC", "L", "XL", "X", "IX", "V", "IV", "I"};
int[] values = {1000, 900, 500, 400, 100, 90, 50, 40, 10, 9, 5, 4, 1};
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < values.length; i++) {
while (s.startsWith(keys[i])) {
s = s.substring(keys[i].length());
sum += values[i];
}
}
return sum;
}
}
该问题与上一道题相似,也是比较讨巧,我们可以把所有可能的希腊字母和对应的阿拉伯数字列举出来,然后每次裁掉已经加过的字符。
14. Longest Common Prefix¶
- String
Write a function to find the longest common prefix string amongst an array of strings.
If there is no common prefix, return an empty string
"".
Example 1:
Input: ["flower","flow","flight"]
Output: "fl"
Example 2:
Input: ["dog","racecar","car"]
Output: ""
Explanation: There is no common prefix among the input strings.
class Solution {
public String longestCommonPrefix(String[] strs) {
final int n = strs.length;
if (n == 0) {
return "";
}
String common = strs[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
common = findCommonPrefix(common, strs[i]);
}
return common;
}
private String findCommonPrefix(String common, String str) {
if (common == null || common.length() == 0) return "";
if (str == null || str.length() == 0) return "";
int end = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < Math.min(common.length(), str.length()); i++) {
if (common.charAt(i) == str.charAt(i)) {
end++;
} else {
return common.substring(0, end);
}
}
return common.substring(0, end);
}
}
该题的思路是两两比较获取其公共前缀,然后把result和下一个字符串进行比较。
15. 3Sum¶
- Array
- Two Pointers
Given an array
numsof n integers, are there elements a, b, c innumssuch that a + b + c = 0? Find all unique triplets in the array which gives the sum of zero.Note:
The solution set must not contain duplicate triplets.
Example :
Given array nums = [-1, 0, 1, 2, -1, -4],
A solution set is:
[
[-1, 0, 1],
[-1, -1, 2]
]
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList();
if (nums.length <= 2) {
return result;
}
Arrays.sort(nums);
int sum = 0, lo, hi;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length - 2; i++) {
if (i == 0 || (i > 0 && nums[i] != nums[i - 1])) {
sum = -nums[i];
lo = i + 1;
hi = nums.length - 1;
while (hi > lo) {
if (nums[hi] + nums[lo] == sum) {
result.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i], nums[lo], nums[hi]));
while (hi > lo && nums[hi] == nums[hi - 1]) hi--;
while (hi > lo && nums[lo] == nums[lo + 1]) lo++;
hi--;
lo++;
} else if (nums[hi] + nums[lo] < sum) {
lo++;
} else {
hi--;
}
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
先排序,对于指定的a[i],从[a[i+1], a[n - 1]]的两头开始找满足条件的组合。
Note:注意需要处理所有位置的相邻位置的值是否相同的问题。
16. 3Sum Closest¶
- Array
- Two Pointers
Given an array
numsof n integers and an integertarget, find three integers innumssuch that the sum is closest totarget. Return the sum of the three integers. You may assume that each input would have exactly one solution.
Example :
Given array nums = [-1, 2, 1, -4], and target = 1.
The sum that is closest to the target is 2. (-1 + 2 + 1 = 2).
class Solution {
public int threeSumClosest(int[] nums, int target) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
int sum = 0, lo, hi, result = nums[0] + nums[1] + nums[2];
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length - 2; i++) {
lo = i + 1;
hi = nums.length - 1;
while (hi > lo) {
sum = nums[i] + nums[lo] + nums[hi];
if (sum > target) {
hi--;
} else if (sum < target){
lo++;
} else {
return sum;
}
if (Math.abs(sum - target) < Math.abs(result - target)) {
result = sum;
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
先排序,对于指定的a[i],从[a[i+1], a[n - 1]]的两头开始找满足条件的组合。
Note:要求的最接近target的sum,而不是差多少。
17. Letter Combinations of a Phone Number¶
- String
- Backtracking
Given a string containing digits from
2-9inclusive, return all possible letter combinations that the number could represent.A mapping of digit to letters (just like on the telephone buttons) is given below. Note that 1 does not map to any letters.
Example :
Input: "23"
Output: ["ad", "ae", "af", "bd", "be", "bf", "cd", "ce", "cf"].
Note:
Although the above answer is in lexicographical order, your answer could be in any order you want.
class Solution {
private static final String[] LETTERS = {"abc", "def", "ghi", "jkl", "mno", "pqrs", "tuv", "wxyz"};
public List<String> letterCombinations(String digits) {
List<String> result = new ArrayList();
for(int i = 0; i < digits.length(); i++) {
result = combinateOneLetter(result, digits.charAt(i));
}
return result;
}
private List<String> combinateOneLetter(List<String> result, char digit) {
List<String> realResult = new ArrayList();
String letter = LETTERS[digit - '2'];
if (result.size() == 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < letter.length(); i++) {
realResult.add(letter.charAt(i) + "");
}
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < letter.length(); j++) {
realResult.add(result.get(i) + letter.charAt(j));
}
}
}
return realResult;
}
}
此题的思路还是两两进行结合,然后将此次结果作为前提条件结合下一个字符进行结合。
18. 4Sum¶
- Array
- Two Pointers
- Hash Table
Given an array
numsof n integers and an integertarget, are there elements a, b, c, and d innumssuch that a + b + c + d =target? Find all unique quadruplets in the array which gives the sum oftarget.Note:
The solution set must not contain duplicate quadruplets.
Example :
Given array nums = [1, 0, -1, 0, -2, 2], and target = 0.
A solution set is:
[
[-1, 0, 0, 1],
[-2, -1, 1, 2],
[-2, 0, 0, 2]
]
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> fourSum(int[] nums, int target) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList();
Arrays.sort(nums);
int sum, lo, hi;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length - 3; i++) {
if (i != 0 && (i == 0 || (nums[i] == nums[i - 1]))) continue;
for (int j = i + 1; j < nums.length - 2; j++) {
if (j != i + 1 && (j == i + 1 || (nums[j] == nums[j - 1]))) continue;
sum = target - (nums[i] + nums[j]);
lo = j + 1;
hi = nums.length - 1;
while (hi > lo) {
if (nums[hi] + nums[lo] == sum) {
result.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i], nums[j], nums[lo], nums[hi]));
while (hi > lo && nums[lo] == nums[lo + 1]) lo++;
while (hi > lo && nums[hi] == nums[hi - 1]) hi--;
lo++;
hi--;
} else if (nums[hi] + nums[lo] > sum) {
hi--;
} else {
lo++;
}
}
}
}
return result;
}
}
此题和3Sum相似,指定前两个数字,对后两个数字进行查找。
Note:注意需要处理所有位置的相邻位置的值是否相同的问题。
19. Remove Nth Node From End of List¶
- Two Pointers
- Linked List
Given a linked list, remove the n-th node from the end of list and return its head.
Example :
Given linked list: 1->2->3->4->5, and n = 2.
After removing the second node from the end, the linked list becomes 1->2->3->5.
Note:
Given n will always be valid.
Follow up:
Could you do this in one pass?
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode result = new ListNode(0);
result.next = head;
ListNode p = result, q = result;
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
p = p.next;
}
while (p != null) {
p = p.next;
q = q.next;
}
q.next = q.next.next;
return result.next;
}
}
此题考察链表的知识
- 给链表手动添加一个头节点,可以有效的简化corner cases。
- 要删除倒数第n个节点,也就是正数N-n个节点,可以先让p指向n,然后p、q同时移动到最后,这样q就指向了N-n
- 移除列表节点:
q.next = q.next.next
20. Valid Parentheses¶
- String
- Stack
Given a string containing just the characters
'(',')','{','}','['and']', determine if the input string is valid.An input string is valid if:
- Open brackets must be closed by the same type of brackets.
- Open brackets must be closed in the correct order.
Note that an empty string is also considered valid.
Example 1:
Input: "()"
Output: true
Example 2:
Input: "()[]{}"
Output: true
Example 3:
Input: "(]"
Output: false
Example 4:
Input: "([)]"
Output: false
Example 5:
Input: "{[]}"
Output: true
class Solution {
public boolean isValid(String s) {
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>();
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
char ch = s.charAt(i);
if (ch == '(' || ch == '{' || ch == '[') {
stack.push(ch);
} else {
if (stack.isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
char pop = stack.pop();
if (pop == '(') {
if (ch == ')')
continue;
else
return false;
} else if (pop == '{') {
if (ch == '}')
continue;
else
return false;
} else if (pop == '[') {
if (ch == ']')
continue;
else
return false;
} else {
return false;
}
}
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}
}
此题考察栈的使用。遇左括号进栈,右括号出栈。
若不是左括号,且栈为空,返回false
最后返回栈是否为空,避免左右括号出现次数不匹配的情况。
