LeetCode(1-10)
1. Two Sum¶
- Array
- HashTable
Given an array of integers, return indices of the two numbers such that they add up to a specific target.
You may assume that each input would have exactly one solution, and you may not use the same element twice.
Example:
Given nums = [2, 7, 11, 15], target = 9,
Because nums[0] + nums[1] = 2 + 7 = 9,
return [0, 1].
Brute Force
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < nums.length; j++) {
if (nums[i] + nums[j] == target) {
return new int[]{i, j};
}
}
}
return new int[]{};
}
}
One-pass Hash Table
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
int complement = target - nums[i];
if (map.containsKey(complement)) {
return new int[] { map.get(complement), i };
}
map.put(nums[i], i);
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException("No two sum solution");
}
可以常规解法,也可以使用HashMap的特性。
2. Add Two Numbers¶
- LinkedList
You are given two non-empty linked lists representing two non-negative integers. The digits are stored in reverse order and each of their nodes contain a single digit. Add the two numbers and return it as a linked list.
You may assume the two numbers do not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
Example:
Input: (2 -> 4 -> 3) + (5 -> 6 -> 4)
Output: 7 -> 0 -> 8
Explanation: 342 + 465 = 807.
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode result = new ListNode(0);
ListNode p = result;
int carry = 0, bit = 0;
while (l1 != null || l2 != null || carry != 0) {
bit = ((l1 == null) ? 0 : l1.val) + ((l2 == null) ? 0 : l2.val) + carry;
carry = bit / 10;
p.next = new ListNode(bit % 10);
p = p.next;
l1 = (l1 == null) ? null : l1.next;
l2 = (l2 == null) ? null : l2.next;
}
return result.next;
}
}
该题几个要点:
- 数字是逆序存储的,即头节点是个位,这就意味着直接算,进位进到next就可以了
- 最后一个节点可能是进位进来的1
- l1、l2不一定长度相等
3. Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters¶
- HashTable
- String
- Two Pointers
Given a string, find the length of the longest substring without repeating characters.
Example:
Given
"abcabcbb", the answer is"abc", which the length is 3.
Given"bbbbb", the answer is"b", with the length of 1.
Given"pwwkew", the answer is"wke", with the length of 3. Note that the answer must be a substring,"pwke"is a subsequence and not a substring.
Sliding Window
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
int i = 0, j = 0, ans = 0, n = s.length();
Set<Character> set = new HashSet();
while (i < n && j < n) {
if (!set.contains(s.charAt(j))) {
set.add(s.charAt(j++));
ans = Math.max(ans, j - i);
} else {
set.remove(s.charAt(i++));
}
}
return ans;
}
}
题目要求最长 无重复字母 的子串,可以用Set的特性
使用滑动窗口方法解,将[i, j]里面的字母用HashSet存储
若a[j]不在Set里面,set.add(s.charAt(j++))
否则set.remove(s.charAt(i++))
4. Median of Two Sorted Arrays¶
- Array
- Binary Search
- Divide and Conquer
There are two sorted arrays nums1 and nums2 of size m and n respectively.
Find the median of the two sorted arrays. The overall run time complexity should be \(O(log(m+n))\).
You may assume nums1 and nums2 cannot be both empty.
Example 1:
nums1 = [1, 3]
nums2 = [2]
The median is 2.0
Example 2:
nums1 = [1, 2]
nums2 = [3, 4]
The median is (2 + 3)/2 = 2.5
Solution
public class Solution {
public double findMedianSortedArrays(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
// Deal with invalid corner case.
if (nums1 == null || nums2 == null || nums1.length == 0 || nums2.length == 0) return 0.0;
int m = nums1.length, n = nums2.length;
int l = (m + n + 1) / 2; //left half of the combined median
int r = (m + n + 2) / 2; //right half of the combined median
// If the nums1.length + nums2.length is odd, the 2 function will return the same number
// Else if nums1.length + nums2.length is even, the 2 function will return the left number and right number that make up a median
return (getKth(nums1, 0, nums2, 0, l) + getKth(nums1, 0, nums2, 0, r)) / 2.0;
}
private double getKth(int[] nums1, int start1, int[] nums2, int start2, int k) {
// This function finds the Kth element in nums1 + nums2
// If nums1 is exhausted, return kth number in nums2
if (start1 > nums1.length - 1) return nums2[start2 + k - 1];
// If nums2 is exhausted, return kth number in nums1
if (start2 > nums2.length - 1) return nums1[start1 + k - 1];
// If k == 1, return the first number
// Since nums1 and nums2 is sorted, the smaller one among the start point of nums1 and nums2 is the first one
if (k == 1) return Math.min(nums1[start1], nums2[start2]);
int mid1 = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int mid2 = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
if (start1 + k / 2 - 1 < nums1.length) mid1 = nums1[start1 + k / 2 - 1];
if (start2 + k / 2 - 1 < nums2.length) mid2 = nums2[start2 + k / 2 - 1];
// Throw away half of the array from nums1 or nums2. And cut k in half
if (mid1 < mid2) {
return getKth(nums1, start1 + k / 2, nums2, start2, k - k / 2); //nums1.right + nums2
} else {
return getKth(nums1, start1, nums2, start2 + k / 2, k - k / 2); //nums1 + nums2.right
}
}
}
该题的难点在于The overall run time complexity should be O(log (m+n))。因此采用 递归二分查找
如果抛开这个限制,这里有一种时间复杂度O(n)、空间复杂度O(1)的解法
class Solution {
public double findMedianSortedArrays(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
final int m = nums1.length;
final int n = nums2.length;
int i = 0, j = 0, mid1, mid2, whichArray = 1, result = 0;
mid1 = (m + n - 1) / 2;
mid2 = (m + n) / 2;
while (i < m || j < n) {
if (i < m && j < n) {
if (nums1[i] < nums2[j]) {
whichArray = 1;
} else {
whichArray = 2;
}
} else if (i < m) {
whichArray = 1;
} else if (j < n) {
whichArray = 2;
}
if (mid1 == i + j) {
result = whichArray == 1 ? nums1[i] : nums2[j];
}
if (mid2 == i + j) {
result += whichArray == 1 ? nums1[i] : nums2[j];
return result / 2.0;
}
if (whichArray == 1) {
i++;
} else {
j++;
}
}
return 0.0;
}
}
5. Longest Palindromic Substring¶
- String
- Dynamic Programming
Given a string s, find the longest palindromic substring in s. You may assume that the maximum length of s is 1000.
Example 1:
Input: "babad"
Output: "bab"
Note: "aba" is also a valid answer.
Example 2:
Input: "cbbd"
Output: "bb"
class Solution {
public String longestPalindrome(String s) {
if (s.length() < 2) {
return s;
}
char[] ca = s.toCharArray();
int rs = 0, re = 0;
int max = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < ca.length; i++) {
if(isPalindrome(ca, i - max - 1, i)) {
rs = i - max - 1; re = i;
max += 2;
} else if (isPalindrome(ca, i - max, i)) {
rs = i - max; re = i;
max += 1;
}
}
return s.substring(rs, re + 1);
}
private boolean isPalindrome(char[] ca, int s, int e) {
if(s < 0) return false;
while(s < e) {
if(ca[s++] != ca[e--]) return false;
}
return true;
}
}
我们只需要以i为end点,以max为标准进行扩展,判断max+1或max+2长度的字符串是不是回数即可。
6. ZigZag Conversion¶
- String
The string
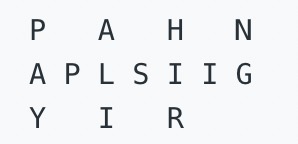
"PAYPALISHIRING"is written in a zigzag pattern on a given number of rows like this: (you may want to display this pattern in a fixed font for better legibility)
And then read line by line:"PAHNAPLSIIGYIR"
Write the code that will take a string and make this conversion given a number of rows:
Example 1:
Input: s = "PAYPALISHIRING", numRows = 3
Output: "PAHNAPLSIIGYIR"
Example 2:
Input: s = "PAYPALISHIRING", numRows = 4
Output: "PINALSIGYAHRPI"
Explanation:
class Solution {
public String convert(String s, int numRows) {
if (numRows <= 1) {
return s;
}
StringBuilder[] results = new StringBuilder[numRows];
for (int i = 0; i < numRows; i++) {
results[i] = new StringBuilder();
}
int currentRow = 0, down = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
results[currentRow].append(s.charAt(i));
if (currentRow == 0) {
down = 1;
} else if (currentRow == numRows - 1) {
down = -1;
}
currentRow += down;
}
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
for (StringBuilder sb : results) {
result.append(sb.toString());
}
return result.toString();
}
}
定义row个StringBuilder,遇到第0行或倒数第1行掉头,按顺序取字符即可。
7. Reverse Integer¶
Given a 32-bit signed integer, reverse digits of an integer.
Example 1:
Input: 123
Output: 321
Example 2:
Input: -123
Output: -321
Example 3:
Input: 120
Output: 21
class Solution {
public int reverse(int x) {
int sign = 1;
int begin = 0;
if (x < 0) {
sign = -1;
begin = 1;
}
String unsignX = String.valueOf(x).substring(begin);
long result = 0;
for (int i = unsignX.length() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
result = result * 10 + (unsignX.charAt(i) - '0');
if (result > Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
return 0;
}
}
return (int) (sign * result);
}
}
先处理无符号int,用long保存临时结果,每次累加后判断是不是溢出,最后加上符号。
8. String to Integer (atoi)¶
- String
Implement
atoiwhich converts a string to an integer.The function first discards as many whitespace characters as necessary until the first non-whitespace character is found. Then, starting from this character, takes an optional initial plus or minus sign followed by as many numerical digits as possible, and interprets them as a numerical value.
The string can contain additional characters after those that form the integral number, which are ignored and have no effect on the behavior of this function.
If the first sequence of non-whitespace characters in str is not a valid integral number, or if no such sequence exists because either str is empty or it contains only whitespace characters, no conversion is performed.
If no valid conversion could be performed, a zero value is returned.
Note:
- Only the space character
' 'is considered as whitespace character.- Assume we are dealing with an environment which could only store integers within the 32-bit signed integer range: [−2^31, 2^31 − 1]. If the numerical value is out of the range of representable values, INT_MAX (2^31 − 1) or INT_MIN (−2^31) is returned.
Example 1:
Input: "42"
Output: 42
Example 2:
Input: " -42"
Output: -42
Explanation: The first non-whitespace character is '-', which is the minus sign. Then take as many numerical digits as possible, which gets 42.
Example 3:
Input: "4193 with words"
Output: 4193
Explanation: Conversion stops at digit '3' as the next character is not a numerical digit.
Example 4:
Input: "words and 987"
Output: 0
Explanation: The first non-whitespace character is 'w', which is not a numerical digit or a ± sign. Therefore no valid conversion could be performed.
Example 5:
Input: "-91283472332"
Output: -2147483648
Explanation: The number "-91283472332" is out of the range of a 32-bit signed integer. Thefore INT_MIN (−231) is returned.
class Solution {
public int myAtoi(String str) {
if (str == null) return 0;
str = str.trim();
int i = 0;
int sign = 1;
if (i < str.length() && (str.charAt(i) == '+' || str.charAt(i) == '-')) {
sign = str.charAt(i++) == '+' ? 1 : -1;
}
long result = 0;
while (i < str.length() && Character.isDigit(str.charAt(i))) {
result = 10 * result + (sign * (str.charAt(i++) - '0'));
if (result >= Integer.MAX_VALUE) return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
if (result <= Integer.MIN_VALUE) return Integer.MIN_VALUE;
}
return (int) result;
}
}
先trim()清除头尾的空白字符串,然后判断第一位是不是符号位,然后在当前位是数字的情况下进行累加,每次累加完成后判断有没有溢出。
9. Palindrome Number¶
Determine whether an integer is a palindrome. An integer is a palindrome when it reads the same backward as forward.
Example 1:
Input: 121
Output: true
Example 2:
Input: -121
Output: false
Explanation: From left to right, it reads -121. From right to left, it becomes 121-. Therefore it is not a palindrome.
Example 3:
Input: 10
Output: false
Explanation: Reads 01 from right to left. Therefore it is not a palindrome.
class Solution {
public boolean isPalindrome(int x) {
if (x < 0) return false;
if (x % 10 == 0 && x != 0) return false;
int rev = 0;
while (x > rev) {
rev = rev * 10 + x % 10;
x /= 10;
}
return rev == x || rev / 10 == x;
}
}
普通解法就是每次取头和尾进行比较,这样需要计算长度,且取头比较繁琐。
示例解法只取尾部进行处理,到中间位置后判断原数字的左边一半和右边一半的逆序是否相等或差10。
10. Regular Expression Matching¶
- String
- Dynamic Programming
- Recursion
Given an input string (
s) and a pattern (p), implement regular expression matching with support for.and*.'.' Matches any single character.
'*' Matches zero or more of the preceding element.The matching should cover the
entireinput string (not partial).Note:
scould be empty and contains only lowercase lettersa-z.pcould be empty and contains only lowercase lettersa-z, and characters like.or*.
Example 1:
Input:
s = "aa"
p = "a"
Output: false
Explanation: "a" does not match the entire string "aa".
Example 2:
Input:
s = "aa"
p = "a*"
Output: true
Explanation: '*' means zero or more of the precedeng element, 'a'. Therefore, by repeating 'a' once, it becomes "aa".
Example 3:
Input:
s = "ab"
p = ".*"
Output: true
Explanation: ".*" means "zero or more (*) of any character (.)".
Example 4:
Input:
s = "aab"
p = "c*a*b"
Output: true
Explanation: c can be repeated 0 times, a can be repeated 1 time. Therefore it matches "aab".
Example 5:
Input:
s = "mississippi"
p = "mis*is*p*."
Output: false
class Solution {
public boolean isMatch(String text, String pattern) {
if (pattern.isEmpty()) return text.isEmpty();
boolean first_match = (!text.isEmpty() &&
(pattern.charAt(0) == text.charAt(0) || pattern.charAt(0) == '.'));
if (pattern.length() >= 2 && pattern.charAt(1) == '*'){
return (isMatch(text, pattern.substring(2)) ||
(first_match && isMatch(text.substring(1), pattern)));
} else {
return first_match && isMatch(text.substring(1), pattern.substring(1));
}
}
}
若p为空,若s也为空,返回true,反之返回false
若p的第二个字符为*,调用递归函数匹配s和去掉前两个字符的p[1];或第一个字符匹配,递归调用s去掉首字母
若p的第二个字符不为*,否则判断首字符是否匹配,且从各自的第二个字符开始调用递归函数匹配
[1]此种情况是为了处理text不是[a-z.]*打头的情况,所以可以直接略过pattern的前两个字符串