策略模式(Strategy)
1. 定义及使用场景¶
策略模式定义了一系列的算法,并将每个算法封装起来,而且使他们还可以相互替换。策略模式让算法独立于使用它的客户而独立变化。
使用场景
- 针对同一类型的多种处理方式,仅仅是具体行为有差别
- 需要安全地封装多种同一类型的操作时
- 出现同一抽象类有多个子类,而又需要使用if-else或者switch-case来选择具体子类时
2. UML图¶
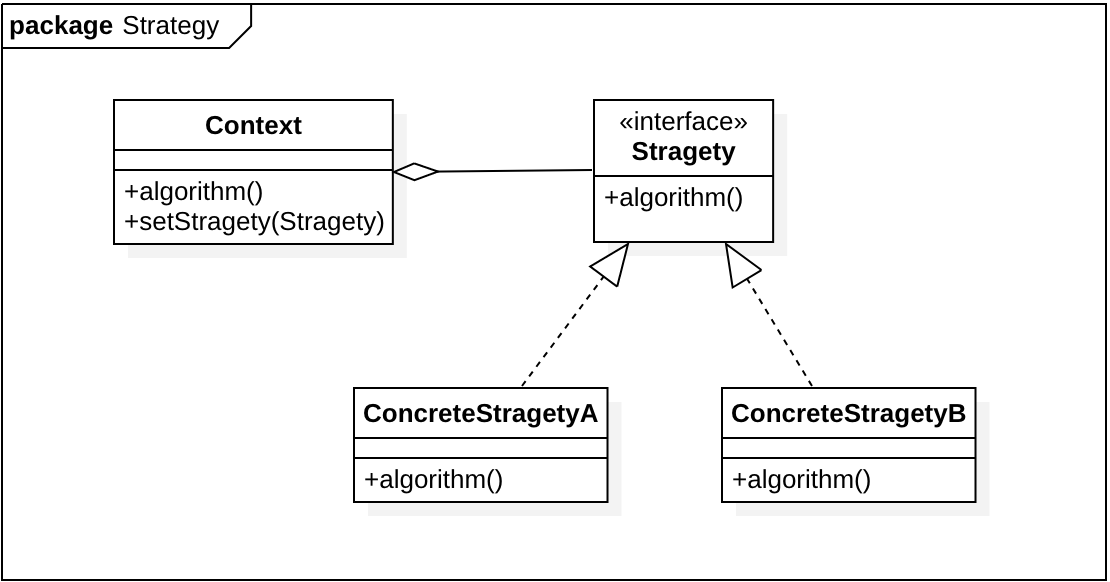
- Context
用来操作策略的环境 - Strategy
策略的抽象 - ConcreteStrategy
具体的策略
3. 举个例子¶
商场商品平时原价,“欢乐时光”时会半价出售。
interface BillStrategy {
fun getActPrice(rawPrice: Double): Double
}
class NormalStrategy : BillStrategy {
override fun getActPrice(rawPrice: Double) = rawPrice
}
class HappyTimeStrategy : BillStrategy {
override fun getActPrice(rawPrice: Double) = rawPrice * 0.5
}
class Customer(var strategy: BillStrategy) {
private var drinks = mutableListOf<Double>()
fun add(price: Double, quantity: Int) {
drinks.add(strategy.getActPrice(price * quantity))
}
fun printBill() {
println("Total due: ${drinks.sum()}")
drinks.clear()
}
}
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
val firstCustomer = Customer(NormalStrategy())
firstCustomer.add(1.0, 1)
firstCustomer.strategy = HappyTimeStrategy()
firstCustomer.add(1.0, 2)
val secondCustomer = Customer(HappyTimeStrategy())
secondCustomer.add(0.8, 1)
firstCustomer.printBill()
secondCustomer.strategy = NormalStrategy()
secondCustomer.add(1.3, 2)
secondCustomer.add(2.5, 1)
secondCustomer.printBill()
}
输出结果如下
Follow Up:
在基本的策略模式中,选择所用具体实现的职责由客户端对象承担,并转给策略模式的Context对象。 这本身并没有解除客户端需要选择判断的压力,可以将策略模式与简单工厂模式相结合,将策略的创建移到简单工厂中,这使得客户端与具体的策略彻底分离。
4. 源码中的例子¶
Android动画框架中的插值器就是典型的策略模式的体现。它的作用是根据时间流逝的百分比来计算出当前属性值改变的百分比,系统预置的有线性插值器(LinearInterpolator)用于匀速动画;加速减速插值器(AccelerateDecelerateInterpolator)用于起始时动画加速,结尾时动画减速;减速插值器(DecelerateInterpolator)用于随着时间的推移动画越来越慢,即减速动画。这些插值器就是策略模型的典型运用。
详情可参考Android动画——理解插值器和估值器