Android中的ClassLoader
本文若无特殊说明,其源码版本为6.0.0_r5
Question¶
话题:Android中的ClassLoader
1、Android中有哪几种ClassLoader?它们的作用和区别是什么?
2、简述ClassLoader的双亲委托模型
3、简述双亲委托模型在热修复领域的应用
Answer¶
1. Android中有哪几种ClassLoader?它们的作用和区别是什么?¶
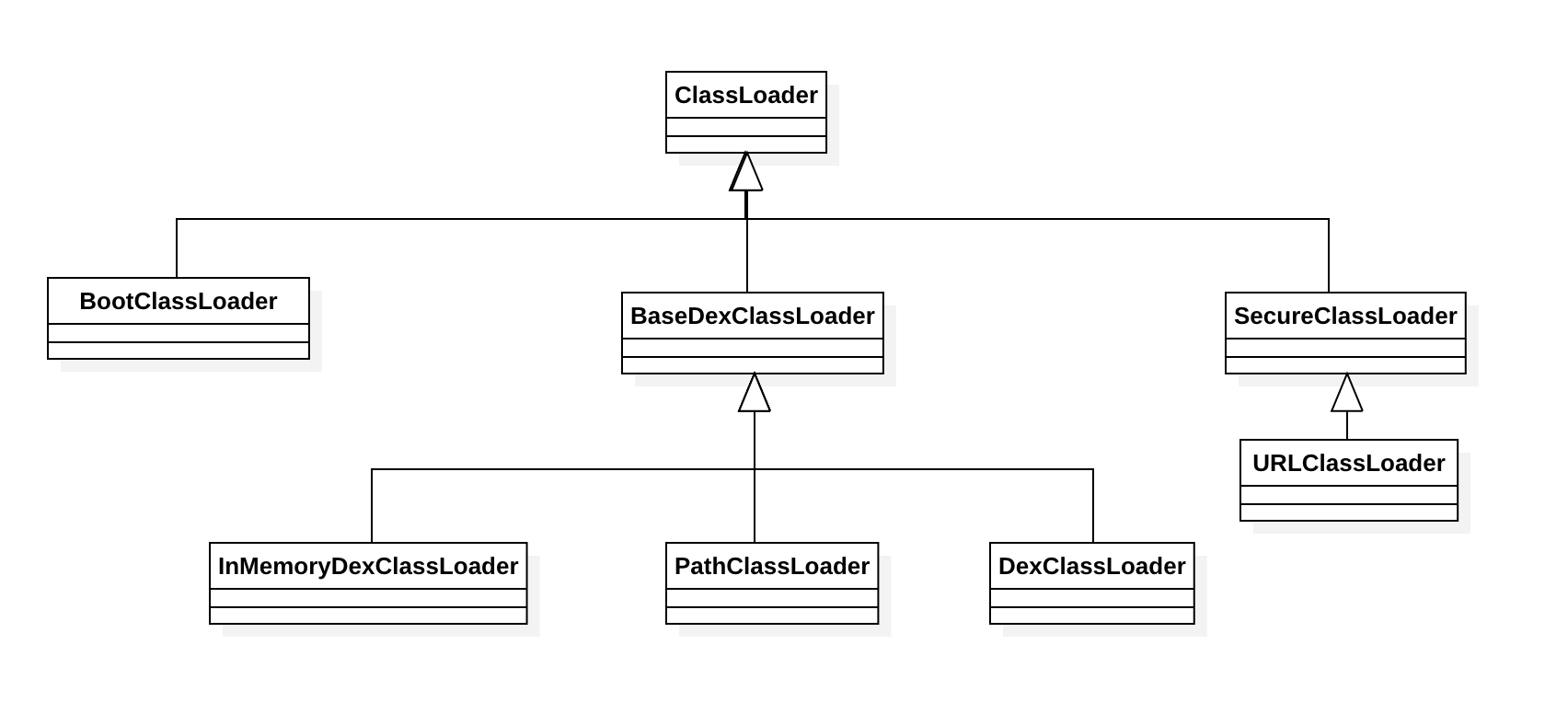
Android中有以下几种ClassLoader
- BootClassLoader
- URLClassLoader
- BaseDexClassLoader
- DexClassLoader
- PathClassLoader
- InMemoryDexClassLoader
它们之间的关系可用下图表示
1.1 BootClassLoader¶
BootClassLoader是ClassLoader的内部类。该类继承至ClassLoader,且构造器调用了super(null)。这表明 BootClassLoader是双亲委托机制中最顶层的ClassLoader 了。
且注意到BootClassLoader访问修饰符是包级的,我们无法使用。
public abstract class ClassLoader {
static private class SystemClassLoader {
public static ClassLoader loader = ClassLoader.createSystemClassLoader();
}
private static ClassLoader createSystemClassLoader() {
String classPath = System.getProperty("java.class.path", ".");
return new PathClassLoader(classPath, BootClassLoader.getInstance());
}
protected ClassLoader() {
this(getSystemClassLoader(), false);
}
protected ClassLoader(ClassLoader parentLoader) {
this(parentLoader, false);
}
ClassLoader(ClassLoader parentLoader, boolean nullAllowed) {
if (parentLoader == null && !nullAllowed) {
throw new NullPointerException("parentLoader == null && !nullAllowed");
}
parent = parentLoader;
}
}
class BootClassLoader extends ClassLoader {
private static BootClassLoader instance;
@FindBugsSuppressWarnings("DP_CREATE_CLASSLOADER_INSIDE_DO_PRIVILEGED")
public static synchronized BootClassLoader getInstance() {
if (instance == null) {
instance = new BootClassLoader();
}
return instance;
}
public BootClassLoader() {
super(null);
}
}
1.2 URLClassLoader¶
URLClassLoader是通过URL加载资源的ClassLoader,其继承至SecureClassLoader,而SecureClassLoader继承至ClassLoader。
SecureClassLoader基于ClassLoader提供了权限机制。
URLClassLoader只能用于加载jar文件,由于dalvik不能直接识别jar,所以在Android中无法使用这个加载器。我们看一下相关代码。
/**
* {@code SecureClassLoader} represents a {@code ClassLoader} which associates
* the classes it loads with a code source and provide mechanisms to allow the
* relevant permissions to be retrieved.
*/
public class SecureClassLoader extends ClassLoader {
protected SecureClassLoader() {
}
protected SecureClassLoader(ClassLoader parent) {
super(parent);
}
}
/**
* This class loader is responsible for loading classes and resources from a
* list of URLs which can refer to either directories or JAR files. Classes
* loaded by this {@code URLClassLoader} are granted permission to access the
* URLs contained in the URL search list.
*/
@FindBugsSuppressWarnings({ "DMI_COLLECTION_OF_URLS", "DP_CREATE_CLASSLOADER_INSIDE_DO_PRIVILEGED" })
public class URLClassLoader extends SecureClassLoader {
public URLClassLoader(URL[] urls) {
this(urls, ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader(), null);
}
public URLClassLoader(URL[] urls, ClassLoader parent) {
this(urls, parent, null);
}
public static URLClassLoader newInstance(final URL[] urls) {
return new URLClassLoader(urls, ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader());
}
public static URLClassLoader newInstance(final URL[] urls, final ClassLoader parentCl) {
return new URLClassLoader(urls, parentCl);
}
/**
* Constructs a new {@code URLClassLoader} instance. The newly created
* instance will have the specified {@code ClassLoader} as its parent and
* use the specified factory to create stream handlers. URLs that end with
* "/" are assumed to be directories, otherwise they are assumed to be JAR
* files.
*
* @param searchUrls
* the list of URLs where a specific class or file could be
* found.
* @param parent
* the {@code ClassLoader} to assign as this loader's parent.
* @param factory
* the factory that will be used to create protocol-specific
* stream handlers.
*/
public URLClassLoader(URL[] searchUrls, ClassLoader parent, URLStreamHandlerFactory factory) {
super(parent);
this.factory = factory;
int nbUrls = searchUrls.length;
originalUrls = new ArrayList<URL>(nbUrls);
handlerList = new ArrayList<URLHandler>(nbUrls);
searchList = Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<URL>(nbUrls));
for (int i = 0; i < nbUrls; i++) {
originalUrls.add(searchUrls[i]);
try {
searchList.add(createSearchURL(searchUrls[i]));
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
}
}
}
}
1.3 BaseDexClassLoader¶
BaseDexClassLoader继承至ClassLoader,用于加载apk/jar/dex中的资源。在该类中,由一个DexPathList对象维护dex文件的路径。
public class BaseDexClassLoader extends ClassLoader {
private final DexPathList pathList;
/**
* Constructs an instance.
*
* @param dexPath the list of jar/apk files containing classes and
* resources, delimited by {@code File.pathSeparator}, which
* defaults to {@code ":"} on Android
* @param optimizedDirectory directory where optimized dex files
* should be written; may be {@code null}
* @param libraryPath the list of directories containing native
* libraries, delimited by {@code File.pathSeparator}; may be
* {@code null}
* @param parent the parent class loader
*/
public BaseDexClassLoader(String dexPath, File optimizedDirectory,
String libraryPath, ClassLoader parent) {
super(parent);
this.pathList = new DexPathList(this, dexPath, libraryPath, optimizedDirectory);
}
}
BaseDexClassLoader的构造器有四个参数
- dexPath
包含classes和资源的apk/jar/zip/dex路径集合,在Android上一般用":"分割。可以从SD卡进行加载 - optimizedDirectory
odex后存放的目录,这个路径必须是一个内部存储路径,一般情况下使用当前应用程序的私有路径:/data/data/{Package Name}/ - libraryPath
native库存放的路径集合,用文件分隔符分割 - parent
父ClassLoader,一般为当前执行类的ClassLoader,例如在Android中以context.getClassLoader()作为父ClassLoader
1.4 DexClassLoader¶
先看DexClassLoader的源码。
public class DexClassLoader extends BaseDexClassLoader {
public DexClassLoader(String dexPath, String optimizedDirectory,
String libraryPath, ClassLoader parent) {
super(dexPath, new File(optimizedDirectory), libraryPath, parent);
}
}
DexClassLoader源码就是简单的继承了BaseDexClassLoader。在构造器中将optimizedDirectory的类型由String转变成了File。
在URLClassLoader中提到 dalvik不能直接识别jar ,而在BaseDexClassLoader支持jar文件的原因是BaseDexClassLoader里面DexPathList.dexElements维持着Element数组,Element有一个DexFile,DexFile支持对apk/jar/zip的处理。
一般都是用DexClassLoader作为动态加载的加载器。
可以参考DexFile.java的部分注释
/**
* Manipulates DEX files. The class is similar in principle to
* {@link java.util.zip.ZipFile}. It is used primarily by class loaders.
* <p>
* Note we don't directly open and read the DEX file here. They're memory-mapped
* read-only by the VM.
*/
public final class DexFile {
private Object mCookie;
private final String mFileName;
private final CloseGuard guard = CloseGuard.get();
/**
* Opens a DEX file from a given File object. This will usually be a ZIP/JAR
* file with a "classes.dex" inside.
*
* The VM will generate the name of the corresponding file in
* /data/dalvik-cache and open it, possibly creating or updating
* it first if system permissions allow. Don't pass in the name of
* a file in /data/dalvik-cache, as the named file is expected to be
* in its original (pre-dexopt) state.
*
* @param file
* the File object referencing the actual DEX file
*
* @throws IOException
* if an I/O error occurs, such as the file not being found or
* access rights missing for opening it
*/
public DexFile(File file) throws IOException {
this(file.getPath());
}
/**
* Opens a DEX file from a given filename. This will usually be a ZIP/JAR
* file with a "classes.dex" inside.
*
* The VM will generate the name of the corresponding file in
* /data/dalvik-cache and open it, possibly creating or updating
* it first if system permissions allow. Don't pass in the name of
* a file in /data/dalvik-cache, as the named file is expected to be
* in its original (pre-dexopt) state.
*
* @param fileName
* the filename of the DEX file
*
* @throws IOException
* if an I/O error occurs, such as the file not being found or
* access rights missing for opening it
*/
public DexFile(String fileName) throws IOException {
mCookie = openDexFile(fileName, null, 0);
mFileName = fileName;
guard.open("close");
//System.out.println("DEX FILE cookie is " + mCookie + " fileName=" + fileName);
}
/**
* Opens a DEX file from a given filename, using a specified file
* to hold the optimized data.
*
* @param sourceName
* Jar or APK file with "classes.dex".
* @param outputName
* File that will hold the optimized form of the DEX data.
* @param flags
* Enable optional features.
*/
private DexFile(String sourceName, String outputName, int flags) throws IOException {
if (outputName != null) {
try {
String parent = new File(outputName).getParent();
if (Libcore.os.getuid() != Libcore.os.stat(parent).st_uid) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Optimized data directory " + parent
+ " is not owned by the current user. Shared storage cannot protect"
+ " your application from code injection attacks.");
}
} catch (ErrnoException ignored) {
// assume we'll fail with a more contextual error later
}
}
mCookie = openDexFile(sourceName, outputName, flags);
mFileName = sourceName;
guard.open("close");
//System.out.println("DEX FILE cookie is " + mCookie + " sourceName=" + sourceName + " outputName=" + outputName);
}
/**
* Open a DEX file, specifying the file in which the optimized DEX
* data should be written. If the optimized form exists and appears
* to be current, it will be used; if not, the VM will attempt to
* regenerate it.
*
* This is intended for use by applications that wish to download
* and execute DEX files outside the usual application installation
* mechanism. This function should not be called directly by an
* application; instead, use a class loader such as
* dalvik.system.DexClassLoader.
*
* @param sourcePathName
* Jar or APK file with "classes.dex". (May expand this to include
* "raw DEX" in the future.)
* @param outputPathName
* File that will hold the optimized form of the DEX data.
* @param flags
* Enable optional features. (Currently none defined.)
* @return
* A new or previously-opened DexFile.
* @throws IOException
* If unable to open the source or output file.
*/
static public DexFile loadDex(String sourcePathName, String outputPathName,
int flags) throws IOException {
/*
* TODO: we may want to cache previously-opened DexFile objects.
* The cache would be synchronized with close(). This would help
* us avoid mapping the same DEX more than once when an app
* decided to open it multiple times. In practice this may not
* be a real issue.
*/
return new DexFile(sourcePathName, outputPathName, flags);
}
}
1.5 PathClassLoader¶
PathClassLoader继承至BaseDexClassLoader,且optimizedDirectory=null。在BaseDexClassLoader中由于optimizedDirectory=null,在创建DexFile时会直接new DexFile(file),从而导致会在/data/dalvik-cache中生成对应的优化文件,具体可以参考DexClassLoader小节的DexFile源码注释。
/**
* Provides a simple {@link ClassLoader} implementation that operates on a list
* of files and directories in the local file system, but does not attempt to
* load classes from the network. Android uses this class for its system class
* loader and for its application class loader(s).
*/
public class PathClassLoader extends BaseDexClassLoader {
/**
* Creates a {@code PathClassLoader} that operates on a given list of files
* and directories. This method is equivalent to calling
* {@link #PathClassLoader(String, String, ClassLoader)} with a
* {@code null} value for the second argument (see description there).
*
* @param dexPath the list of jar/apk files containing classes and
* resources, delimited by {@code File.pathSeparator}, which
* defaults to {@code ":"} on Android
* @param parent the parent class loader
*/
public PathClassLoader(String dexPath, ClassLoader parent) {
super(dexPath, null, null, parent);
}
/**
* Creates a {@code PathClassLoader} that operates on two given
* lists of files and directories. The entries of the first list
* should be one of the following:
*
* <ul>
* <li>JAR/ZIP/APK files, possibly containing a "classes.dex" file as
* well as arbitrary resources.
* <li>Raw ".dex" files (not inside a zip file).
* </ul>
*
* The entries of the second list should be directories containing
* native library files.
*
* @param dexPath the list of jar/apk files containing classes and
* resources, delimited by {@code File.pathSeparator}, which
* defaults to {@code ":"} on Android
* @param libraryPath the list of directories containing native
* libraries, delimited by {@code File.pathSeparator}; may be
* {@code null}
* @param parent the parent class loader
*/
public PathClassLoader(String dexPath, String libraryPath,
ClassLoader parent) {
super(dexPath, null, libraryPath, parent);
}
}
PathClassLoader在dalvik虚拟机上只能加载已安装apk的dex,而在art虚拟机上可以加载未安装的apk的dex。注意到类注释中的 Android uses this class for its system classloader and for its application class loader(s) ,因此不建议开发者使用。
1.6 InMemoryDexClassLoader¶
InMemoryDexClassLoader是Android 8.0, Level 26上新增的类加载器。其继承至BaseDexClassLoader,并将dexBuffers交给BaseDexClassLoader中的DexPathList处理。
/**
* A {@link ClassLoader} implementation that loads classes from a
* buffer containing a DEX file. This can be used to execute code that
* has not been written to the local file system.
*/
public final class InMemoryDexClassLoader extends BaseDexClassLoader {
/**
* Create an in-memory DEX class loader with the given dex buffers.
*
* @param dexBuffers array of buffers containing DEX files between
* <tt>buffer.position()</tt> and <tt>buffer.limit()</tt>.
* @param parent the parent class loader for delegation.
* @hide
*/
public InMemoryDexClassLoader(ByteBuffer[] dexBuffers, ClassLoader parent) {
super(dexBuffers, parent);
}
/**
* Creates a new in-memory DEX class loader.
*
* @param dexBuffer buffer containing DEX file contents between
* <tt>buffer.position()</tt> and <tt>buffer.limit()</tt>.
* @param parent the parent class loader for delegation.
*/
public InMemoryDexClassLoader(ByteBuffer dexBuffer, ClassLoader parent) {
this(new ByteBuffer[] { dexBuffer }, parent);
}
}
2. 简述ClassLoader的双亲委托模型¶
ClassLoader的双亲委托模型具体体现在ClassLoader#loadClass方法中:
/**
* Loads the class with the specified name, optionally linking it after
* loading. The following steps are performed:
* <ol>
* <li> Call {@link #findLoadedClass(String)} to determine if the requested
* class has already been loaded.</li>
* <li>If the class has not yet been loaded: Invoke this method on the
* parent class loader.</li>
* <li>If the class has still not been loaded: Call
* {@link #findClass(String)} to find the class.</li>
* </ol>
* <p>
* <strong>Note:</strong> In the Android reference implementation, the
* {@code resolve} parameter is ignored; classes are never linked.
* </p>
*
* @return the {@code Class} object.
* @param className
* the name of the class to look for.
* @param resolve
* Indicates if the class should be resolved after loading. This
* parameter is ignored on the Android reference implementation;
* classes are not resolved.
* @throws ClassNotFoundException
* if the class can not be found.
*/
protected Class<?> loadClass(String className, boolean resolve) throws ClassNotFoundException {
Class<?> clazz = findLoadedClass(className);
if (clazz == null) {
ClassNotFoundException suppressed = null;
try {
clazz = parent.loadClass(className, false);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
suppressed = e;
}
if (clazz == null) {
try {
clazz = findClass(className);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.addSuppressed(suppressed);
throw e;
}
}
}
return clazz;
}
具体过程在方法注释中很清楚:
- 调用
findLoadedClass(String)看看该类是否已经加载过了 - 如果还没有加载,调用
parent.loadClass()方法 - 如果该类仍然没有被加载,调用自身
findClass(String)进行加载
Success
使用双亲委托模式的好处
1.可以避免重复加载
2.考虑安全因素,可以避免恶意程序使用自定义的String来动态替代java api中定义的类型。
3. 简述双亲委托模型在热修复领域的应用¶
双亲委托模型在热修复领域的应用主要体现在BaseDexClassLoader#findClass方法中。
在上面一节中我们知道如果某个class从来没有加载过,那么会调用自身的findClass方法进行加载。
而在BaseDexClassLoader#findClass中,会调用pathList.findClass(name, suppressedExceptions)进行处理。下面是两个方法的源码。
@Override
protected Class<?> findClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
List<Throwable> suppressedExceptions = new ArrayList<Throwable>();
Class c = pathList.findClass(name, suppressedExceptions);
if (c == null) {
ClassNotFoundException cnfe = new ClassNotFoundException("Didn't find class \"" + name + "\" on path: " + pathList);
for (Throwable t : suppressedExceptions) {
cnfe.addSuppressed(t);
}
throw cnfe;
}
return c;
}
/**
* Finds the named class in one of the dex files pointed at by
* this instance. This will find the one in the earliest listed
* path element. If the class is found but has not yet been
* defined, then this method will define it in the defining
* context that this instance was constructed with.
*
* @param name of class to find
* @param suppressed exceptions encountered whilst finding the class
* @return the named class or {@code null} if the class is not
* found in any of the dex files
*/
public Class findClass(String name, List<Throwable> suppressed) {
for (Element element : dexElements) {
DexFile dex = element.dexFile;
if (dex != null) {
Class clazz = dex.loadClassBinaryName(name, definingContext, suppressed);
if (clazz != null) {
return clazz;
}
}
}
if (dexElementsSuppressedExceptions != null) {
suppressed.addAll(Arrays.asList(dexElementsSuppressedExceptions));
}
return null;
}
DexPathList#findClass在查找指定类时,会按顺序遍历dexElements数组,只要找到就会立刻返回。而且由于双亲委托模型的存在,不会重复加载同一个class。
因此,只要我们先加载修复好bug的class文件,那么就不会加载有bug的class了。