App内自定义软键盘
最近由于项目需要,需要自定义软键盘。直接摆Button真是low爆了,所以想试试系统关于键盘这方面的API。尝试了一下,用着还行,就是有一点点注意事项。
键盘分为常规的数字键盘+字母键盘两部分,先上效果图:
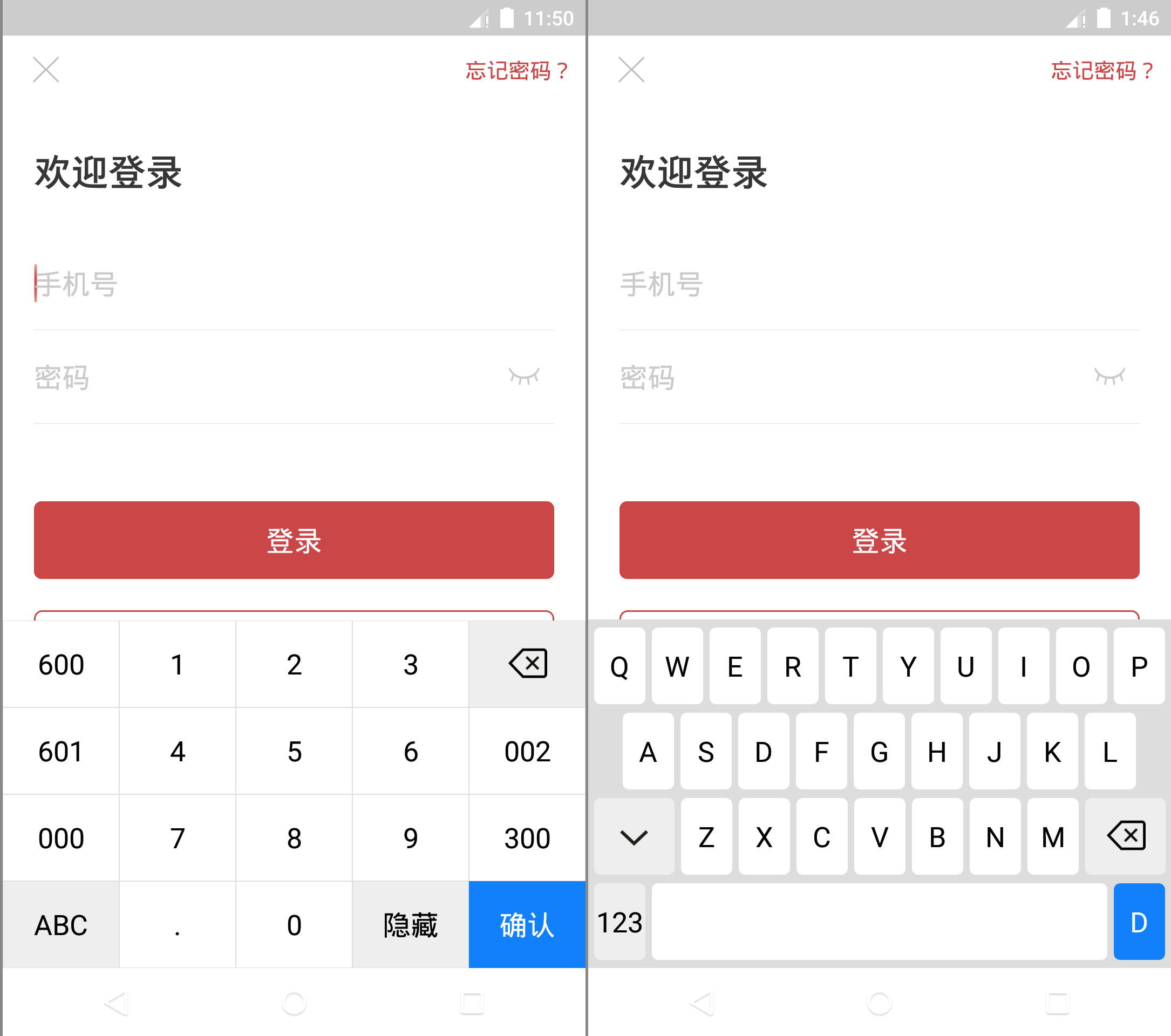
创建App内软键盘非常简单,只需要一个或多个描述键盘如何布局的Keyboard以及容器KeyboardView,其中Keyboard中键盘布局靠xml进行。
自定义的过程可以分为以下几步
- 在xml中为某种类型的软键盘进行布局,供
Keyboard创建时使用 - 自定义
KeyboardView,重写其onDraw方法为每个键绘制文字、Icon以及背景色;若有多种键盘类型,可为其提供切换键盘的API - 定义一个类实现
KeyboardView.OnKeyboardActionListener接口来处理按键点击事件;并监听EditText的点击、触摸、焦点改变事件来弹出、隐藏自定义的KeyboardView - 将自定义的
KeyboardView加入布局中,开始使用
下面一步步操作并将源码附上。
1. 按键布局¶
按键布局用xml实现,放在res/xml目录下。该资源决定了一种Keyboard的按键如何布局。可以根据项目需要,创建多种键盘的布局文件,然后在KeyboardView中进行切换。
在上面的项目中,有两种键盘:数字键盘和字母键盘。我们这里创建了两个文件:keyboard_number.xml和keyboard_qwerty.xml。
先上代码keyboard_number.xml,随后会进行分析。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<Keyboard xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:verticalGap="0px"
android:horizontalGap="0px"
android:keyHeight="9%p"
android:keyWidth="20%p">
<Row>
<Key
android:codes="-1004,-1004"
android:keyLabel="600" />
<Key
android:codes="49"
android:keyLabel="1" />
<Key
android:codes="50"
android:keyLabel="2" />
<Key
android:codes="51"
android:keyLabel="3" />
<Key
android:codes="-5"
android:isRepeatable="true"
android:keyEdgeFlags="right"
android:keyIcon="@drawable/kb_ic_keyboard_delete_n" />
</Row>
<Row>
<Key
android:codes="-1005,-1005"
android:keyLabel="601" />
<Key
android:codes="52"
android:keyLabel="4" />
<Key
android:codes="53"
android:keyLabel="5" />
<Key
android:codes="54"
android:keyLabel="6" />
<Key
android:codes="-1002,-1002"
android:keyLabel="002" />
</Row>
<Row>
<Key
android:codes="-1001,-1001"
android:keyLabel="000" />
<Key
android:codes="55"
android:keyLabel="7" />
<Key
android:codes="56"
android:keyLabel="8" />
<Key
android:codes="57"
android:keyLabel="9" />
<Key
android:codes="-1003,-1003"
android:keyLabel="300" />
</Row>
<Row>
<Key
android:codes="-2"
android:keyLabel="ABC" />
<Key
android:codes="46"
android:keyLabel="." />
<Key
android:codes="48"
android:keyLabel="0" />
<Key
android:codes="-3"
android:keyLabel="隐藏" />
<Key
android:codes="-4"
android:keyEdgeFlags="right"
android:keyLabel="确认" />
</Row>
</Keyboard>
对于键盘整体来说
- 所有按键之间不需要间隔,所以水平间隙和竖直间隙都设置为0
- 按键每排5个,所以keyWidth为20%p
- 键盘的高度固定为36%p,因此keyHeight为9%p
对于单个按键来说,宽高都不需要单独指定,只需要指定按键表示的android:codes、怎么显示(显示图标android:keyIcon还是文字android:keyLabel)、按下时是否一直发送事件android:isRepeatable,至于android:keyEdgeFlags指不指定没有多大关系。
android:codes会由我们自己进行处理。方面起见,可以用UNICODE码表示的就是UNICODE码,一些控制键可以使用系统预留的值,自定义按键的值建议使用负数。下面是定义在Keyboard中的所有控制键:
public static final int KEYCODE_SHIFT = -1;
public static final int KEYCODE_MODE_CHANGE = -2;
public static final int KEYCODE_CANCEL = -3;
public static final int KEYCODE_DONE = -4;
public static final int KEYCODE_DELETE = -5;
public static final int KEYCODE_ALT = -6;
在数字键盘中,我们使用了-2至-5,这四个值。
另外,我们自定义的特殊按键(比如600),其android:codes是两个一样的数字。这个做是为了让KeyboardView绘制文字时,不把600进行加粗。其源码如下:
if (label != null) {
// For characters, use large font. For labels like "Done", use small font.
if (label.length() > 1 && key.codes.length < 2) {
paint.setTextSize(mLabelTextSize);
paint.setTypeface(Typeface.DEFAULT_BOLD);
} else {
paint.setTextSize(mKeyTextSize);
paint.setTypeface(Typeface.DEFAULT);
}
// Draw a drop shadow for the text
paint.setShadowLayer(mShadowRadius, 0, 0, mShadowColor);
// Draw the text
canvas.drawText(label,
(key.width - padding.left - padding.right) / 2
+ padding.left,
(key.height - padding.top - padding.bottom) / 2
+ (paint.getTextSize() - paint.descent()) / 2 + padding.top,
paint);
// Turn off drop shadow
paint.setShadowLayer(0, 0, 0, 0);
}
我们可以看到,如果label长度超过1且其codes长度小于1,就使用mLabelTextSize并进行加粗;否则使用mKeyTextSize,正常字体。
如果我们在xml中不加double的code,自定义的特殊按键就是粗体,而其他普通文字都是正常,这样看起来就很怪。当然,此处double处理了,在KeyboardView.OnKeyboardActionListener中也需要进行过滤处理,后面再说。
下面是字母键盘keyboard_qwerty.xml,还是先上代码在分析。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<Keyboard
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:horizontalGap="0.91%p"
android:verticalGap="0.8%p"
android:keyWidth="9%p"
android:keyHeight="8%p">
<Row android:keyHeight="0px"/>
<Row>
<Key android:codes="81" android:keyLabel="Q" android:keyEdgeFlags="left" />
<Key android:codes="87" android:keyLabel="W" />
<Key android:codes="69" android:keyLabel="E" />
<Key android:codes="82" android:keyLabel="R" />
<Key android:codes="84" android:keyLabel="T" />
<Key android:codes="89" android:keyLabel="Y" />
<Key android:codes="85" android:keyLabel="U" />
<Key android:codes="73" android:keyLabel="I" />
<Key android:codes="79" android:keyLabel="O" />
<Key android:codes="80" android:keyLabel="P" android:keyEdgeFlags="right" />
</Row>
<Row>
<Key android:codes="65" android:keyLabel="A" android:horizontalGap="5.86%p" android:keyEdgeFlags="left" />
<Key android:codes="83" android:keyLabel="S" />
<Key android:codes="68" android:keyLabel="D" />
<Key android:codes="70" android:keyLabel="F" />
<Key android:codes="71" android:keyLabel="G" />
<Key android:codes="72" android:keyLabel="H" />
<Key android:codes="74" android:keyLabel="J" />
<Key android:codes="75" android:keyLabel="K" />
<Key android:codes="76" android:keyLabel="L" android:keyEdgeFlags="right" />
</Row>
<Row>
<Key android:codes="-3" android:keyIcon="@drawable/kb_ic_keyboard_arrow_n" android:keyWidth="13.95%p" android:keyEdgeFlags="left"/>
<Key android:codes="90" android:keyLabel="Z" />
<Key android:codes="88" android:keyLabel="X" />
<Key android:codes="67" android:keyLabel="C" />
<Key android:codes="86" android:keyLabel="V" />
<Key android:codes="66" android:keyLabel="B" />
<Key android:codes="78" android:keyLabel="N" />
<Key android:codes="77" android:keyLabel="M" />
<Key android:codes="-5" android:keyIcon="@drawable/kb_ic_keyboard_delete_n" android:keyWidth="13.95%p" android:keyEdgeFlags="right" android:isRepeatable="true" />
</Row>
<Row>
<Key android:codes="-2" android:keyLabel="123"/>
<Key android:codes="32" android:keyLabel="" android:keyWidth="78.36%p" android:isRepeatable="true" />
<Key android:codes="-4" android:keyLabel="D" android:keyEdgeFlags="right" />
</Row>
<Row android:keyHeight="0px" android:rowEdgeFlags="bottom" />
</Keyboard>
对于键盘整体来说
-
为了使键盘高度和数字键盘一致,总间距+按键高度*4要等于36%p。而
android:verticalGap指定的间距只会在两两Row之间,也就是第一行默认是置顶的,最后一行同理。所以为了让第一行、最后一行与顶部、底部之间有空隙,在键盘第一行和最后一行插入一个0高度的空行,这样就完美了。 如图所示,绿线即为0高度的空行。这样5space+4row=36%,调整一下比例,row取8%p,space取0.8%p。

字母键盘 绿线即为0高度的空行 -
android:horizontalGap不像竖直方向的,此属性在最左端与第一列之间也会生效。所以11space+10col=100%p,space取10/11,col取9%p。
第一行无需做任何调整,开始第二行。第二行只有9个按键,100-(10space+9col)=109/11,也就说两边多余的间隙为109/22,再加上本来就有的10/11的间隙,第二行第一个键的空隙应该为129/22=5.863636364。
第三行7个标准按键,两个大按键,所以这里要计算大按键的宽度,2big+7col+10space=100 ===> big=307/22=13.954545455。
最后一行,两个标准按键,一个长按键,large+2col+4space=100 ===> large=862/11=78.363636364
另外,需要注意,如果某个按键需要跨多行或多列,那么直接设置宽或高的值即可
2. KeyboardView¶
在该步骤中我们继承了KeyboardView并重写了其onDraw方法,来**实现所有的绘制逻辑**,所以其实上一步中讲到的android:codes进行double是可有可无的。
由于数字键盘和字母键盘中按键的背景是两套(数字键盘没有圆角,字母键盘全部加了圆角),而KeyboardView没有提供修改android:keyBackground值的API接口,无法实现切换键盘时也随着切换android:keyBackground,所以只能自己绘制普通按键的背景。
此时如果在自己的绘制逻辑之前调用super.onDraw方法,会导致看不见普通按键的文字;如果在自己的绘制逻辑之后调用,会导致自己的绘制逻辑失效。所以干脆不调用super.onDraw,全部自己绘制。
此外,由于有两种键盘需要切换,所以切换逻辑也内聚到了该类中。
直接上该部分代码:
class RSKeyboardView(
context: Context,
attrs: AttributeSet? = null
) : KeyboardView(context, attrs) {
// 键盘背景色
private var mBackground: Drawable = ColorDrawable(0xFF000000.toInt())
// 键盘文字大小
private var mLabelTextSize: Int = 14
// 普通按键的文字颜色
private var mKeyTextColor: Int = 0xFF000000.toInt()
private val mPaint: Paint by lazy {
Paint().apply {
textAlign = Paint.Align.CENTER
isAntiAlias = true
}
}
// 数字键盘
private val mKeyboardNumber: Keyboard by lazy { Keyboard(context, R.xml.keyboard_number) }
// 字母键盘
private val mKeyboardQwerty: Keyboard by lazy { Keyboard(context, R.xml.keyboard_qwerty) }
// 按键背景资源
private var mKeyBackgroundResourceTriple = NUMBER_KEY_BACKGROUND
// 默认键盘模式
var keyboardMode = KEYBOARD_MODE_NUMBER
private set
/**
* 切换键盘模式
*/
fun toggleMode() {
if (keyboardMode == RSKeyboardView.KEYBOARD_MODE_QWERTY) {
keyboard = mKeyboardNumber
keyboardMode = RSKeyboardView.KEYBOARD_MODE_NUMBER
mKeyBackgroundResourceTriple = NUMBER_KEY_BACKGROUND
} else {
keyboard = mKeyboardQwerty
keyboardMode = RSKeyboardView.KEYBOARD_MODE_QWERTY
mKeyBackgroundResourceTriple = QWERTY_KEY_BACKGROUND
}
}
init {
// 从xml中读取设置
val set = arrayOf(
android.R.attr.background,
android.R.attr.labelTextSize,
android.R.attr.keyTextColor
).toIntArray()
val a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, set)
mBackground = a.getDrawable(0) ?: mBackground
@SuppressLint("ResourceType")
mLabelTextSize = a.getDimensionPixelSize(1, mLabelTextSize)
@SuppressLint("ResourceType")
mKeyTextColor = a.getColor(2, mKeyTextColor)
a.recycle()
// 设置键盘
this.keyboard = mKeyboardNumber
this.isEnabled = true
this.isPreviewEnabled = false
}
override fun onDraw(canvas: Canvas?) {
canvas ?: return
val keys = keyboard?.keys ?: return
for (key in keys) {
when (key.codes[0]) {
Keyboard.KEYCODE_DONE -> {
// DONE按键
drawKeyBackground(mKeyBackgroundResourceTriple.first, canvas, key)
drawText(canvas, key, Color.WHITE)
drawIcon(canvas, key)
}
Keyboard.KEYCODE_MODE_CHANGE,
Keyboard.KEYCODE_DELETE,
Keyboard.KEYCODE_CANCEL -> {
// 控制按键
drawKeyBackground(mKeyBackgroundResourceTriple.second, canvas, key)
drawText(canvas, key, mKeyTextColor)
drawIcon(canvas, key)
}
else -> {
// 普通按键
drawKeyBackground(mKeyBackgroundResourceTriple.third, canvas, key)
drawText(canvas, key, mKeyTextColor)
drawIcon(canvas, key)
}
}
}
}
/**
* 绘制按键背景
*/
private fun drawKeyBackground(@DrawableRes drawableId: Int, canvas: Canvas, key: Keyboard.Key) {
val drawable = ContextCompat.getDrawable(context, drawableId) ?: return
val drawableState = key.currentDrawableState
if (key.codes[0] != 0) {
drawable.state = drawableState
}
key.run {
drawable.setBounds(x + paddingStart, y + paddingTop, x + paddingStart + width, y + paddingTop + height)
}
drawable.draw(canvas)
}
/**
* 绘制按键label
*/
private fun drawText(canvas: Canvas, key: Keyboard.Key, color: Int) {
key.label ?: return
mPaint.color = color
mPaint.textSize = mLabelTextSize.toFloat()
canvas.drawText(
key.label.toString(),
(key.x + ((key.width - paddingLeft - paddingRight) / 2 + paddingLeft)).toFloat(),
key.y + ((key.height - paddingTop - paddingBottom) / 2).toFloat() + (mPaint.textSize - mPaint.descent()) / 2 + paddingTop.toFloat(),
mPaint
)
}
/**
* 绘制按键icon
*/
private fun drawIcon(canvas: Canvas, key: Keyboard.Key) {
key.icon ?: return
key.icon.setBounds(
key.x + (key.width - key.icon.intrinsicWidth) / 2 + paddingStart,
key.y + (key.height - key.icon.intrinsicHeight) / 2 + paddingTop,
key.x + (key.width - key.icon.intrinsicWidth) / 2 + key.icon.intrinsicWidth + paddingStart,
key.y + (key.height - key.icon.intrinsicHeight) / 2 + key.icon.intrinsicHeight + paddingTop
)
key.icon.draw(canvas)
}
companion object {
// 数字键盘模式
const val KEYBOARD_MODE_NUMBER = 1
// 字母键盘模式
const val KEYBOARD_MODE_QWERTY = 2
// 数字键盘模式模式下按键背景
private val NUMBER_KEY_BACKGROUND = Triple(
R.drawable.selector_kb_number_keyboard_done,
R.drawable.selector_kb_number_keyboard_action,
R.drawable.selector_kb_number_keyboard_normal
)
// 字母键盘模式模式下按键背景
private val QWERTY_KEY_BACKGROUND = Triple(
R.drawable.selector_kb_qwerty_keyboard_done,
R.drawable.selector_kb_qwerty_keyboard_action,
R.drawable.selector_kb_qwerty_keyboard_normal
)
}
}
可以看到,切换键盘逻辑非常简单,主需要把事先创建好的Keyboard传入KeyboardView.setKeyboard方法中即可。
此外,代码中提到的按键背景资源就是一个个selector,例子如下:
selector_kb_number_keyboard_normal.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<selector
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<item android:state_pressed="true">
<shape android:shape="rectangle">
<solid android:color="#EEEEEE" />
<stroke android:color="#dfdfdf"
android:width="1px" />
</shape>
</item>
<item>
<shape android:shape="rectangle">
<solid android:color="#FFFFFF" />
<stroke android:color="#dfdfdf"
android:width="1px" />
</shape>
</item>
</selector>
3. 键盘辅助类¶
现在KeyboardView以及xml都写好了,还需要一个类实现KeyboardView.OnKeyboardActionListener接口来处理按键点击事件;并监听EditText的点击、触摸、焦点改变事件来弹出、隐藏自定义的KeyboardView。
这部分代码也很简单:
/**
* 软键盘辅助类
* @param rootView 页面的根布局 会在里面findViewById(R.id.keyboard_view)
*/
class RSKeyboard(
rootView: View
) {
/**
* 点击KEYCODE_CANCEL时的回调
*/
interface OnKeyboardCancelListener {
fun onCancel()
}
/**
* 点击KEYCODE_DONE时的回调
*/
interface OnKeyboardDoneListener {
fun onDone()
}
private val mKeyboardView: RSKeyboardView = rootView.findViewById(R.id.keyboard_view)
// 要使用自定义键盘进行输入的输入框
private var mAttachedEditText: EditText? = null
// 点击按键时的回调
private val mOnKeyboardActionListener =
object : KeyboardView.OnKeyboardActionListener {
/**
* code值到文字的映射
* -1001 -> 000
* -1002 -> 002
* -1003 -> 300
* -1004 -> 600
* -1005 -> 601
*/
private val code2StringMap = SparseArray<String>(5)
private val KEY_000 = "000"
private val KEY_002 = "002"
private val KEY_300 = "300"
private val KEY_600 = "600"
private val KEY_601 = "601"
private val KEY_000_CODE = -1001
private val KEY_002_CODE = -1002
private val KEY_300_CODE = -1003
private val KEY_600_CODE = -1004
private val KEY_601_CODE = -1005
init {
code2StringMap[KEY_000_CODE] = KEY_000
code2StringMap[KEY_002_CODE] = KEY_002
code2StringMap[KEY_300_CODE] = KEY_300
code2StringMap[KEY_600_CODE] = KEY_600
code2StringMap[KEY_601_CODE] = KEY_601
}
override fun swipeRight() {}
override fun onPress(primaryCode: Int) {}
override fun onRelease(primaryCode: Int) {}
override fun swipeLeft() {}
override fun swipeUp() {}
override fun swipeDown() {}
override fun onText(text: CharSequence?) {}
override fun onKey(primaryCode: Int, keyCodes: IntArray?) {
mAttachedEditText?.let {
val editable = it.text
val start = it.selectionStart
when (primaryCode) {
Keyboard.KEYCODE_DELETE -> {
// primaryCode=-1004 keyCodes=[-1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1]
// primaryCode=-5 keyCodes=[-5]
// primaryCode=-1004 keyCodes=[-1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1]
// primaryCode=-5 keyCodes=[-1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1]
// 连续点击多个codes的键时 会触发delete 此时keyCodes为[-5]
if (keyCodes?.size == 1) {
return
}
if (editable != null && editable.isNotEmpty() && start > 0) {
editable.delete(start - 1, start)
} else {
}
}
Keyboard.KEYCODE_CANCEL -> {
hideKeyBoard()
onKeyBoardCancelListener?.onCancel()
mAttachedEditText?.performHapticFeedback(HapticFeedbackConstants.KEYBOARD_TAP)
}
Keyboard.KEYCODE_DONE -> {
hideKeyBoard()
onKeyboardOkListener?.onDone()
mAttachedEditText?.performHapticFeedback(HapticFeedbackConstants.KEYBOARD_TAP)
}
Keyboard.KEYCODE_MODE_CHANGE -> {
mKeyboardView.toggleMode()
mAttachedEditText?.performHapticFeedback(HapticFeedbackConstants.KEYBOARD_TAP)
}
else -> {
if (code2StringMap.containsKey(primaryCode)) {
editable.insert(start, code2StringMap[primaryCode])
} else {
editable.insert(start, primaryCode.toChar().toString())
}
mAttachedEditText?.performHapticFeedback(HapticFeedbackConstants.KEYBOARD_TAP)
}
}
}
}
}
/**
* 点击KEYCODE_DONE时的回调
*/
var onKeyboardOkListener: OnKeyboardDoneListener? = null
/**
* 点击KEYCODE_CANCEL时的回调
*/
var onKeyBoardCancelListener: OnKeyboardCancelListener? = null
@SuppressLint("ClickableViewAccessibility")
fun attachTo(editText: EditText) {
mAttachedEditText = editText
// 设置按键回调
mKeyboardView.setOnKeyboardActionListener(mOnKeyboardActionListener)
// 处理弹出、关闭键盘的逻辑
editText.setOnClickListener {
showKeyBoard()
}
editText.setOnTouchListener { _, _ ->
editText.requestFocus()
editText.requestFocusFromTouch()
hideSystemSoftKeyboard(context, editText)
return@setOnTouchListener false
}
editText.setOnFocusChangeListener { _, hasFocus ->
if (!hasFocus) {
hideKeyBoard()
}
}
}
/**
* 显示键盘
*/
fun showKeyBoard() {
if (mKeyboardView.visibility != View.VISIBLE) {
mKeyboardView.visibility = View.VISIBLE
}
}
/**
* 隐藏键盘
*/
fun hideKeyBoard() {
if ( mKeyboardView.visibility == View.VISIBLE) {
mKeyboardView.visibility = View.GONE
}
}
companion object {
/**
* 隐藏系统键盘
*/
@SuppressLint("ObsoleteSdkInt")
fun hideSystemSoftKeyboard(context: Context, editText: EditText) {
when {
Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP -> {
editText.showSoftInputOnFocus = false
}
Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.HONEYCOMB -> {
try {
val clazz = EditText::class.java
val setShowSoftInputOnFocus = clazz.getMethod("setShowSoftInputOnFocus", Boolean::class.javaPrimitiveType)
setShowSoftInputOnFocus.isAccessible = true
setShowSoftInputOnFocus.invoke(editText, false)
} catch (e: Exception) { }
}
else -> {
editText.inputType = InputType.TYPE_NULL
}
}
val imm = context.getSystemService(Context.INPUT_METHOD_SERVICE) as? InputMethodManager ?: return
imm.hideSoftInputFromWindow(editText.windowToken, 0)
}
}
}
上面这段代码只有一点需要注意一下,这点在第一节中也说到了,这就是处理doubleandroid:codes的问题。
多codes的按键,在连续快速点击时,中间会发出KEYCODE_DELETE事件。以<Key android:codes="-1004,-1004" android:keyLabel="600" />为例,如果我们快速连击两次,会发出如下事件:
primaryCode=-1004 keyCodes=[-1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1]
primaryCode=-5 keyCodes=[-5]
primaryCode=-1004 keyCodes=[-1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1]
而正常的KEYCODE_DELETE是这样的:
所以我们在处理KEYCODE_DELETE时,要过滤keyCodes长度为1的情况。
4. 使用准备¶
由于我们在自定义的KeyboardView中没有调用super.onDraw,所以KeyboardView的很多xml属性都没有必要设置。
可以设置的样式只有三个(见第二节的自定义KeyboardView源码):
android:background
键盘背景颜色android:labelTextSize
按键文字大小android:keyTextColor
按键文字颜色
所以,我们可以写一个layout等待inculde:
include_keyboard.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<com.redstock.android.core.keyboard.RSKeyboardView
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/keyboard_view"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#DDDDDD"
android:labelTextSize="18sp"
android:keyTextColor="#030303"
android:visibility="gone"/>
然后在需要软键盘的页面中include进来:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<layout>
<data>
...
</data>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:background="@color/colorWindow">
...
<include
layout="@layout/include_keyboard"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
</layout>
最后在页面代码中初始化一下即可:
class LoginActivity : BaseActivity() {
...
@Inject
lateinit var dataBinding: ViewDataBinding
private val mRSKeyboard by lazy { RSKeyboard(dataBinding.root) }
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
...
mRSKeyboard.attachTo(etPhone)
mRSKeyboard.onKeyboardOkListener = object : RSKeyboard.OnKeyboardDoneListener {
override fun onDone() {
viewModel.toastString.value = "DONE"
}
}
mRSKeyboard.onKeyBoardCancelListener = object : RSKeyboard.OnKeyboardCancelListener {
override fun onCancel() {
viewModel.toastString.value = "CANCEL"
}
}
}
}
完工