NestedScrolling机制
NestedScrolling机制是解决嵌套滑动的一大神器,在Android 5.0 Lollipop (API 21)中提出,但是以兼容包的形式出现在了v4 support包中,所以兼容性是得到了保证的。
嵌套滑动既然是嵌套的,那么肯定有parent与child之分,与这两个角色相关的接口分别是NestedScrollingParent和NestedScrollingChild。但是对于fling的传递,child只是简单的将fling结果抛给parent。它的处理只有两种结果,要么child消费fling,要么parent消费fling,但它并不能让child消费一部分,再由parent消费剩余fling这样的消费效果。为了解决这个问题,在8.0之后推出了NestedScrollingParent2和NestedScrollingChild2。v2接口也是以兼容包的形式出现在了v4 support包中,兼容性也得到了保证,所以可以使用v2来代替v1。
v1与v2之间的差别在于,v2在接口的方法中新增了一个type用来表示是scroll还是fling,type取值如下:
/**
* @hide
*/
@IntDef({TYPE_TOUCH, TYPE_NON_TOUCH})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)
@RestrictTo(LIBRARY_GROUP)
public @interface NestedScrollType {}
/**
* Indicates that the input type for the gesture is from a user touching the screen.
*/
public static final int TYPE_TOUCH = 0;
/**
* Indicates that the input type for the gesture is caused by something which is not a user
* touching a screen. This is usually from a fling which is settling.
*/
public static final int TYPE_NON_TOUCH = 1;
注释中已经注释的很清楚了,TYPE_TOUCH是用户触摸屏幕造成的scroll,TYPE_NON_TOUCH通常是fling。
另外,从5.0开始,View和ViewParent都默认实现了v1 接口里面的 方法,而ViewGroup实现了ViewParent接口。因此,NestedScrolling机制就一共涉及到三对对象了,这三个Parent侧的对象的统一调用靠ViewParentCompat,调用规则为:如果Parent实现了NestedScrollingParent2接口,就调用v2的相关接口,否则会转交给IMPL。而IMPL是版本相关的,如果API >= 21,就调用ViewParent的接口,否则调用v1接口。
ViewParentCompat.java
static final ViewParentCompatBaseImpl IMPL;
static {
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 21) {
IMPL = new ViewParentCompatApi21Impl();
} else if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 19) {
IMPL = new ViewParentCompatApi19Impl();
} else {
IMPL = new ViewParentCompatBaseImpl();
}
}
static class ViewParentCompatBaseImpl {
public boolean onStartNestedScroll(ViewParent parent, View child, View target,
int nestedScrollAxes) {
if (parent instanceof NestedScrollingParent) {
return ((NestedScrollingParent) parent).onStartNestedScroll(child, target,
nestedScrollAxes);
}
return false;
}
...
}
@RequiresApi(19)
static class ViewParentCompatApi19Impl extends ViewParentCompatBaseImpl {
...
}
@RequiresApi(21)
static class ViewParentCompatApi21Impl extends ViewParentCompatApi19Impl {
@Override
public boolean onStartNestedScroll(ViewParent parent, View child, View target,
int nestedScrollAxes) {
try {
return parent.onStartNestedScroll(child, target, nestedScrollAxes);
} catch (AbstractMethodError e) {
Log.e(TAG, "ViewParent " + parent + " does not implement interface "
+ "method onStartNestedScroll", e);
return false;
}
}
...
}
public static boolean onStartNestedScroll(ViewParent parent, View child, View target,
int nestedScrollAxes) {
return onStartNestedScroll(parent, child, target, nestedScrollAxes, ViewCompat.TYPE_TOUCH);
}
public static boolean onStartNestedScroll(ViewParent parent, View child, View target,
int nestedScrollAxes, int type) {
if (parent instanceof NestedScrollingParent2) {
// First try the NestedScrollingParent2 API
return ((NestedScrollingParent2) parent).onStartNestedScroll(child, target,
nestedScrollAxes, type);
} else if (type == ViewCompat.TYPE_TOUCH) {
// Else if the type is the default (touch), try the NestedScrollingParent API
return IMPL.onStartNestedScroll(parent, child, target, nestedScrollAxes);
}
return false;
}
此外,Parent和Child两边各有一个辅助对象,Child侧的辅助对象会进行事件的分发,Parent侧的辅助对象则很简单了。
总结一下NestedScrolling机制出现的几个对象:
| 类名 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| NestedScrollingChild | 让View产生嵌套滑动事件 |
| NestedScrollingParent | 让ViewGroup能够接收从子View发送过来的嵌套滑动事件 |
| NestedScrollingChildHelper | 在实现NestedScrollChild接口的View里面使用,用来将子View产生的嵌套滑动事件分发给Parent |
| NestedScrollingParentHelper | 在实现NestedScrollingParent接口的View中使用,用来记录axes |
NestedScrollingParent和NestedScrollingChild的v1、v2接口以及解释如下:
public interface NestedScrollingChild {
// View是否允许嵌套滑动
void setNestedScrollingEnabled(boolean enabled);
boolean isNestedScrollingEnabled();
// View将在axes表示的方向上开始进行滚动
// axes可以是SCROLL_AXIS_NONE、SCROLL_AXIS_HORIZONTAL、SCROLL_AXIS_VERTICAL中的一个或多个
boolean startNestedScroll(@ScrollAxis int axes);
// 停止嵌套滑动
void stopNestedScroll();
// 是否有正在接收嵌套滑动的Parent
boolean hasNestedScrollingParent();
// 分发正在进行中的嵌套滑动
boolean dispatchNestedScroll(int dxConsumed, int dyConsumed,
int dxUnconsumed, int dyUnconsumed, @Nullable int[] offsetInWindow);
// 分发正在进行中的未消耗的嵌套滑动
boolean dispatchNestedPreScroll(int dx, int dy, @Nullable int[] consumed,
@Nullable int[] offsetInWindow);
// 分发正在进行中的嵌套fling
boolean dispatchNestedFling(float velocityX, float velocityY, boolean consumed);
// 分发正在进行中的未消耗的嵌套fling
boolean dispatchNestedPreFling(float velocityX, float velocityY);
}
// 在NestedScrollingChild的基础上新增了5个带type的方法,方法作用相同
public interface NestedScrollingChild2 extends NestedScrollingChild {
boolean startNestedScroll(@ScrollAxis int axes, @NestedScrollType int type);
void stopNestedScroll(@NestedScrollType int type);
boolean hasNestedScrollingParent(@NestedScrollType int type);
boolean dispatchNestedScroll(int dxConsumed, int dyConsumed,
int dxUnconsumed, int dyUnconsumed, @Nullable int[] offsetInWindow,
@NestedScrollType int type);
boolean dispatchNestedPreScroll(int dx, int dy, @Nullable int[] consumed,
@Nullable int[] offsetInWindow, @NestedScrollType int type);
}
public interface NestedScrollingParent {
// 是否要对子View的嵌套滑动做出反应
boolean onStartNestedScroll(@NonNull View child, @NonNull View target, @ScrollAxis int axes);
// 接受子View的嵌套滑动事件,需要调用Helper记录axes
void onNestedScrollAccepted(@NonNull View child, @NonNull View target, @ScrollAxis int axes);
// 子View的嵌套滑动终止时调用
void onStopNestedScroll(@NonNull View target);
// 对进行中的嵌套滑动做出处理
void onNestedScroll(@NonNull View target, int dxConsumed, int dyConsumed,
int dxUnconsumed, int dyUnconsumed);
// 对进行中的还没有开始消耗的嵌套滑动做出处理
void onNestedPreScroll(@NonNull View target, int dx, int dy, @NonNull int[] consumed);
// 对进行中的嵌套fling做出处理
boolean onNestedFling(@NonNull View target, float velocityX, float velocityY, boolean consumed);
// 对进行中的还没有开始消耗的嵌套fling做出处理
boolean onNestedPreFling(@NonNull View target, float velocityX, float velocityY);
// 返回进行中的嵌套滑动的axes
@ScrollAxis
int getNestedScrollAxes();
}
// 在NestedScrollingParent的基础上新增了5个带type的方法,方法作用相同
public interface NestedScrollingParent2 extends NestedScrollingParent {
boolean onStartNestedScroll(@NonNull View child, @NonNull View target, @ScrollAxis int axes,
@NestedScrollType int type);
void onNestedScrollAccepted(@NonNull View child, @NonNull View target, @ScrollAxis int axes,
@NestedScrollType int type);
void onStopNestedScroll(@NonNull View target, @NestedScrollType int type);
void onNestedScroll(@NonNull View target, int dxConsumed, int dyConsumed,
int dxUnconsumed, int dyUnconsumed, @NestedScrollType int type);
void onNestedPreScroll(@NonNull View target, int dx, int dy, @NonNull int[] consumed,
@NestedScrollType int type);
}
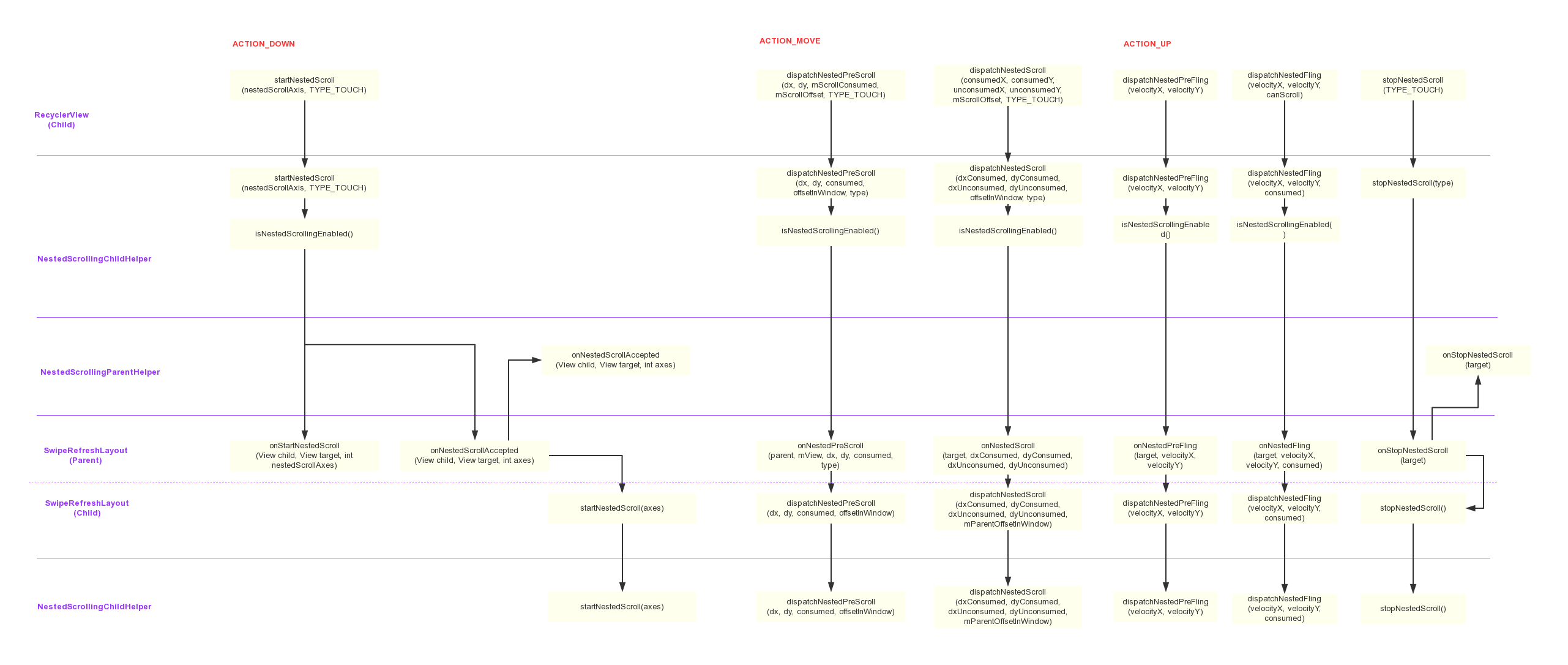
上面理论知识介绍得差不多了,只缺少一个Child与Parent两侧联动的顺序图了,这里给出典型的RecyclerView与SwipeRefreshLayout两者的嵌套滑动顺序图:
值得一提的是,这里SwipeRefreshLayout相对RecyclerView而言是Parent;相对于自己的Parent而言又是Child。所以这里SwipeRefreshLayout也会将嵌套滑动事件分发给上一级,这就是一个三级嵌套滑动的典型例子了。但是,本章只研究两级,SwipeRefreshLayout的Parent暂不考虑。
在上面介绍了这么多理论之后,我们通过源码验证一下。源码并不难,只需要我们有足够的勇气去看一眼。
1. NestedScrolling机制源码解析¶
嵌套滑动的事件分发与一般的事件传递机制相反,嵌套滑动是由子View向父View传递的,但嵌套滑动的实现还是基于事件传递机制的,具体思想可以参考View的滑动冲突处理——内部拦截法。由于本章是以RecyclerView与SwipeRefreshLayout两者的嵌套滑动为例,显然RecyclerView是作为Child的,因此嵌套滑动事件也是从它的onTouchEvent开始。
在ACTION_DOWN时,RecyclerView借助NestedScrollingChildHelper向Parent发出通知,表明自己即将开始滚动。RecyclerView相关代码如下:
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent e) {
...
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN: {
mScrollPointerId = e.getPointerId(0);
mInitialTouchX = mLastTouchX = (int) (e.getX() + 0.5f);
mInitialTouchY = mLastTouchY = (int) (e.getY() + 0.5f);
int nestedScrollAxis = ViewCompat.SCROLL_AXIS_NONE;
if (canScrollHorizontally) {
nestedScrollAxis |= ViewCompat.SCROLL_AXIS_HORIZONTAL;
}
if (canScrollVertically) {
nestedScrollAxis |= ViewCompat.SCROLL_AXIS_VERTICAL;
}
startNestedScroll(nestedScrollAxis, TYPE_TOUCH);
} break;
...
}
@Override
public boolean startNestedScroll(int axes, int type) {
return getScrollingChildHelper().startNestedScroll(axes, type);
}
private NestedScrollingChildHelper getScrollingChildHelper() {
if (mScrollingChildHelper == null) {
mScrollingChildHelper = new NestedScrollingChildHelper(this);
}
return mScrollingChildHelper;
}
RecyclerView的代码就转接到了NestedScrollingChildHelper中了,接着看看相关代码:
NestedScrollingChildHelper.java
public boolean startNestedScroll(@ScrollAxis int axes, @NestedScrollType int type) {
if (hasNestedScrollingParent(type)) {
// Already in progress
return true;
}
if (isNestedScrollingEnabled()) {
ViewParent p = mView.getParent();
View child = mView;
while (p != null) {
if (ViewParentCompat.onStartNestedScroll(p, child, mView, axes, type)) {
setNestedScrollingParentForType(type, p);
ViewParentCompat.onNestedScrollAccepted(p, child, mView, axes, type);
return true;
}
if (p instanceof View) {
child = (View) p;
}
p = p.getParent();
}
}
return false;
}
首先调用hasNestedScrollingParent方法看看嵌套滑动Parent是否已经设置,如果有设置,表明正在进行嵌套滑动。接着判断Child侧接口的代理方法isNestedScrollingEnabled()是否Child允许嵌套滑动。如果允许滑动,会从Child的Parent开始,看看当前的ViewParent是否响应此处的嵌套滑动(ViewParentCompat.onStartNestedScroll返回true),如果当前ViewParent不响应,则判断ViewParent的Parent,就这么沿着控件树一直往上一直找到一个可以响应的。
一旦有一个ViewParent响应了,就会调用setNestedScrollingParentForType方法设置正在嵌套滑动的Parent,这样后面调用第2行的hasNestedScrollingParent方法就会返回true了。然后调用ViewParentCompat.onNestedScrollAccepted方法通知SwipeRefreshLayout.onNestedScrollAccepted方法,此时SwipeRefreshLayout已经接受了此次的嵌套滑动请求:
SwipeRefreshLayout.java
@Override
public boolean onStartNestedScroll(View child, View target, int nestedScrollAxes) {
return isEnabled() && !mReturningToStart && !mRefreshing
&& (nestedScrollAxes & ViewCompat.SCROLL_AXIS_VERTICAL) != 0;
}
@Override
public void onNestedScrollAccepted(View child, View target, int axes) {
// Reset the counter of how much leftover scroll needs to be consumed.
mNestedScrollingParentHelper.onNestedScrollAccepted(child, target, axes);
// Dispatch up to the nested parent
startNestedScroll(axes & ViewCompat.SCROLL_AXIS_VERTICAL);
mTotalUnconsumed = 0;
mNestedScrollInProgress = true;
}
在SwipeRefreshLayout.onNestedScrollAccepted方法中会调用Helper对象的相同签名方法,并且会以Child的身份向Parent发出嵌套滑动的事件,最后会设置一下自身的变量,等待后续处理嵌套滑动。
NestedScrollingParentHelper.onNestedScrollAccepted方法只是很简单的记录了一下嵌套滑动的axes,在最后onStopNestedScroll方法中复位了变量,此类的源码非常简单,所以一次性贴出来:
NestedScrollingParentHelper.java
public void onNestedScrollAccepted(@NonNull View child, @NonNull View target,
@ScrollAxis int axes) {
onNestedScrollAccepted(child, target, axes, ViewCompat.TYPE_TOUCH);
}
public void onNestedScrollAccepted(@NonNull View child, @NonNull View target,
@ScrollAxis int axes, @NestedScrollType int type) {
mNestedScrollAxes = axes;
}
public void onStopNestedScroll(@NonNull View target) {
onStopNestedScroll(target, ViewCompat.TYPE_TOUCH);
}
public void onStopNestedScroll(@NonNull View target, @NestedScrollType int type) {
mNestedScrollAxes = 0;
}
目前为止,伴随着手指按下触发的ACTION_DOWN事件,Child与Parent之间的嵌套滑动的关系已经建立了,下面手指滑动触发的ACTION_MOVE事件会真正开始嵌套滑动。
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent e) {
...
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE: {
final int index = e.findPointerIndex(mScrollPointerId);
if (index < 0) {
Log.e(TAG, "Error processing scroll; pointer index for id "
+ mScrollPointerId + " not found. Did any MotionEvents get skipped?");
return false;
}
final int x = (int) (e.getX(index) + 0.5f);
final int y = (int) (e.getY(index) + 0.5f);
int dx = mLastTouchX - x;
int dy = mLastTouchY - y;
if (dispatchNestedPreScroll(dx, dy, mScrollConsumed, mScrollOffset, TYPE_TOUCH)) {
dx -= mScrollConsumed[0];
dy -= mScrollConsumed[1];
vtev.offsetLocation(mScrollOffset[0], mScrollOffset[1]);
// Updated the nested offsets
mNestedOffsets[0] += mScrollOffset[0];
mNestedOffsets[1] += mScrollOffset[1];
}
if (mScrollState != SCROLL_STATE_DRAGGING) {
boolean startScroll = false;
if (canScrollHorizontally && Math.abs(dx) > mTouchSlop) {
if (dx > 0) {
dx -= mTouchSlop;
} else {
dx += mTouchSlop;
}
startScroll = true;
}
if (canScrollVertically && Math.abs(dy) > mTouchSlop) {
if (dy > 0) {
dy -= mTouchSlop;
} else {
dy += mTouchSlop;
}
startScroll = true;
}
if (startScroll) {
setScrollState(SCROLL_STATE_DRAGGING);
}
}
if (mScrollState == SCROLL_STATE_DRAGGING) {
mLastTouchX = x - mScrollOffset[0];
mLastTouchY = y - mScrollOffset[1];
if (scrollByInternal(
canScrollHorizontally ? dx : 0,
canScrollVertically ? dy : 0,
vtev)) {
getParent().requestDisallowInterceptTouchEvent(true);
}
if (mGapWorker != null && (dx != 0 || dy != 0)) {
mGapWorker.postFromTraversal(this, dx, dy);
}
}
} break;
...
}
在17行会将原始的没有经过消耗的dx、dy经过NestedScrollingChildHelper分发给Parent的onNestedPreScroll方法,Parent在需要的时候会消耗部分dx和dy并做出滑动响应,并在二维数组consumed中减掉这部分的消耗。NestedScrollingChildHelper部分的处理比较简单,这里直接看Parent也就是SwipeRefreshLayout.onNestedPreScroll方法是如何做出响应的:
SwipeRefreshLayout.java
@Override
public void onNestedPreScroll(View target, int dx, int dy, int[] consumed) {
// If we are in the middle of consuming, a scroll, then we want to move the spinner back up
// before allowing the list to scroll
if (dy > 0 && mTotalUnconsumed > 0) {
if (dy > mTotalUnconsumed) {
consumed[1] = dy - (int) mTotalUnconsumed;
mTotalUnconsumed = 0;
} else {
mTotalUnconsumed -= dy;
consumed[1] = dy;
}
moveSpinner(mTotalUnconsumed);
}
// If a client layout is using a custom start position for the circle
// view, they mean to hide it again before scrolling the child view
// If we get back to mTotalUnconsumed == 0 and there is more to go, hide
// the circle so it isn't exposed if its blocking content is moved
if (mUsingCustomStart && dy > 0 && mTotalUnconsumed == 0
&& Math.abs(dy - consumed[1]) > 0) {
mCircleView.setVisibility(View.GONE);
}
// Now let our nested parent consume the leftovers
final int[] parentConsumed = mParentScrollConsumed;
if (dispatchNestedPreScroll(dx - consumed[0], dy - consumed[1], parentConsumed, null)) {
consumed[0] += parentConsumed[0];
consumed[1] += parentConsumed[1];
}
}
抛开最后一段作为Child的代码不谈,这里消耗dx、dy的情况只有第5行的if里面的代码了。在这行代码中会先计算dy消耗量,然后移动指示器的位置。
回到RecyclerView.onTouchEvent的ACTION_MOVE方法中,随着手指的移动,mScrollState会由初始状态变成SCROLL_STATE_DRAGGING状态,这样会调用第53行的scrollByInternal方法。在该方法中会先由LayoutManager进行滚动,消耗掉一部分的dx、dy,然后在第28行会调用dispatchNestedScroll方法将消息分发给Parent:
boolean scrollByInternal(int x, int y, MotionEvent ev) {
int unconsumedX = 0, unconsumedY = 0;
int consumedX = 0, consumedY = 0;
consumePendingUpdateOperations();
if (mAdapter != null) {
eatRequestLayout();
onEnterLayoutOrScroll();
TraceCompat.beginSection(TRACE_SCROLL_TAG);
fillRemainingScrollValues(mState);
if (x != 0) {
consumedX = mLayout.scrollHorizontallyBy(x, mRecycler, mState);
unconsumedX = x - consumedX;
}
if (y != 0) {
consumedY = mLayout.scrollVerticallyBy(y, mRecycler, mState);
unconsumedY = y - consumedY;
}
TraceCompat.endSection();
repositionShadowingViews();
onExitLayoutOrScroll();
resumeRequestLayout(false);
}
if (!mItemDecorations.isEmpty()) {
invalidate();
}
if (dispatchNestedScroll(consumedX, consumedY, unconsumedX, unconsumedY, mScrollOffset,
TYPE_TOUCH)) {
// Update the last touch co-ords, taking any scroll offset into account
mLastTouchX -= mScrollOffset[0];
mLastTouchY -= mScrollOffset[1];
if (ev != null) {
ev.offsetLocation(mScrollOffset[0], mScrollOffset[1]);
}
mNestedOffsets[0] += mScrollOffset[0];
mNestedOffsets[1] += mScrollOffset[1];
} else if (getOverScrollMode() != View.OVER_SCROLL_NEVER) {
if (ev != null && !MotionEventCompat.isFromSource(ev, InputDevice.SOURCE_MOUSE)) {
pullGlows(ev.getX(), unconsumedX, ev.getY(), unconsumedY);
}
considerReleasingGlowsOnScroll(x, y);
}
if (consumedX != 0 || consumedY != 0) {
dispatchOnScrolled(consumedX, consumedY);
}
if (!awakenScrollBars()) {
invalidate();
}
return consumedX != 0 || consumedY != 0;
}
dispatchNestedScroll还是经过NestedScrollingChildHelper的代理分发到Parent上,Parent这边会拿着dyUnconsumed进行一些操作:
SwipeRefreshLayout.java
@Override
public void onNestedScroll(final View target, final int dxConsumed, final int dyConsumed,
final int dxUnconsumed, final int dyUnconsumed) {
// Dispatch up to the nested parent first
dispatchNestedScroll(dxConsumed, dyConsumed, dxUnconsumed, dyUnconsumed,
mParentOffsetInWindow);
// This is a bit of a hack. Nested scrolling works from the bottom up, and as we are
// sometimes between two nested scrolling views, we need a way to be able to know when any
// nested scrolling parent has stopped handling events. We do that by using the
// 'offset in window 'functionality to see if we have been moved from the event.
// This is a decent indication of whether we should take over the event stream or not.
final int dy = dyUnconsumed + mParentOffsetInWindow[1];
if (dy < 0 && !canChildScrollUp()) {
mTotalUnconsumed += Math.abs(dy);
moveSpinner(mTotalUnconsumed);
}
}
可以看到,在ACTION_MOVE阶段,SwipeRefreshLayout会响应RecyclerView的嵌套滑动,此时刷新指示器会随着用的操作而上下移动。在我们自定义二级嵌套滑动时,这两个方法就是所有需要我们自己处理的Parent内容了,因为RecyclerView会自动发送嵌套滑动事件。
在经历若干个ACTION_MOVE之后,伴随着用户的操作,就会触发ACTION_UP事件,这里会先尝试fling,最后stop。
RecyclerView.java
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent e) {
...
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP: {
mVelocityTracker.addMovement(vtev);
eventAddedToVelocityTracker = true;
mVelocityTracker.computeCurrentVelocity(1000, mMaxFlingVelocity);
final float xvel = canScrollHorizontally
? -mVelocityTracker.getXVelocity(mScrollPointerId) : 0;
final float yvel = canScrollVertically
? -mVelocityTracker.getYVelocity(mScrollPointerId) : 0;
if (!((xvel != 0 || yvel != 0) && fling((int) xvel, (int) yvel))) {
setScrollState(SCROLL_STATE_IDLE);
}
resetTouch();
} break;
...
}
第12行中会调用fling方法进行fling,这里面和scroll一样会调用dispatchNestedPreFling和dispatchNestedFling方法,这两个方法SwipeRefreshLayout的实现都是作为Child转发给Parent了。在最后在开始fling前会调用startNestedScroll(nestedScrollAxis, TYPE_NON_TOUCH),注意这里的type就是TYPE_NON_TOUCH了:
public boolean fling(int velocityX, int velocityY) {
if (mLayout == null) {
Log.e(TAG, "Cannot fling without a LayoutManager set. "
+ "Call setLayoutManager with a non-null argument.");
return false;
}
if (mLayoutFrozen) {
return false;
}
final boolean canScrollHorizontal = mLayout.canScrollHorizontally();
final boolean canScrollVertical = mLayout.canScrollVertically();
if (!canScrollHorizontal || Math.abs(velocityX) < mMinFlingVelocity) {
velocityX = 0;
}
if (!canScrollVertical || Math.abs(velocityY) < mMinFlingVelocity) {
velocityY = 0;
}
if (velocityX == 0 && velocityY == 0) {
// If we don't have any velocity, return false
return false;
}
if (!dispatchNestedPreFling(velocityX, velocityY)) {
final boolean canScroll = canScrollHorizontal || canScrollVertical;
dispatchNestedFling(velocityX, velocityY, canScroll);
if (mOnFlingListener != null && mOnFlingListener.onFling(velocityX, velocityY)) {
return true;
}
if (canScroll) {
int nestedScrollAxis = ViewCompat.SCROLL_AXIS_NONE;
if (canScrollHorizontal) {
nestedScrollAxis |= ViewCompat.SCROLL_AXIS_HORIZONTAL;
}
if (canScrollVertical) {
nestedScrollAxis |= ViewCompat.SCROLL_AXIS_VERTICAL;
}
startNestedScroll(nestedScrollAxis, TYPE_NON_TOUCH);
velocityX = Math.max(-mMaxFlingVelocity, Math.min(velocityX, mMaxFlingVelocity));
velocityY = Math.max(-mMaxFlingVelocity, Math.min(velocityY, mMaxFlingVelocity));
mViewFlinger.fling(velocityX, velocityY);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
fling完成后调用resetTouch方法进行,里面会调用stopNestedScroll(TYPE_TOUCH)方法,该方法还是经过NestedScrollingChildHelper转发给Parent的onStopNestedScroll方法了:
SwipeRefreshLayout.java
@Override
public void onStopNestedScroll(View target) {
mNestedScrollingParentHelper.onStopNestedScroll(target);
mNestedScrollInProgress = false;
// Finish the spinner for nested scrolling if we ever consumed any
// unconsumed nested scroll
if (mTotalUnconsumed > 0) {
finishSpinner(mTotalUnconsumed);
mTotalUnconsumed = 0;
}
// Dispatch up our nested parent
stopNestedScroll();
}
这里SwipeRefreshLayout会将刷新指示器复位,并重置一些变量。
限于篇幅,且代码比较简单,所以上面也只是大致理了一下整个流程。整个流程可以按照MotionEvent的action分为三个步骤:
ACTION_DOWN阶段 —— Child准备开始嵌套滑动,此时会通知可以响应的Parent做好准备ACTION_MOVE阶段 —— Child进行嵌套滑动,Parent根据情况消耗dx、dyACTION_UP阶段 —— Child和Parent开始fling,最后进行stop状态
Child的事件通过NestedScrollingChildHelper分发到Parent中。此时回过头来看RecyclerView与SwipeRefreshLayout两者的嵌套滑动顺序图,应该有进一步的认识了。
2. 嵌套滑动实战¶
在嵌套滑动中,基本上都是RecyclerView作为Child,所以我们只需要处理一下Parent就好了。
下面来一个非常简单又常见的例子,效果图如下:

整个页面的整体是一个线性布局,为了能够响应RecyclerView的滑动,我们需要自定义一下LinearLayout。布局代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<yorek.demoandtest.nestedscroll.NestedScrollingLinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<FrameLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<ImageView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="200dp"
android:src="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:background="@color/colorAccent"/>
</FrameLayout>
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@color/colorPrimary"
android:text="Title"
android:textAlignment="center"
android:textSize="20sp"
android:textColor="#FF0000"/>
<android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView
android:id="@+id/list"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" />
</yorek.demoandtest.nestedscroll.NestedScrollingLinearLayout>
页面逻辑代码只需要向RecyclerView中填充数据就好了,代码如下:
class NestedScrollActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_nested_scroll)
list.layoutManager = LinearLayoutManager(this)
list.adapter = object : RecyclerView.Adapter<Holder>() {
override fun onCreateViewHolder(parent: ViewGroup, viewType: Int): Holder {
val itemView = LayoutInflater.from(this@NestedScrollActivity).inflate(android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, parent, false)
return Holder(itemView)
}
override fun onBindViewHolder(holder: Holder, position: Int) {
holder.textView.text = "item $position"
}
override fun getItemCount() = 100
}
}
class Holder(
itemView: View
) : RecyclerView.ViewHolder(itemView) {
val textView: TextView = itemView.findViewById(android.R.id.text1)
}
}
最关键的自定义的LinearLayout代码如下:
class NestedScrollingLinearLayout(
context: Context,
attributeSet: AttributeSet? = null
) : LinearLayout(context, attributeSet),
NestedScrollingParent2 {
private lateinit var mHeader: View
private lateinit var mTarget: View
private var mHeaderHeight = 0
private val mNestedScrollingParentHelper by lazy { NestedScrollingParentHelper(this) }
override fun onFinishInflate() {
super.onFinishInflate()
if (childCount > 0) {
mHeader = getChildAt(0)
// 遍历出RecyclerView
for (i in 0 until childCount) {
if (getChildAt(i) is RecyclerView) {
mTarget = getChildAt(i)
break
}
}
}
}
override fun onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec: Int, heightMeasureSpec: Int) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec)
mHeaderHeight = mHeader.measuredHeight
// 需要正确的测量出RecyclerView在header折叠时的高度,不然ReclcyerView显示不全
mTarget.measure(
widthMeasureSpec,
MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(
mHeaderHeight + mTarget.measuredHeight,
MeasureSpec.EXACTLY)
)
}
override fun onStartNestedScroll(child: View, target: View, axes: Int, type: Int): Boolean {
// 允许竖直方向上的滑动
return isEnabled && (axes and ViewCompat.SCROLL_AXIS_VERTICAL != 0)
}
override fun onNestedScrollAccepted(child: View, target: View, axes: Int, type: Int) {
// 代理给NestedScrollingParentHelper
mNestedScrollingParentHelper.onNestedScrollAccepted(child, target, axes, type)
}
override fun onNestedPreScroll(target: View, dx: Int, dy: Int, consumed: IntArray, type: Int) {
onNestedPreScroll(target, dx, dy, consumed)
// dy大于0说明在向上滑动,此时需要判断header是不是还能显示
val canScrollUp = dy > 0 && mHeaderHeight > scrollY
// dy小于0说明在向下滑动,此时需要判断header是不是已经显示完整
val canScrollDown = dy < 0 && scrollY > 0
if (canScrollUp || canScrollDown) {
scrollBy(0, dy)
consumed[1] = dy
}
}
override fun onNestedScroll(
target: View,
dxConsumed: Int,
dyConsumed: Int,
dxUnconsumed: Int,
dyUnconsumed: Int,
type: Int
) {
onNestedScroll(target, dxConsumed, dyConsumed, dxUnconsumed, dyUnconsumed)
}
override fun onStopNestedScroll(target: View, type: Int) {
// 代理给NestedScrollingParentHelper
mNestedScrollingParentHelper.onStopNestedScroll(target, type)
}
override fun scrollTo(x: Int, y: Int) {
val clampY = max(0, min(y, mHeaderHeight))
super.scrollTo(x, clampY)
}
}
在自定义Parent时有一些坑
- 让header显示缩小,有很多方式,这里采用了整体scroll的方法;scroll的时候需要判断y的值,要clamp在[0, mHeaderHeight]之间,不然dy一旦过大,就会导致header上边留白或者其他部位被scroll。
- 测量时,需要注意正确测量出RecyclerView的高度,不然当header折叠时,RecyclerView没有占满剩余空间
- Parent最好实现
NestedScrollingParent2接口,这样可以响应fling时的scroll事件,体验更好(对比图如下,注意最后一个fling事件)