JNI与NDK编程简介
1 JNI与NDK简介¶
JNI指Java Native Interface,它可以使Java调用C/C++代码。
NDK是Android提供的一个工具集合,通过NDK可以在Android中更加方便的通过JNI来访问本地代码。NDK还提供了交叉编译器,开发人员只需要简单的修改mk文件就可以生成特定CPU平台的动态库。NDK的好处有如下几点:
- 提高代码安全性。由于so库反编译比较困难,因此NDK提高了Android程序的安全性。
- 可以很方便的使用目前已拥有的C/C++开源库。
- 便于平台间的移植。 通过C/C++实现的动态库可以很方便的在其他平台上使用。
- 提高程序在某些特定情况下的执行效率,但不能明显提升Android程序的性能。
2 JNI的开发流程¶
JNI的开发流程有如下几步:
- 在Java中声明native方法
- 编译Java源文件得到class文件,然后通过javah命令导出JNI的头文件
- 实现JNI方法
- 编译so库并在Java中调用
2.1 在Java中声明native方法¶
创建一个类,声明两个native方法:get和set(String)。
package com.example;
import java.lang.System;
public class JniTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JniTest jniTest = new JniTest();
System.out.println(jniTest.get());
jniTest.set("hello world");
}
public native String get();
public native String set(String str);
}
2.2 编译Java源文件得到class文件,然后通过javah命令导出JNI的头文件¶

输入上面命令后会在当前目录生成com_example_JniTest.h文件,它是javah命令生成的。内容如下所示:
/* DO NOT EDIT THIS FILE - it is machine generated */
#include <jni.h>
/* Header for class com_example_JniTest */
#ifndef _Included_com_example_JniTest
#define _Included_com_example_JniTest
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
/*
* Class: com_example_JniTest
* Method: get
* Signature: ()Ljava/lang/String;
*/
JNIEXPORT jstring JNICALL Java_com_example_JniTest_get
(JNIEnv *, jobject);
/*
* Class: com_example_JniTest
* Method: set
* Signature: (Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/String;
*/
JNIEXPORT jstring JNICALL Java_com_example_JniTest_set
(JNIEnv *, jobject, jstring);
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
#endif
从上面我可以看出,函数的命名格式遵循如下规则:Java_包名_类名_方法名。比如Demo中的get方法,到这里就变成了JNIEXPORT jstring JNICALL Java_com_example_JniTest_get(JNIEnv *, jobject);方法。这里面都是JNI标准定义的类型或者宏:
- JNIEnv*:表示一个指向JNI环境的指针,可以通过它访问JNI提供的借口方法
- jobject:表示Java对象中的this
- JNIEXPORT和JNICALL:JNI中所指定的宏,可以在
jni.h头文件中查找到。
2.3 实现JNI方法¶
JNI方法是指Java中声明的native方法,这里可以选用C++或者C来实现,它们的实现过程是类似的。
下面分别选用两者来实现JNI方法。首先,在工程的主目录下创建一个子目录,名称随意,这里选择jni作为子目录的名称,然后将之前通过javah生成的头文件com_example_JniTest.h复制到jni目录下,接着创建test.cpp和test.c两个文件,它们的实现如下。
// test.cpp
#include "com_example_JniTest.h"
#include <stdio.h>
/*
* Class: com_example_JniTest
* Method: get
* Signature: ()Ljava/lang/String;
*/
JNIEXPORT jstring JNICALL Java_com_example_JniTest_get(JNIEnv *env, jobject thiz) {
printf("invoke get in c++\n");
return env->NewStringUTF("Hello from JNI !");
}
/*
* Class: com_example_JniTest
* Method: set
* Signature: (Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/String;
*/
JNIEXPORT jstring JNICALL Java_com_example_JniTest_set(JNIEnv *env, jobject thiz, jstring string) {
printf("invoke set from c++\n");
char* str = (char*)env->GetStringUTFChars(string, NULL);
printf("%s\n", str);
env->ReleaseStringUTFChars(string, str);
}
// test.c
#include "com_example_JniTest.h"
#include <stdio.h>
/*
* Class: com_example_JniTest
* Method: get
* Signature: ()Ljava/lang/String;
*/
JNIEXPORT jstring JNICALL Java_com_example_JniTest_get(JNIEnv *env, jobject thiz) {
printf("invoke get in c\n");
return (*env)->NewStringUTF(env, "Hello from JNI !");
}
/*
* Class: com_example_JniTest
* Method: set
* Signature: (Ljava/lang/String;)Ljava/lang/String;
*/
JNIEXPORT jstring JNICALL Java_com_example_JniTest_set(JNIEnv *env, jobject thiz, jstring string) {
printf("invoke set from c\n");
char* str = (char*)(*env)->GetStringUTFChars(env, string, NULL);
printf("%s\n", str);
(*env)->ReleaseStringUTFChars(env, string, str);
}
2.4 编译so库并在Java中调用¶
编译命令与操作系统相关,此处作者用的是OSX系统。
编译的命令如下: 在jni目录下
gcc -I /System/Library/Frameworks/JavaVM.framework/Headers/ -c test.c
gcc -dynamiclib -o libjni-test.jnilib test.o
libjni-test.jnilib文件。 然后在我们的Java文件中加载动态库:
package com.example;
import java.lang.System;
public class JniTest {
static {
System.loadLibrary("jni-test");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
JniTest jniTest = new JniTest();
System.out.println(jniTest.get());
jniTest.set("hello world");
}
public native String get();
public native String set(String str);
}
最后重新编译Java文件并通过java命令执行:

JNI方法的动态注册
上述演示中使用的JNI函数的注册叫做静态注册,JNI还提供了另外一种动态注册的方式。我们可以在int JNI_OnLoad(JavaVM *vm, void *reserved)函数中通过JniEnv->RegisterNatives方式动态注册。
JNI_OnLoad方法还有另外一个生命周期方法:JNI_OnUnload
3 NDK的开发流程¶
NDK开发的基本框架官方已经很方便的支持了,查看Getting Started with the NDK
3.1 NDK使用实例(Makefile)¶
- 准备一个简单的Android项目
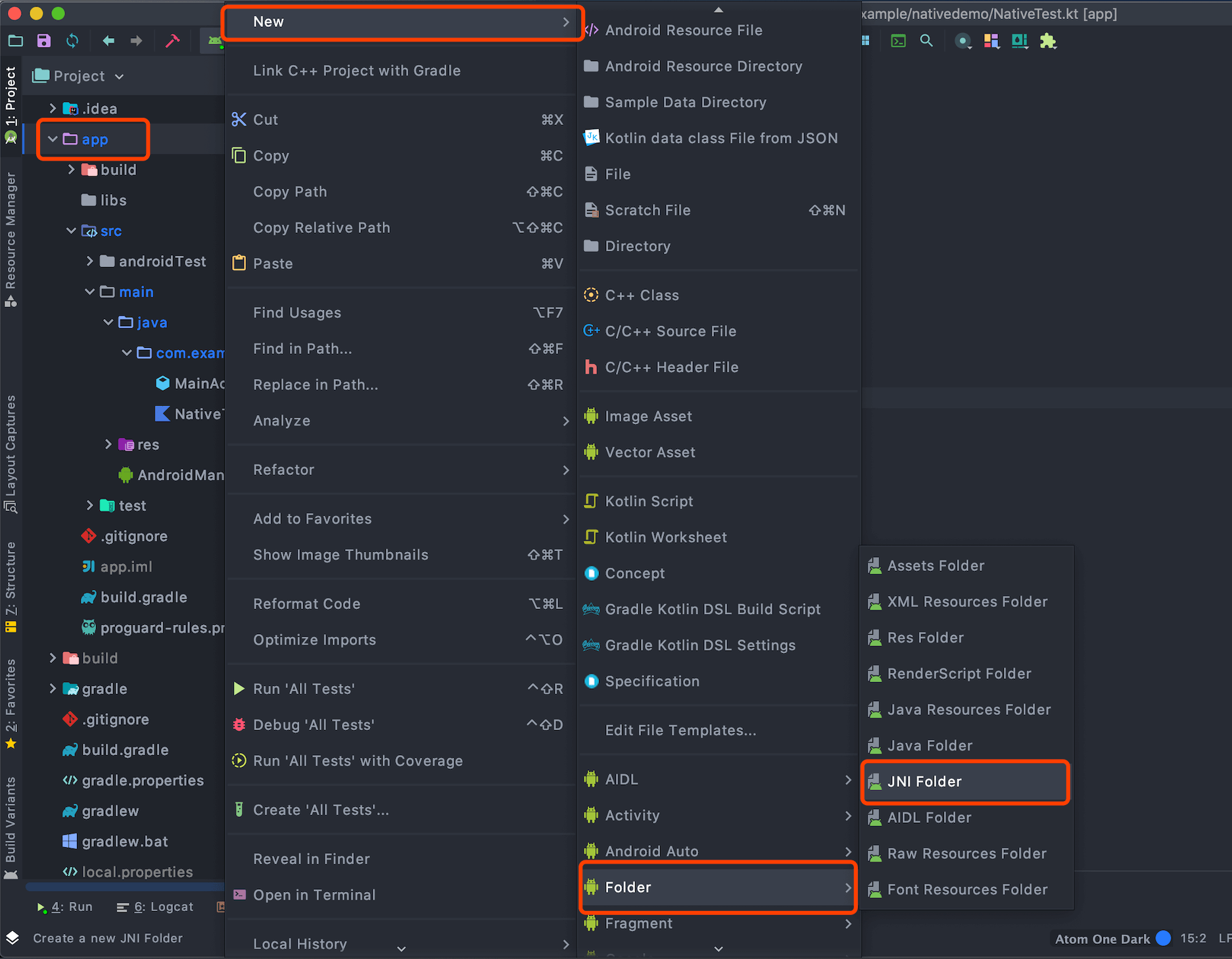
- 创建jni文件夹,如下所示:
选中app module -> 右键New -> Folder -> JNI Folder
- 准备一个JNI Java层文件
NativeTest.java - 编译一下,这时候会为NativeTest生成class文件,目录在
app/build/intermediates/javac/debug/classes/com/example/nativedemo/NativeTest.class - 在项目根目录下执行下面命令,生成对应的jni头文件到jni目录下
生成的头文件javah -d app/src/main/jni -cp app/build/intermediates/javac/debug/classes com.example.nativedemo.NativeTestcom_example_nativedemo_NativeTest.h如下:/* DO NOT EDIT THIS FILE - it is machine generated */ #include <jni.h> /* Header for class com_example_nativedemo_NativeTest */ #ifndef _Included_com_example_nativedemo_NativeTest #define _Included_com_example_nativedemo_NativeTest #ifdef __cplusplus extern "C" { #endif /* * Class: com_example_nativedemo_NativeTest * Method: getHelloWorld * Signature: ()Ljava/lang/String; */ JNIEXPORT jstring JNICALL Java_com_example_nativedemo_NativeTest_getHelloWorld (JNIEnv *, jclass); #ifdef __cplusplus } #endif #endif - 在jni目录下实现该头文件:
- 在jni目录下放置
Application.mk和Android.mk两个文件
# Application.mk #APP_ABI := armeabi armeabi-v7a x86 mips mips-r2 mips-r2-sf APP_ABI := armeabi-v7a arm64-v8a x86 x86_64 #APP_ABI := armeabi-v7a arm64-v8a APP_PLATFORM := android-14 #APP_OPTIM := debug # Android.mk LOCAL_PATH := $(call my-dir) include $(CLEAR_VARS) LOCAL_MODULE := nativetest LOCAL_SRC_FILES := \ com_example_nativedemo_NativeTest.cpp \ include $(BUILD_SHARED_LIBRARY) - 在jni目录下执行
ndk-build命令,执行完毕后就会生成指定的so库 - 在build.gradle中配置so的目录:
- 最后在NativeTest.java中load一下就可以使用了:
3.2 NDK使用实例(CMake)¶
在 Android Studio Arctic Fox 的版本上,先在 Java或者Kotlin文件中写一个native 方法,然后右键这个文件有一个 Add C++ to Module。这个功能可以快速的生成CMakeList文件以及其他的配置,后面专注于实现生成的cpp文件即可。
生成的代码涉及到的文件有如下:
build.gradle
android {
defaultConfig {
...
externalNativeBuild {
cmake {
cppFlags ''
}
}
}
...
externalNativeBuild {
cmake {
path file('src/main/cpp/CMakeLists.txt')
version '3.10.2'
}
}
}
CMakeList.txt
# For more information about using CMake with Android Studio, read the
# documentation: https://d.android.com/studio/projects/add-native-code.html
# Sets the minimum version of CMake required to build the native library.
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.10.2)
# Declares and names the project.
project("database")
# Creates and names a library, sets it as either STATIC
# or SHARED, and provides the relative paths to its source code.
# You can define multiple libraries, and CMake builds them for you.
# Gradle automatically packages shared libraries with your APK.
add_library( # Sets the name of the library.
database
# Sets the library as a shared library.
SHARED
# Provides a relative path to your source file(s).
database.cpp )
# Searches for a specified prebuilt library and stores the path as a
# variable. Because CMake includes system libraries in the search path by
# default, you only need to specify the name of the public NDK library
# you want to add. CMake verifies that the library exists before
# completing its build.
find_library( # Sets the name of the path variable.
log-lib
# Specifies the name of the NDK library that
# you want CMake to locate.
log )
# Specifies libraries CMake should link to your target library. You
# can link multiple libraries, such as libraries you define in this
# build script, prebuilt third-party libraries, or system libraries.
target_link_libraries( # Specifies the target library.
database
# Links the target library to the log library
# included in the NDK.
${log-lib} )
database.cpp,系统自动生成的文件,需要我们在里面从JNI开始实现。
// Write C++ code here.
//
// Do not forget to dynamically load the C++ library into your application.
//
// For instance,
//
// In MainActivity.java:
// static {
// System.loadLibrary("database");
// }
//
// Or, in MainActivity.kt:
// companion object {
// init {
// System.loadLibrary("database")
// }
// }
4 JNI的数据类型和类型签名¶
JNI的数据包含两大种:基本类型和引用类型,基本类型主要有jboolean、jchar、jint等,它们和Java中的数据类型的对应关系如下:
| JNI类型 | Java类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| jboolean | boolean | 无符号8位整型 |
| jbyte | byte | 有符号8位整型 |
| jchar | char | 无符号16位整型 |
| jshort | short | 有符号16位整型 |
| jint | int | 32位整型 |
| jlong | long | 64位整型 |
| jfloat | float | 32位浮点型 |
| jdouble | double | 64位浮点型 |
| void | void | 无类型 |
JNI中的引用类型主要有类、对象和数组,它们和Java中的引用类型的对应关系如表所示:
| JNI类型 | Java类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| jobject | Object | Object类型 |
| jclass | Class | Class类型 |
| jstring | String | 字符串 |
| jobjectArray | Object[] | 对象数组 |
| jbooleanArray | boolean[] | boolean数组 |
| jbyteArray | byte[] | byte数组 |
| jcharArray | char[] | char数组 |
| jshortArray | short[] | short数组 |
| jintArray | int[] | int数组 |
| jlongArray | long[] | long数组 |
| jfloatArray | float[] | float数组 |
| jdoubleArray | double[] | double数组 |
| jthrowable | Throwable | Throwable |
JNI的类型签名标识了一个特定的Java类型,这个类型可以是类和方法,也可以是数据类型。类的签名比较简单,它采用L+包名+类名+;的形式,只需要将其中的"."替换为"/"即可,比如java.lang.String的签名为Ljava/lang/System;,末尾的";"也是签名的一部分。
基本数据类型的签名采用一系列大写字母来表示:
| Java类型 | 签名 |
|---|---|
| boolean | Z |
| byte | B |
| char | C |
| short | S |
| int | I |
| long | J |
| float | F |
| Double | D |
| void | V |
从上表可以看出,基本数据类型的签名都是有规律的,一般为首字母的大写,但是boolean除外,因为B已经被byte占用了;而long的签名不是L的原因是类的签名是用L表示的。
对象和数组的签名稍微复杂点。
对于对象来说,它的签名就是对象所属的类的签名,比如String对象,它的签名为Ljava/lang/String;。
对于数组来说,它的签名为[+类型签名,比如int数组,其签名就是[I。
对于多位数组来说,它的签名为n个[+类型签名,比如int[][]的签名就是[[I。
方法的签名为(+参数类型签名+)+返回值类型签名。比如
boolean func1(int a, double b, int[] c) → (ID[I)Z
boolean func1(int a, String b, int[] c) → (ILjava/lang/String;[I)Z
5 JNI调用Java方法的流程¶
JNI调用Java方法的流程是先通过类名找到类,然后在根据方法名找到方法id,最后就可以调用这个方法了。如果调用Java中非静态方法,那么需要构造出来的对象后才能调用它。
1.调用非静态方法
JNIEXPORT void JNICALL Java_cn_itcast_ndkcallback_DataProvider_callmethod1
(JNIEnv * env, jobject obj){
//1 . 找到java代码的 class文件
jclass dpclazz = (*env)->FindClass(env, "cn/itcast/ndkcallback/DataProvider");
if(dpclazz == 0){
LOGI("find class error");
return;
}
LOGI("find class ");
//2 寻找class里面的方法
jmethodID method1 = (*env)->GetMethodID(env, dpclazz, "helloFromJava", "()V");
if(method1 == 0){
LOGI("find method1 error");
return;
}
LOGI("find method1 ");
//3 .调用这个方法
(*env)->CallVoidMethod(env, obj, method1);
}
注意在根据方法名查找id时需要传入方法的签名。
2.调用静态方法
JNIEXPORT void JNICALL Java_cn_itcast_ndkcallback_DataProvider_callmethod4
(JNIEnv * env, jobject obj){
//1 . 找到java代码的 class文件
jclass dpclazz = (*env)->FindClass(env, "cn/itcast/ndkcallback/DataProvider");
if(dpclazz == 0){
LOGI("find class error");
return;
}
LOGI("find class ");
//2 寻找class里面的方法
jmethodID method4 = (*env)->GetStaticMethodID(env, dpclazz, "printStaticStr", "(Ljava/lang/String;)V");
if(method4 == 0){
LOGI("find method4 error");
return;
}
LOGI("find method4 ");
//3.调用一个静态的java方法
(*env)->CallStaticVoidMethod(env, dpclazz, method4, (*env)->NewStringUTF(env, "static haha in c"));
}