Glide v4 源码解析(四)
Tip
本系列文章参考3.7.0版本的guolin - Glide最全解析,并按此思路结合4.9.0版本源码以及使用文档进行更新。
➟ Glide v4.9.0
➟ 中文文档
➟ 英文文档🚀🚀
Glide系列文章目录
- Glide1——Glide v4 的基本使用
- Glide2——从源码的角度理解Glide三步的执行流程
- Glide3——深入探究Glide缓存机制
- Glide4——RequestBuilder中高级点的API以及Target
- Glide5——Glide内置的transform以及自定义BitmapTransformation
- Glide6——Glide利用AppGlideModule、LibraryGlideModule更改默认配置、扩展Glide功能;GlideApp与Glide的区别在哪?
- Glide7——利用OkHttp、自定义Drawable、自定义ViewTarget实现带进度的图片加载功能
- 杂记:从Picasso迁移至Glide
本章主要内容为Target的相关知识、RequestBuilder的高级API。
1. Target¶
在本系列文章的第二章中比较详细地介绍了Glide.with(xx).load(xx).into(xx)的过程。回想一下,在into(ImageView)过程中(Link),会将ImageView包装成为一个ViewTarget类。如果调用过asBitmap()方法,那么此处会是BitmapImageViewTarget,否则都将会是DrawableImageViewTarget。BitmapImageViewTarget和DrawableImageViewTarget除了setResource方法中调用的设置图片的API不同外,没有任何区别。
ImageViewTargetFactory.java
public class ImageViewTargetFactory {
@NonNull
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <Z> ViewTarget<ImageView, Z> buildTarget(@NonNull ImageView view,
@NonNull Class<Z> clazz) {
if (Bitmap.class.equals(clazz)) {
return (ViewTarget<ImageView, Z>) new BitmapImageViewTarget(view);
} else if (Drawable.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz)) {
return (ViewTarget<ImageView, Z>) new DrawableImageViewTarget(view);
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Unhandled class: " + clazz + ", try .as*(Class).transcode(ResourceTranscoder)");
}
}
}
DrawableImageView的继承链如下:DrawableImageView -> ImageViewTarget -> ViewTarget -> BaseTarget -> Target。
Target是一个继承了LifecycleListener接口的接口类,该类提供了资源加载过程中的回调操作。
典型的生命周期为onLoadStarted->onResourceReady/onLoadFailed->onLoadCleared,但不保证所有的都是这样。如果资源在内存中或者由于model为null而加载失败,onLoadStarted不会被调用。同样,如果target不会清除,那么onLoadCleared方法也不会被调用。BaseTarget是一个实现了Target接口的抽象类。
该类实现了setRequest(Request)、getRequest()两个方法,其他方法相当于适配器模式的实现。ViewTarget
该类虽然继承了BaseTarget类,但其重写了setRequest(Request)、getRequest()两个方法,这两个方法会调用View.setTag方法将Request对象传入。In addition, for
ViewTargets only, you can pass in a new instance to each load or clear call and allow Glide to retrieve information about previous loads from the Views tags
This will not work unless yourTargetextendsViewTargetor implementssetRequest()andgetRequest()in a way that allows you to retrieve previous requests in newTarget instances.
Cancellation and re-useImageViewTarget
该类的作用就是在加载的生命周期回调中给ImageView设置对应的资源。但由于加载成功后返回的资源可能是Bitmap或者Drawable,所以这个不确定类型的加载由setResource抽象方法声明,待子类BitmapImageViewTarget和DrawableImageViewTarget实现。DrawableImageViewTarget
继承了ImageViewTarget类,唯一的作用就是实现setResource(Drawable)方法。
在了解了DrawableImageViewTarget以及相关的类之后,我们看一下其他的Target。下面是Glide v4中出现的所有的Target:
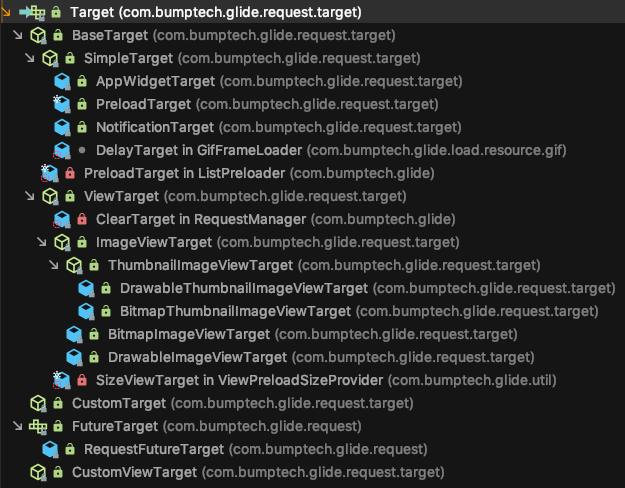
虽然,Target很多,但是我们自定义只需要继承CustomViewTarget或者CustomTarget就行了。
为什么要继承
CustomViewTarget而不是ViewTarget?
ViewTarget已经被标记为废弃了,建议我们使用CustomViewTarget。这是因为,如果子类没有实现ViewTarget.onLoadCleared方法,将会导致被回收的bitmap仍然被UI所引用,从而导致崩溃。而CustomViewTarget.onLoadCleared方法是final类型的,并且提供了一个抽象方法onResourceCleared强制我们实现。除此之外,两个类基本没有任何区别。为什么要继承
CustomTarget而不是SimpleTarget?
原因同上
下面举一个实际例子,在某些场景下,此时我们需要获取到加载成功后的Bitmap对象(虽然这样有点蠢,因为有其他更好的方式):
Glide.with(this)
.asBitmap()
.load(file)
.into(object : CustomTarget<Bitmap>() {
override fun onResourceReady(
resource: Bitmap,
transition: Transition<in Bitmap>?
) {
ivFace.setImageBitmap(resource)
}
override fun onLoadCleared(placeholder: Drawable?) {
ivFace.setImageDrawable(placeholder)
}
})
2. RequestBuilder高级API¶
在了解了Target之后,我们再看看RequestBuilder中高级一点的API。
下面这些都是Target的应用:
preload
将资源预加载到缓存中submit
返回一个Future对象,其get()方法会阻塞住,所以需要在后台线程中调用downloadOnly
下载原始的无修改的data文件。
内部调用的是**修改过配置**的into/submit方法,但RequestBuilder.downloadOnly方法已经被废弃;建议采用RequestManager的downloadOnly()方法和into/submit方法
此外还有还需要注意的一个API:
listener/addListener
2.1 preload¶
preload的重载方法如下:
/**
* Preloads the resource into the cache using the given width and height.
*
* <p> Pre-loading is useful for making sure that resources you are going to to want in the near
* future are available quickly. </p>
*
* @param width The desired width in pixels, or {@link Target#SIZE_ORIGINAL}. This will be
* overridden by
* {@link com.bumptech.glide.request.RequestOptions#override(int, int)} if
* previously called.
* @param height The desired height in pixels, or {@link Target#SIZE_ORIGINAL}. This will be
* overridden by
* {@link com.bumptech.glide.request.RequestOptions#override(int, int)}} if
* previously called).
* @return A {@link Target} that can be used to cancel the load via
* {@link RequestManager#clear(Target)}.
* @see com.bumptech.glide.ListPreloader
*/
@NonNull
public Target<TranscodeType> preload(int width, int height) {
final PreloadTarget<TranscodeType> target = PreloadTarget.obtain(requestManager, width, height);
return into(target);
}
/**
* Preloads the resource into the cache using {@link Target#SIZE_ORIGINAL} as the target width and
* height. Equivalent to calling {@link #preload(int, int)} with {@link Target#SIZE_ORIGINAL} as
* the width and height.
*
* @return A {@link Target} that can be used to cancel the load via
* {@link RequestManager#clear(Target)}
* @see #preload(int, int)
*/
@NonNull
public Target<TranscodeType> preload() {
return preload(Target.SIZE_ORIGINAL, Target.SIZE_ORIGINAL);
}
注意,在注释中出现了一个
ListPreload类,该类是在ListView中做item预加载的一个工具类,使用方法为AbsListView#setOnScrollListener(android.widget.AbsListView.OnScrollListener)。该类代码很简单,要点就是在滚动时计算需要预处理的item。这么好用,那我要是
RecyclerView怎么办?Glide也提供了RecyclerView的版本,不过需要添加新的依赖recyclerview-integration,详情可以查看文档INTEGRATION LIBRARIES - RecyclerView。
我们可以看到,在preload的实现中关键点就在于PreloadTarget类。该类实现非常简单,就是在onResourceReady回调发生后,经过Handler中转,最后由构造参数之一的RequestManager对象clear掉。代码如下:
/**
* A one time use {@link com.bumptech.glide.request.target.Target} class that loads a resource into
* memory and then clears itself.
*
* @param <Z> The type of resource that will be loaded into memory.
*/
public final class PreloadTarget<Z> extends SimpleTarget<Z> {
private static final int MESSAGE_CLEAR = 1;
private static final Handler HANDLER = new Handler(Looper.getMainLooper(), new Callback() {
@Override
public boolean handleMessage(Message message) {
if (message.what == MESSAGE_CLEAR) {
((PreloadTarget<?>) message.obj).clear();
return true;
}
return false;
}
});
private final RequestManager requestManager;
/**
* Returns a PreloadTarget.
*
* @param width The width in pixels of the desired resource.
* @param height The height in pixels of the desired resource.
* @param <Z> The type of the desired resource.
*/
public static <Z> PreloadTarget<Z> obtain(RequestManager requestManager, int width, int height) {
return new PreloadTarget<>(requestManager, width, height);
}
private PreloadTarget(RequestManager requestManager, int width, int height) {
super(width, height);
this.requestManager = requestManager;
}
@Override
public void onResourceReady(@NonNull Z resource, @Nullable Transition<? super Z> transition) {
HANDLER.obtainMessage(MESSAGE_CLEAR, this).sendToTarget();
}
@SuppressWarnings("WeakerAccess")
@Synthetic void clear() {
requestManager.clear(this);
}
}
2.2 submit¶
submit的两个重载方法如下:
/**
* Returns a future that can be used to do a blocking get on a background thread.
*
* <p>This method defaults to {@link Target#SIZE_ORIGINAL} for the width and the height. However,
* since the width and height will be overridden by values passed to {@link
* RequestOptions#override(int, int)}, this method can be used whenever {@link RequestOptions}
* with override values are applied, or whenever you want to retrieve the image in its original
* size.
*
* @see #submit(int, int)
* @see #into(Target)
*/
@NonNull
public FutureTarget<TranscodeType> submit() {
return submit(Target.SIZE_ORIGINAL, Target.SIZE_ORIGINAL);
}
/**
* Returns a future that can be used to do a blocking get on a background thread.
*
* @param width The desired width in pixels, or {@link Target#SIZE_ORIGINAL}. This will be
* overridden by
* {@link com.bumptech.glide.request.RequestOptions#override(int, int)} if
* previously called.
* @param height The desired height in pixels, or {@link Target#SIZE_ORIGINAL}. This will be
* overridden by
* {@link com.bumptech.glide.request.RequestOptions#override(int, int)}} if
* previously called).
*/
@NonNull
public FutureTarget<TranscodeType> submit(int width, int height) {
final RequestFutureTarget<TranscodeType> target = new RequestFutureTarget<>(width, height);
return into(target, target, Executors.directExecutor());
}
由于方法会生成一个RequestFutureTarget对象,而其getSize的实现就是构造参数。所以,此处的值会覆盖掉RequestOptions设置的值。
submit之后生成了一个RequestFutureTarget对象,调用该对象的get方法可以在资源加载成功后立即获得资源对象,在获得之前会阻塞,所以get方法需要在后台线程中执行,否则会报错。
RequestFutureTarget的示例代码如下:
FutureTarget<File> target = null;
RequestManager requestManager = Glide.with(context);
try {
target = requestManager
.downloadOnly()
.load(model)
.submit();
File downloadedFile = target.get();
// ... do something with the file (usually throws IOException)
} catch (ExecutionException | InterruptedException | IOException e) {
// ... bug reporting or recovery
} finally {
// make sure to cancel pending operations and free resources
if (target != null) {
target.cancel(true); // mayInterruptIfRunning
}
}
2.3 downloadOnly¶
downloadOnly内部调用的是**修改过配置**的into/submit方法,但downloadOnly方法已经被废弃;建议采用RequestManager的downloadOnly()方法和into/submit方法。
实际上RequestBuilder.downloadOnly方法与RequestManager.downloadOnly()、RequestBuilder.into/submit方法组合没有什么区别。
两处代码如下,各位可自行对比:
@Deprecated
@CheckResult
public <Y extends Target<File>> Y downloadOnly(@NonNull Y target) {
return getDownloadOnlyRequest().into(target);
}
@Deprecated
@CheckResult
public FutureTarget<File> downloadOnly(int width, int height) {
return getDownloadOnlyRequest().submit(width, height);
}
@NonNull
@CheckResult
protected RequestBuilder<File> getDownloadOnlyRequest() {
return new RequestBuilder<>(File.class, this).apply(DOWNLOAD_ONLY_OPTIONS);
}
@NonNull
public <Y extends Target<TranscodeType>> Y into(@NonNull Y target) {
return into(target, /*targetListener=*/ null, Executors.mainThreadExecutor());
}
public FutureTarget<TranscodeType> submit(int width, int height) {
final RequestFutureTarget<TranscodeType> target = new RequestFutureTarget<>(width, height);
return into(target, target, Executors.directExecutor());
}
@NonNull
@CheckResult
public RequestBuilder<File> downloadOnly() {
return as(File.class).apply(DOWNLOAD_ONLY_OPTIONS);
}
所以,这里的DOWNLOAD_ONLY_OPTIONS才是downloadOnly的精髓,我们看看该变量的值:
protected static final RequestOptions DOWNLOAD_ONLY_OPTIONS =
new RequestOptions().diskCacheStrategy(DiskCacheStrategy.DATA).priority(Priority.LOW)
.skipMemoryCache(true);
果然是下载的是原始的无修改的data资源。
2.4 listener/addListener¶
listener与addListener不同之处在于,前者只会保留当前的Listener,而后者会保留之前的Listener。
@NonNull
@CheckResult
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public RequestBuilder<TranscodeType> listener(
@Nullable RequestListener<TranscodeType> requestListener) {
this.requestListeners = null;
return addListener(requestListener);
}
@NonNull
@CheckResult
public RequestBuilder<TranscodeType> addListener(
@Nullable RequestListener<TranscodeType> requestListener) {
if (requestListener != null) {
if (this.requestListeners == null) {
this.requestListeners = new ArrayList<>();
}
this.requestListeners.add(requestListener);
}
return this;
}
这些listener会在资源记载失败或者成功的时候被调用,代码如下:
private synchronized void onResourceReady(Resource<R> resource, R result, DataSource dataSource) {
// We must call isFirstReadyResource before setting status.
boolean isFirstResource = isFirstReadyResource();
status = Status.COMPLETE;
this.resource = resource;
isCallingCallbacks = true;
try {
boolean anyListenerHandledUpdatingTarget = false;
if (requestListeners != null) {
for (RequestListener<R> listener : requestListeners) {
anyListenerHandledUpdatingTarget |=
listener.onResourceReady(result, model, target, dataSource, isFirstResource);
}
}
anyListenerHandledUpdatingTarget |=
targetListener != null
&& targetListener.onResourceReady(result, model, target, dataSource, isFirstResource);
if (!anyListenerHandledUpdatingTarget) {
Transition<? super R> animation =
animationFactory.build(dataSource, isFirstResource);
target.onResourceReady(result, animation);
}
} finally {
isCallingCallbacks = false;
}
notifyLoadSuccess();
}
private synchronized void onLoadFailed(GlideException e, int maxLogLevel) {
stateVerifier.throwIfRecycled();
e.setOrigin(requestOrigin);
loadStatus = null;
status = Status.FAILED;
isCallingCallbacks = true;
try {
//TODO: what if this is a thumbnail request?
boolean anyListenerHandledUpdatingTarget = false;
if (requestListeners != null) {
for (RequestListener<R> listener : requestListeners) {
anyListenerHandledUpdatingTarget |=
listener.onLoadFailed(e, model, target, isFirstReadyResource());
}
}
anyListenerHandledUpdatingTarget |=
targetListener != null
&& targetListener.onLoadFailed(e, model, target, isFirstReadyResource());
if (!anyListenerHandledUpdatingTarget) {
setErrorPlaceholder();
}
} finally {
isCallingCallbacks = false;
}
notifyLoadFailed();
}
调用逻辑是这样:在requestListeners集合、targetListener中依次调用对应的回调,找到第一个能够处理的(返回true),后面的就不再调用。
同时,如果有一个回调返回了true,那么资源的对应方法会被拦截:
- 对于
onResourceReady方法来说,Target的onResourceReady方法不会被回调 - 对于
onLoadFailed方法来说,setErrorPlaceholder调用不会调用,即不会显示任何失败的占位符